Anar
Species
Families
Local Names
Genus
Native/Introduced
DNA Barcode
Description
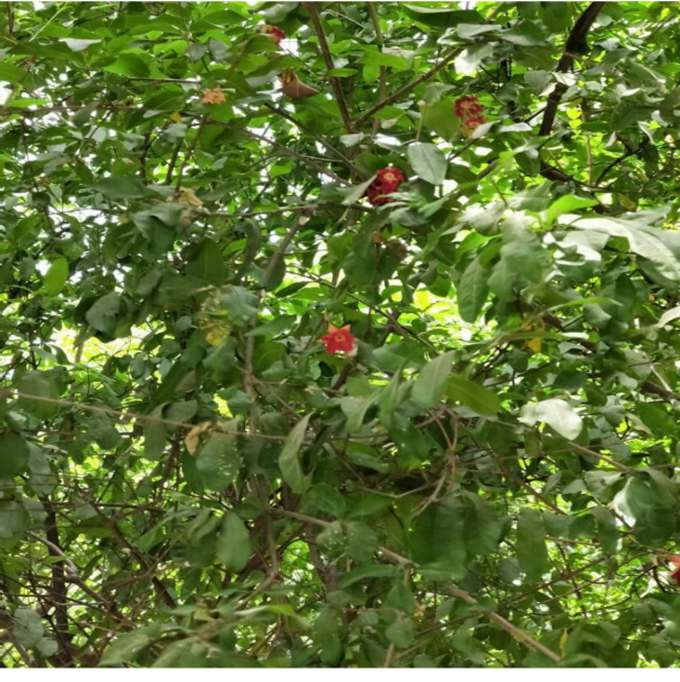
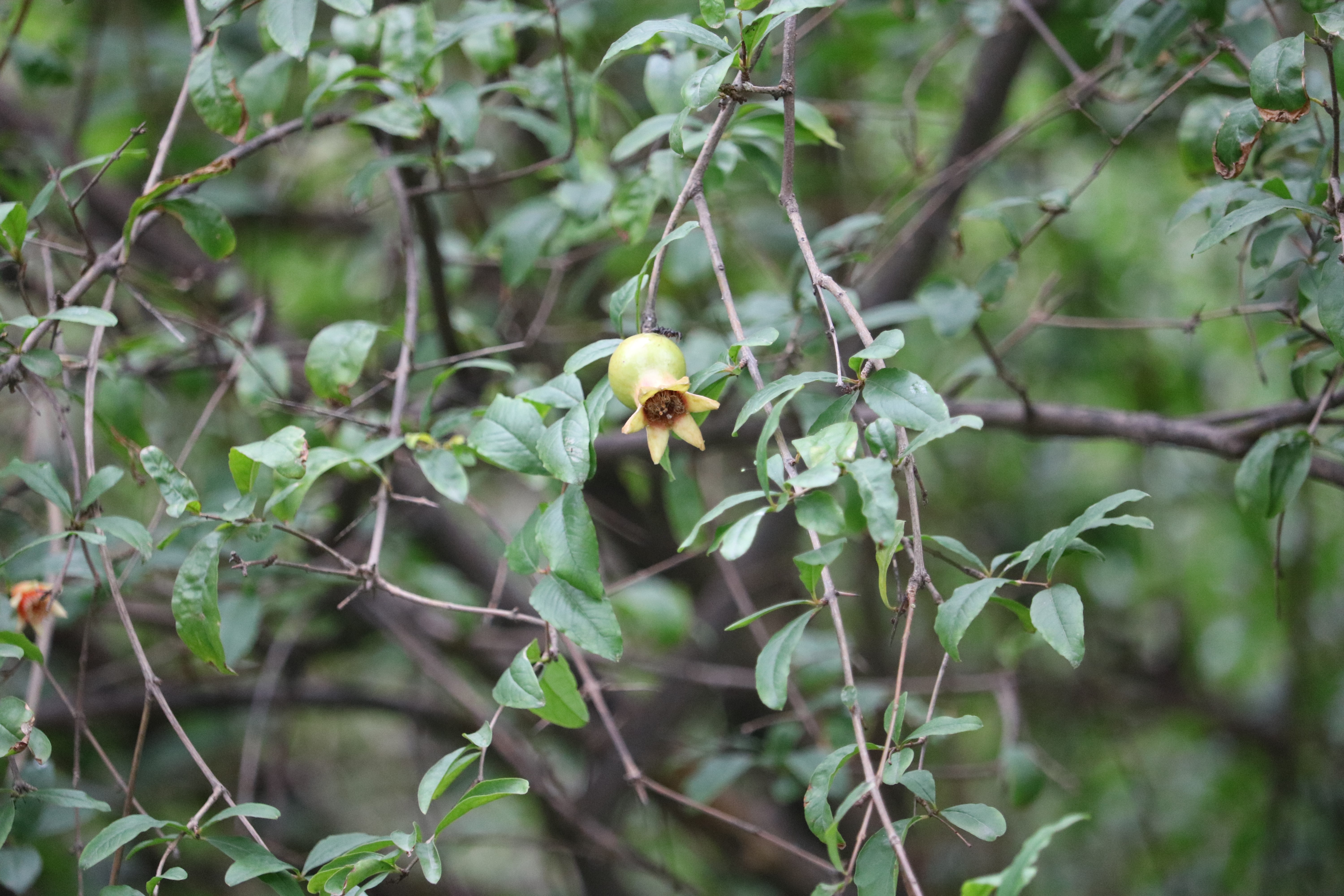
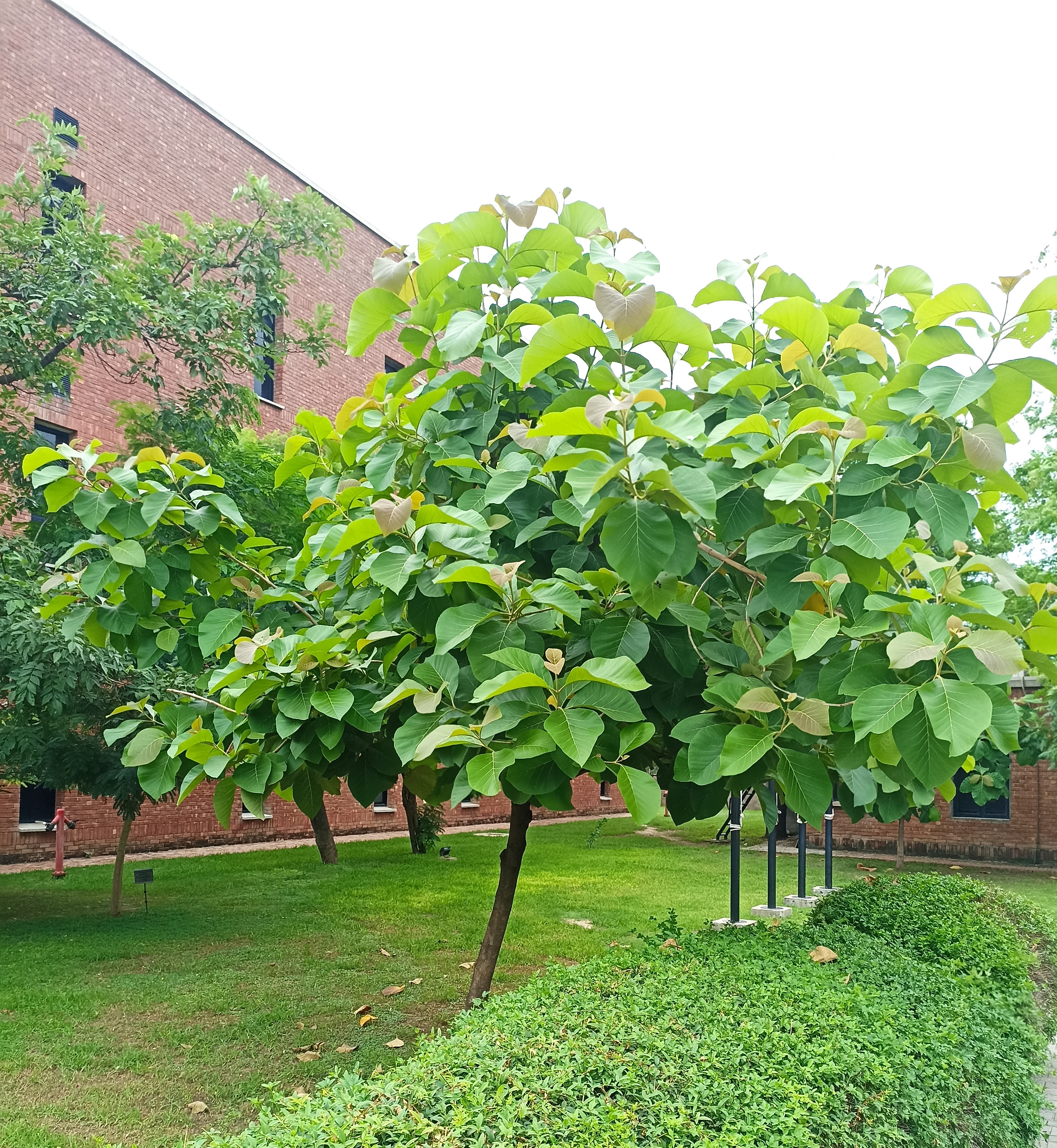
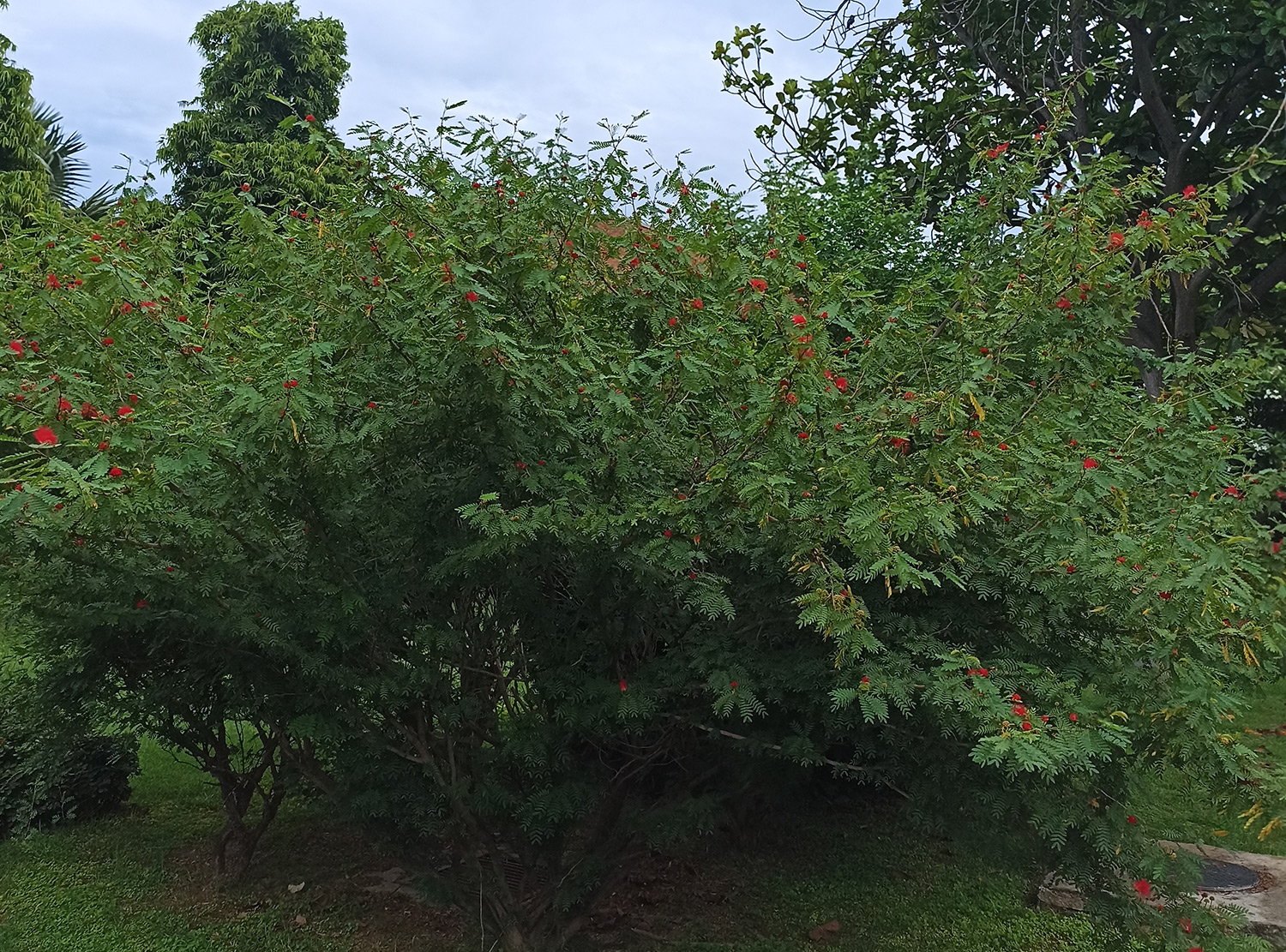
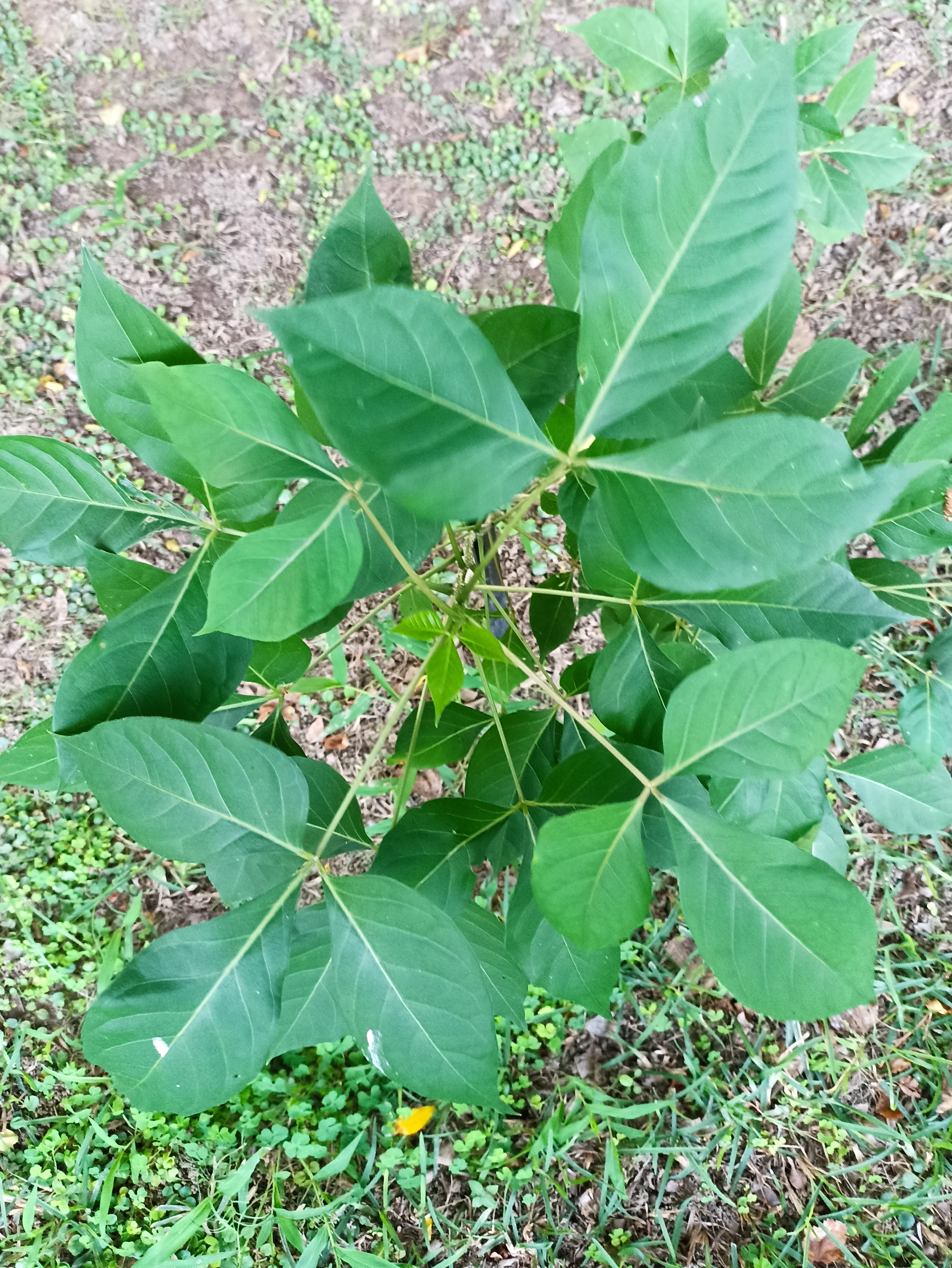
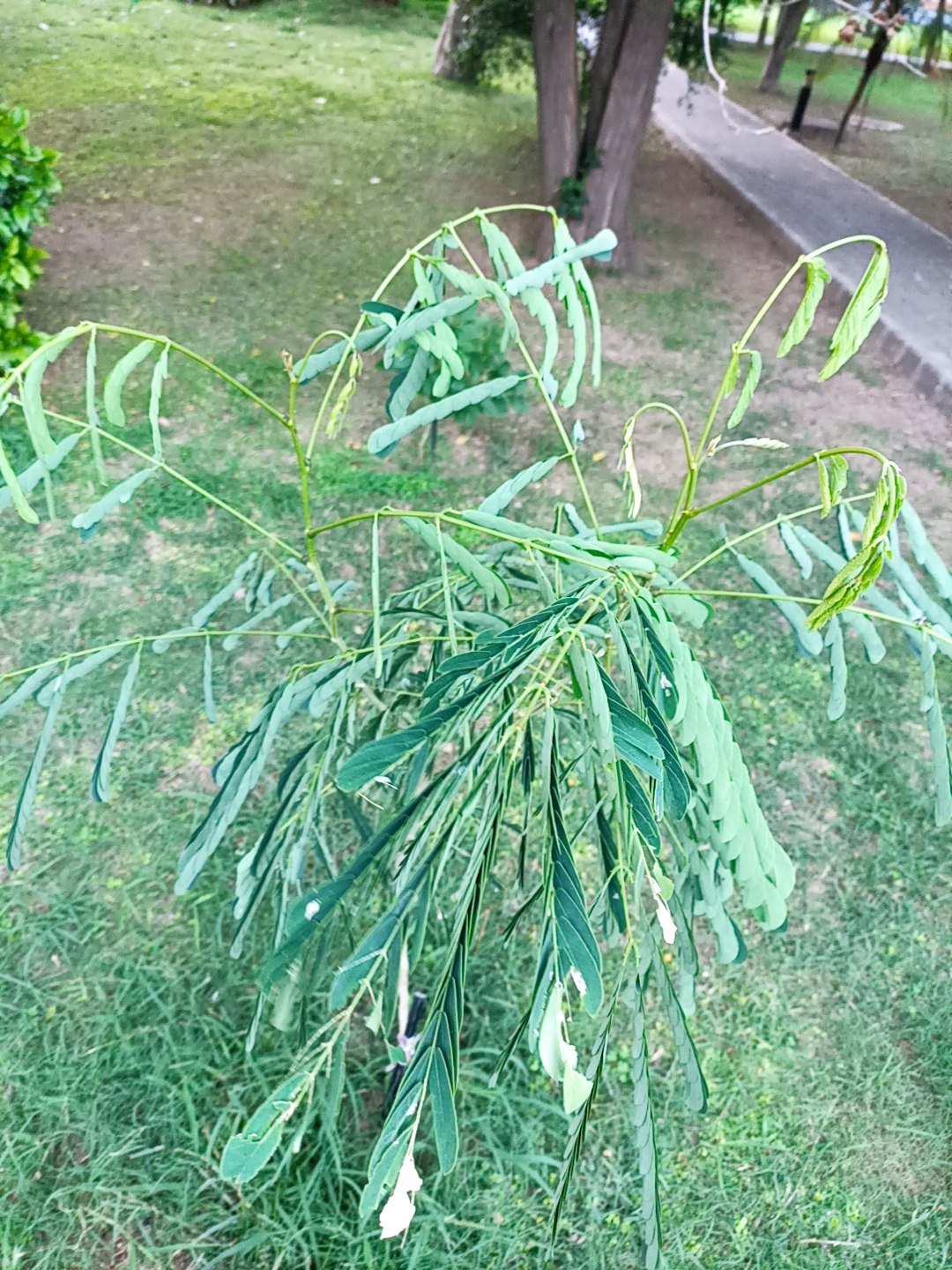
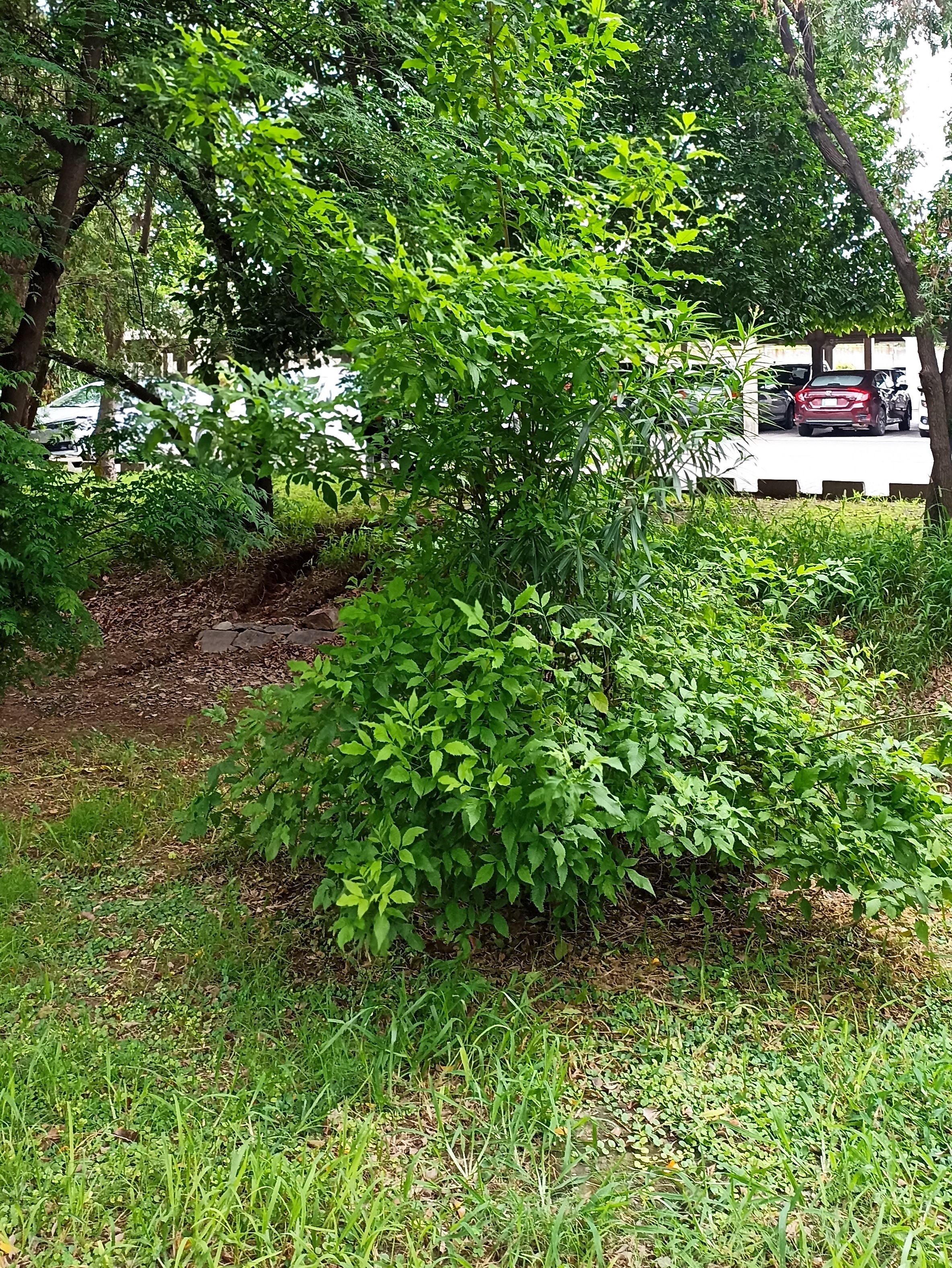
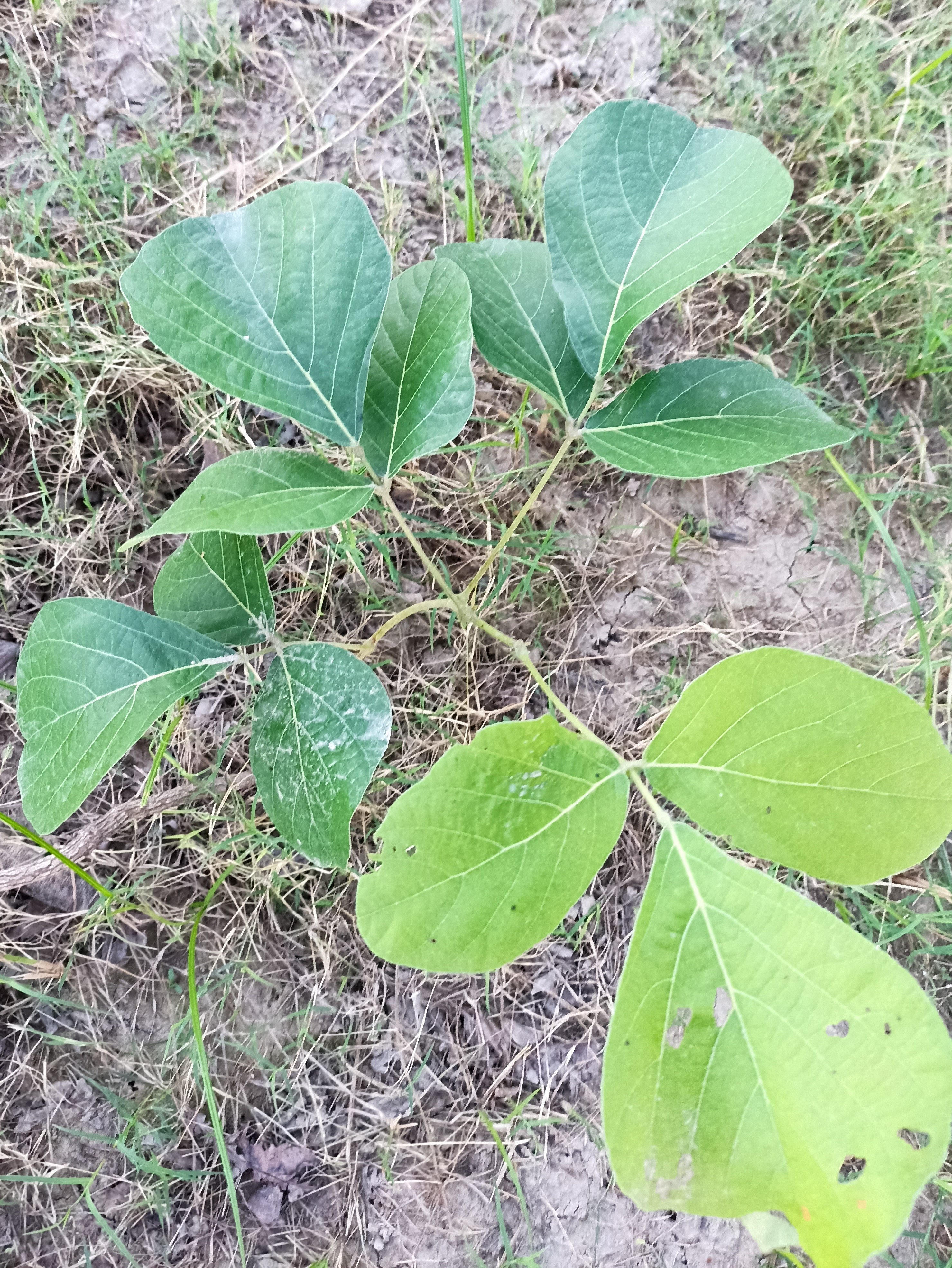
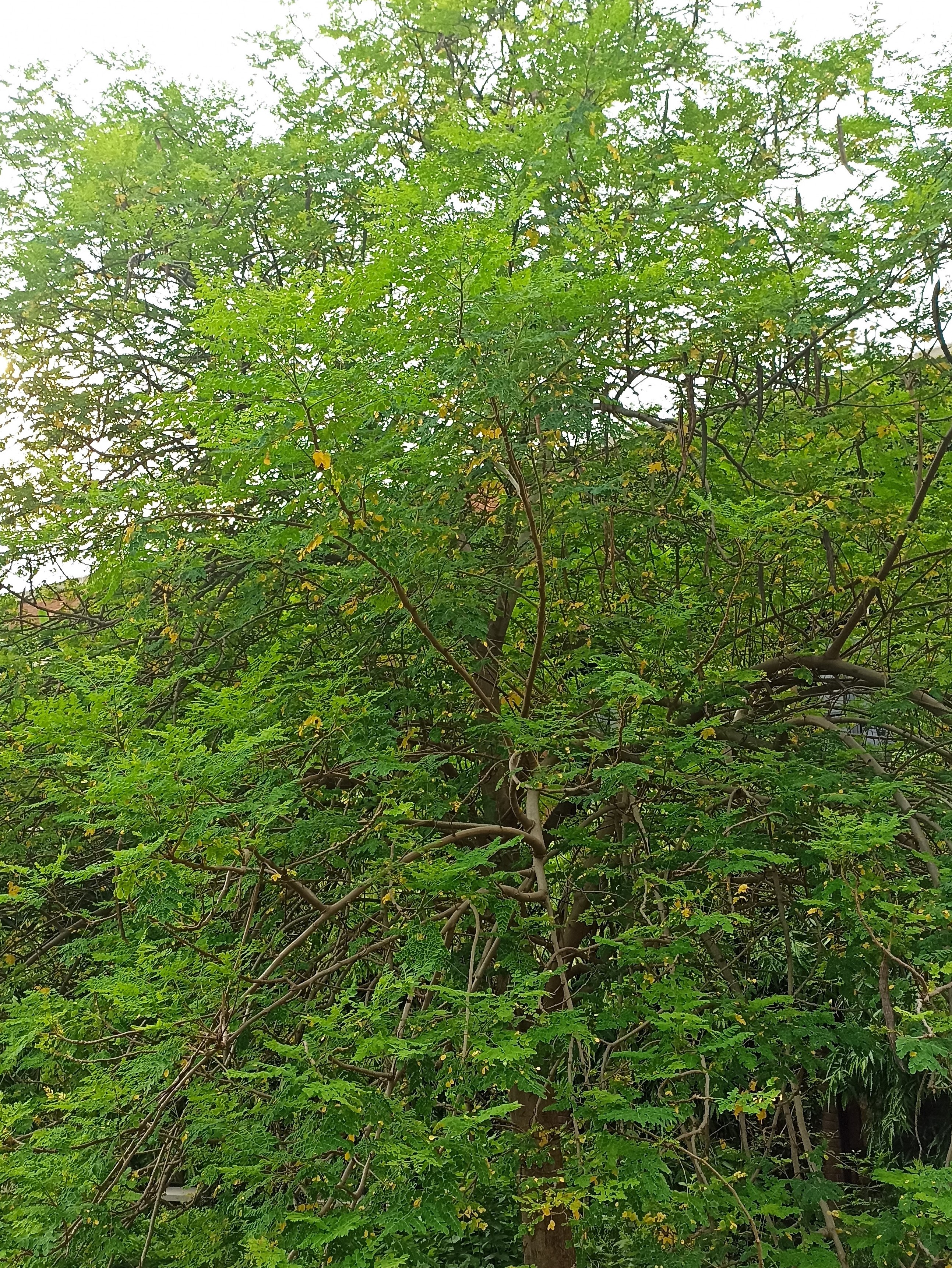
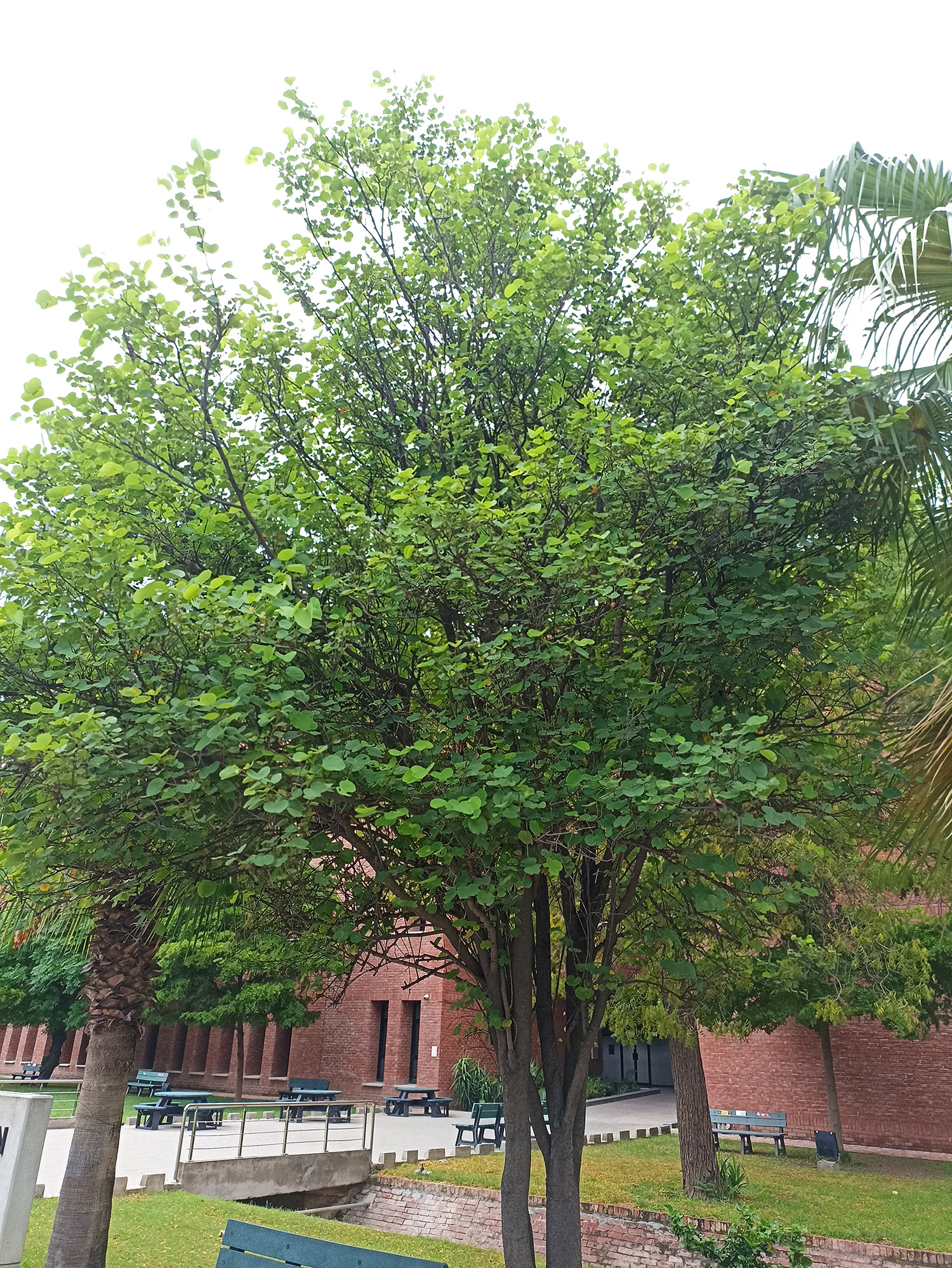
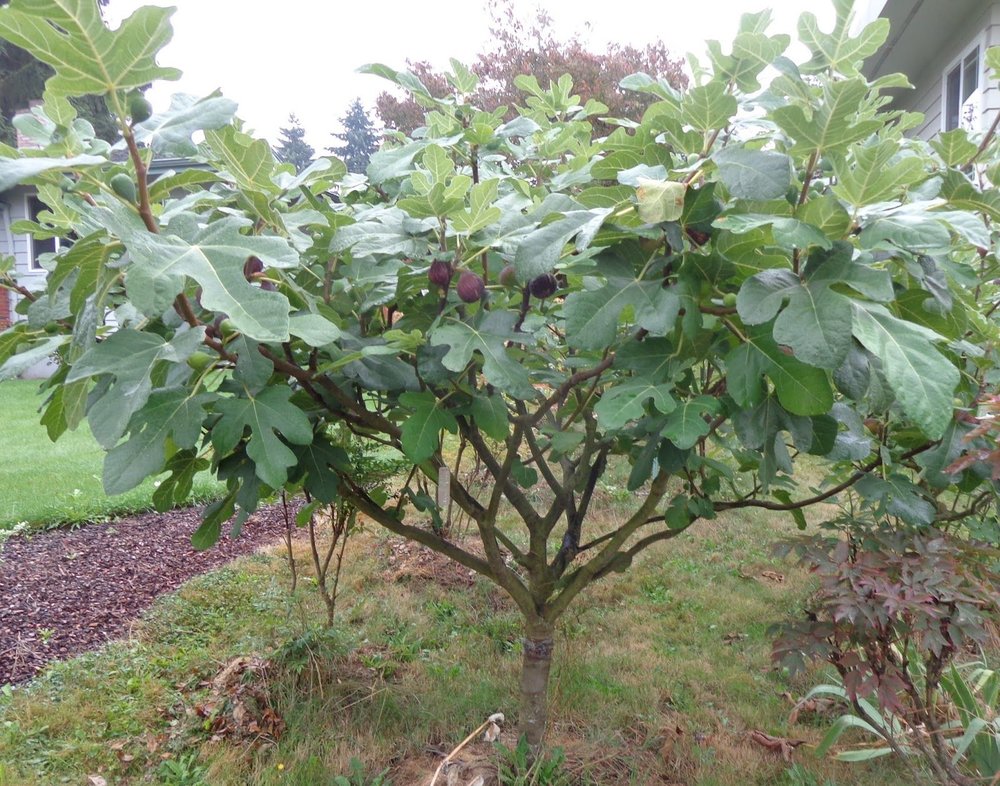
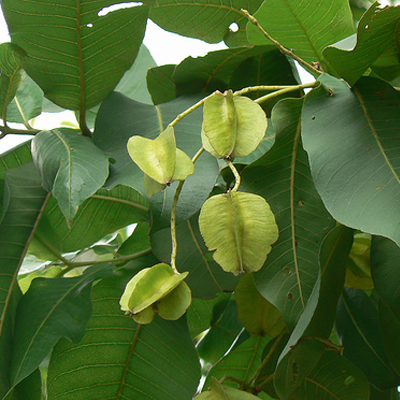
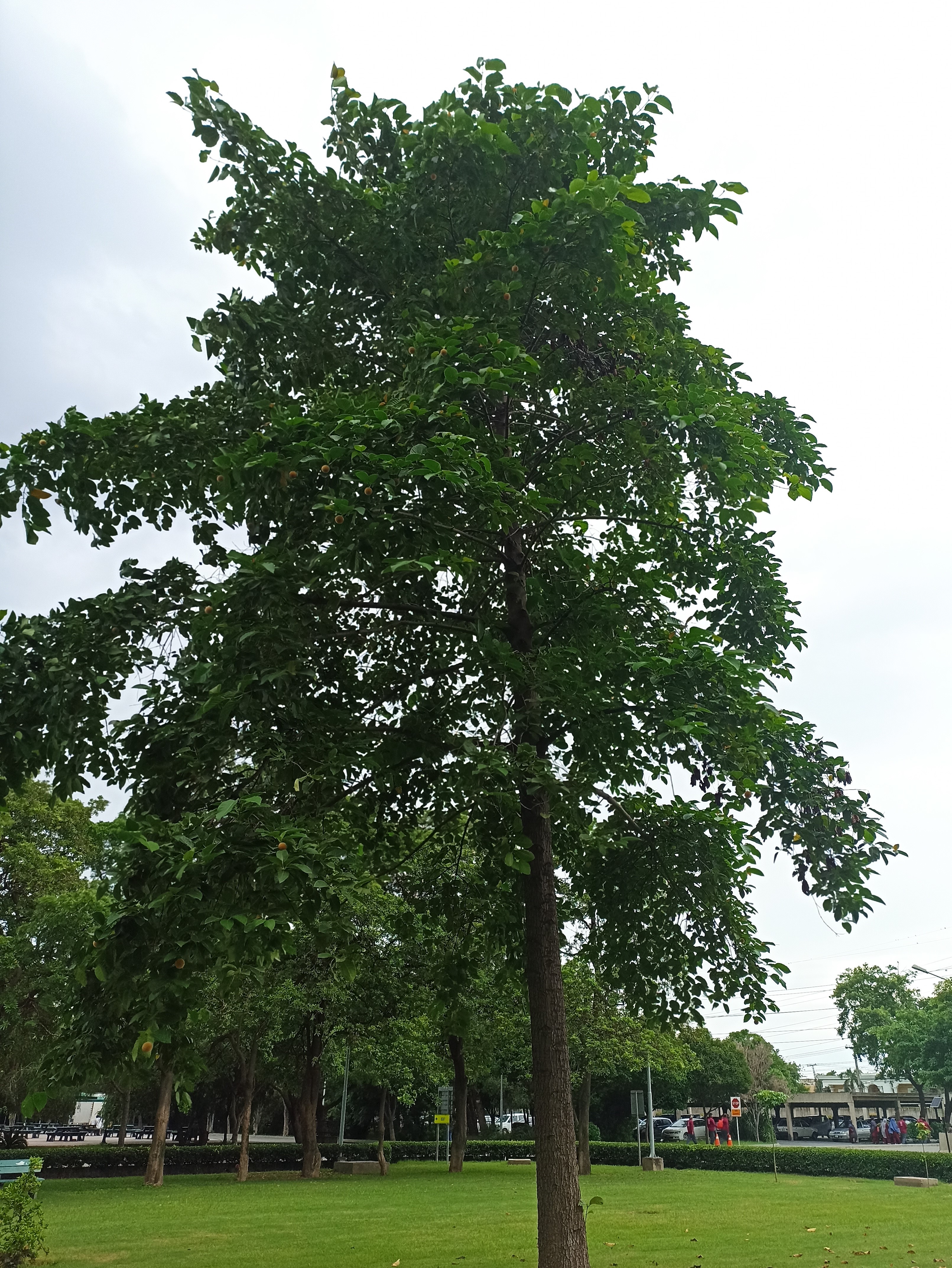
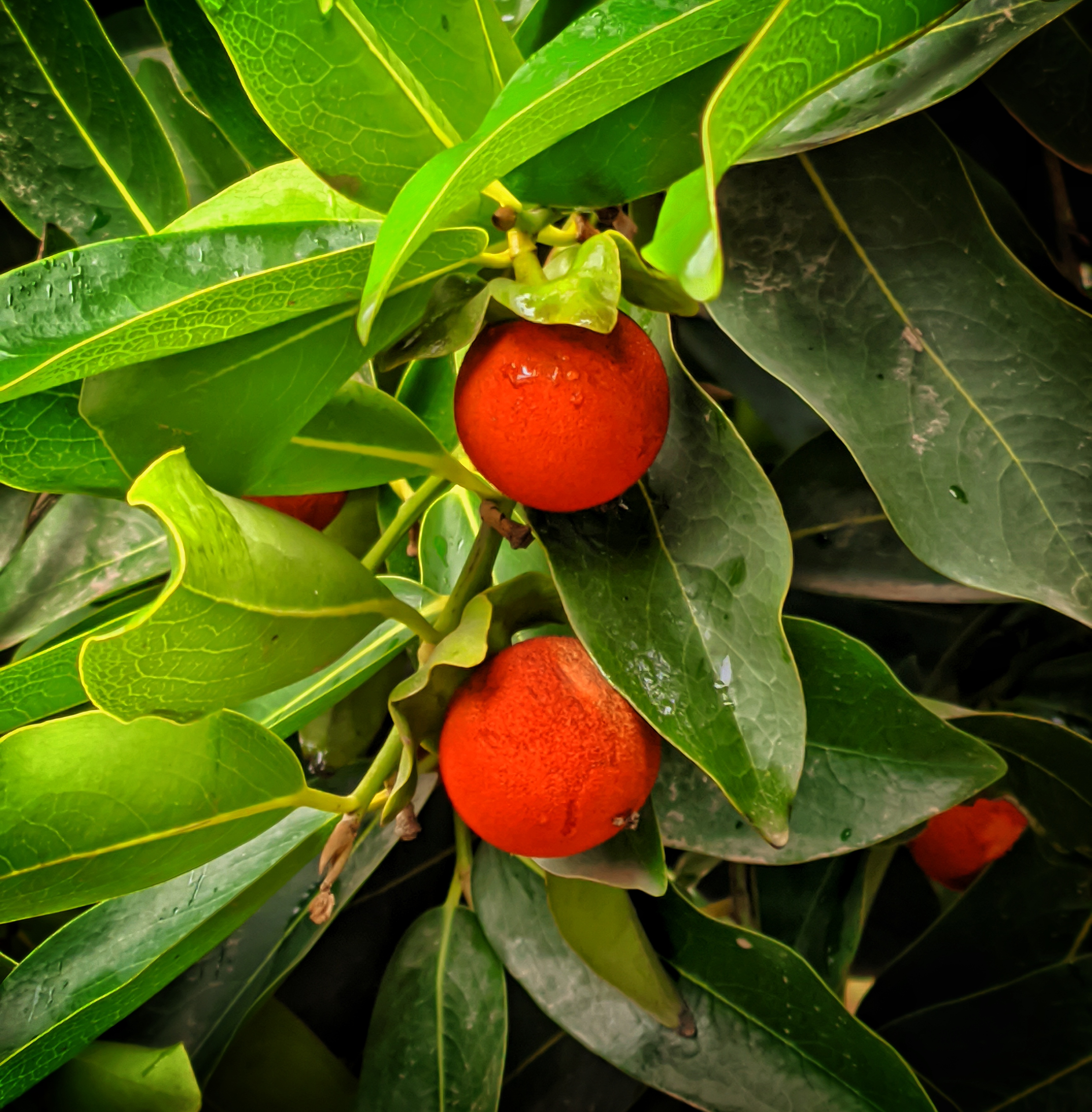
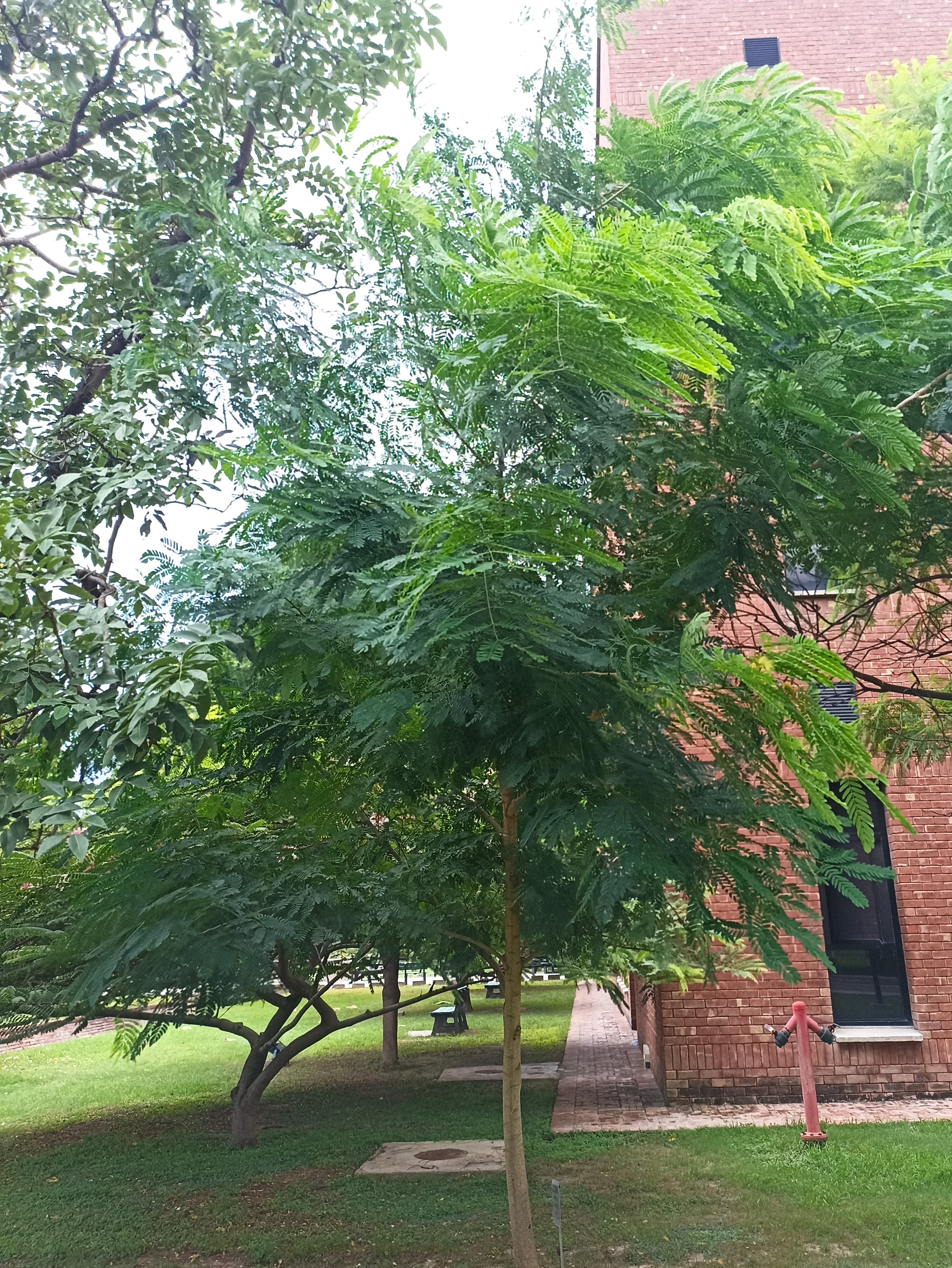
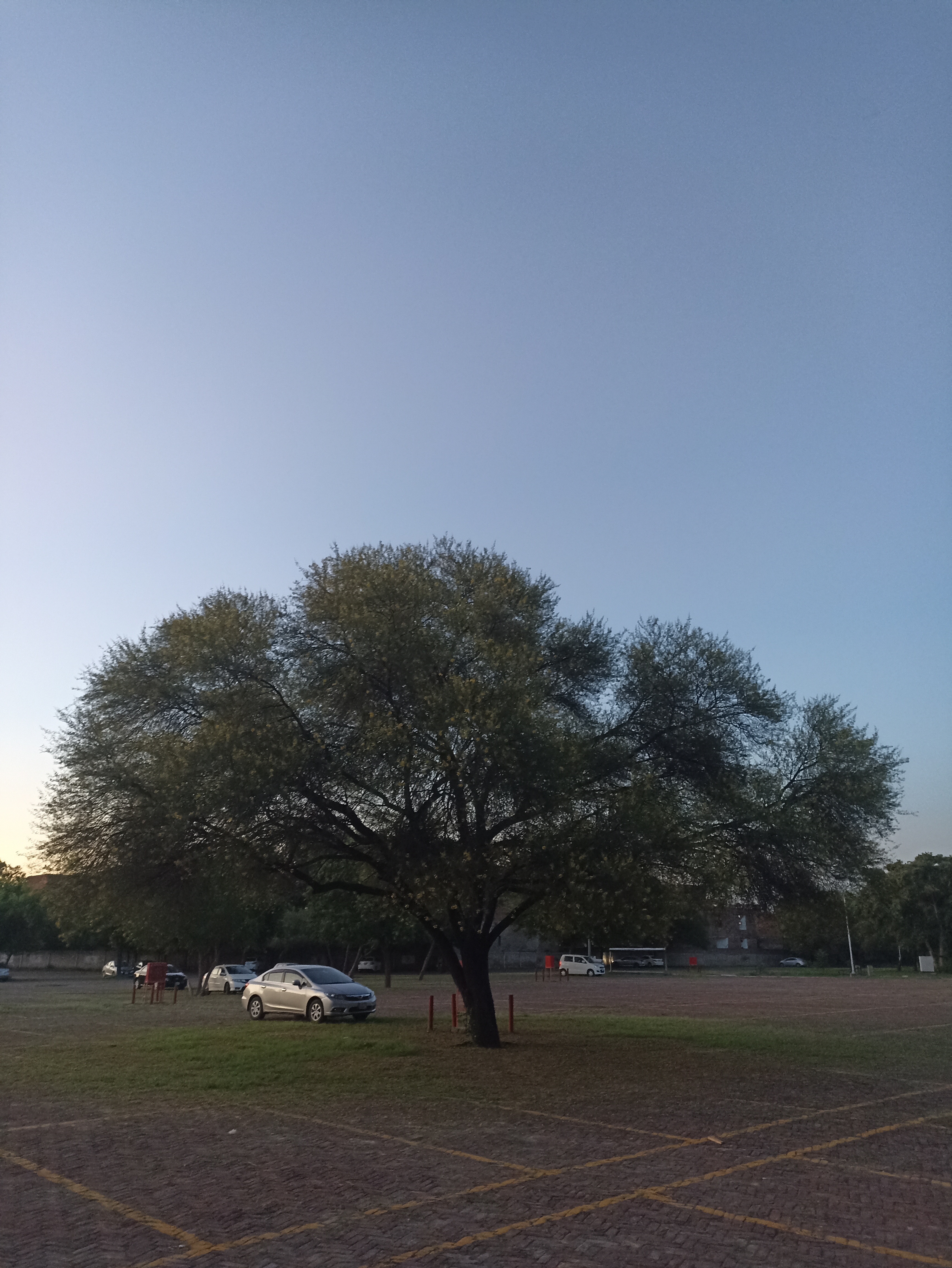
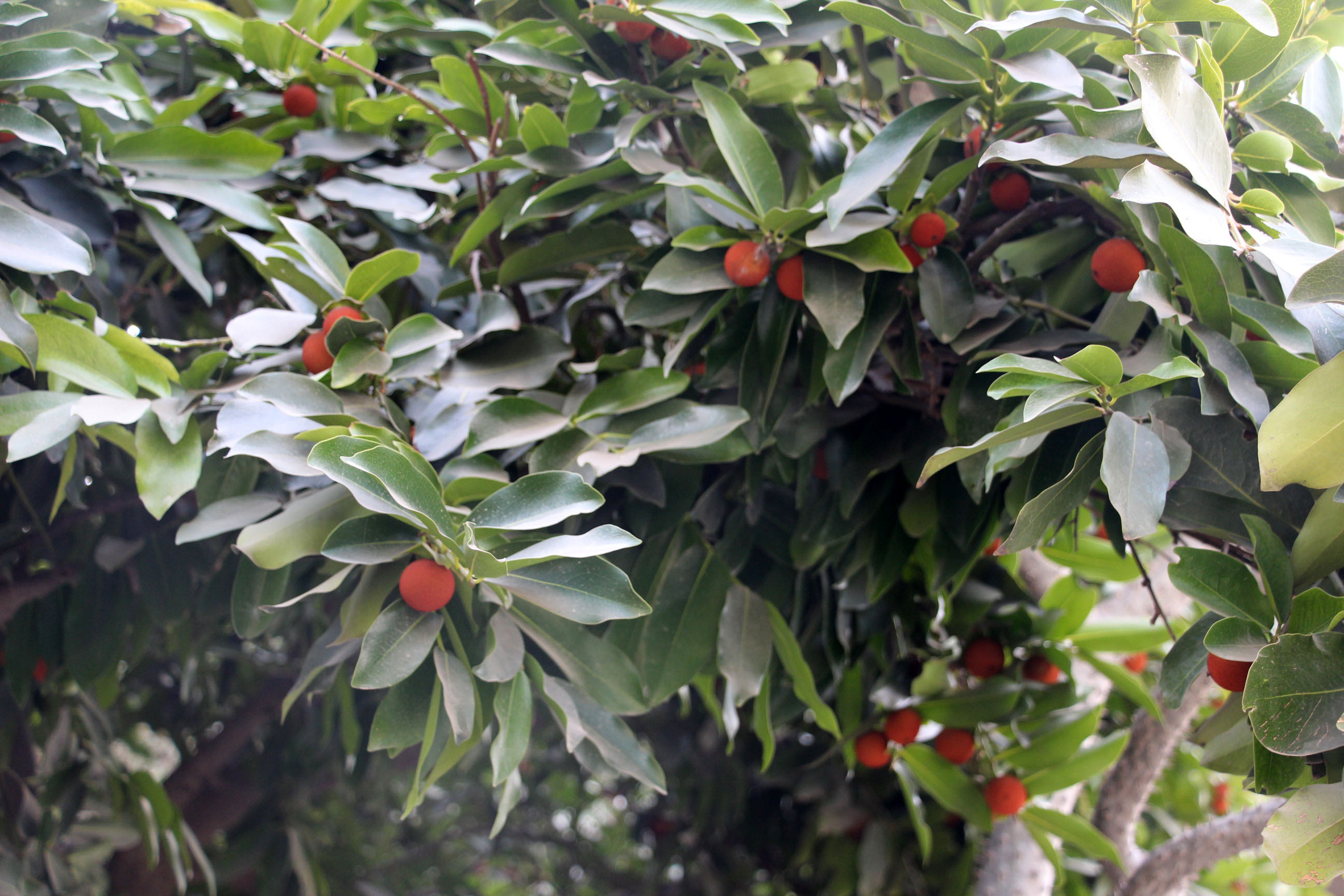
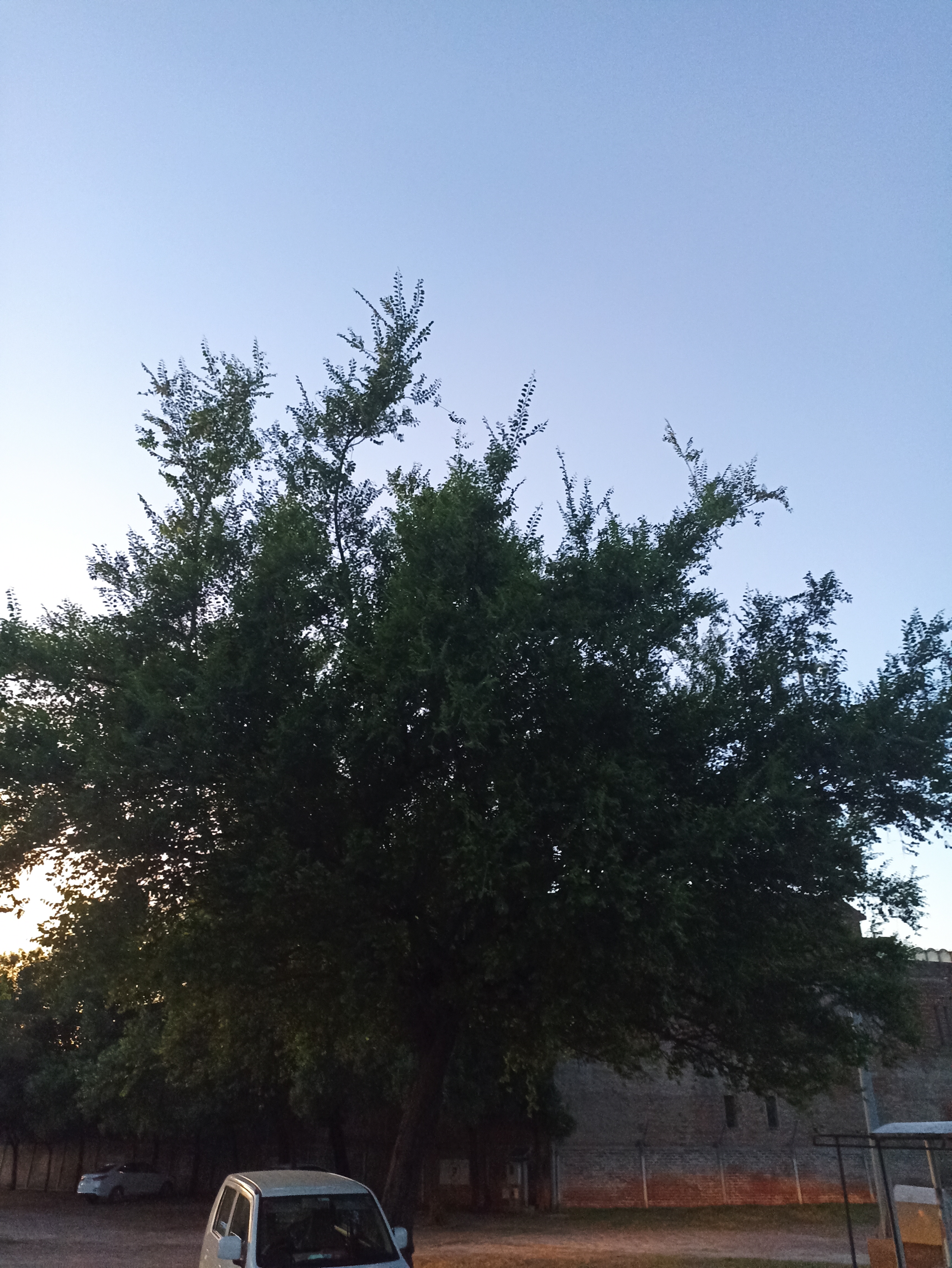
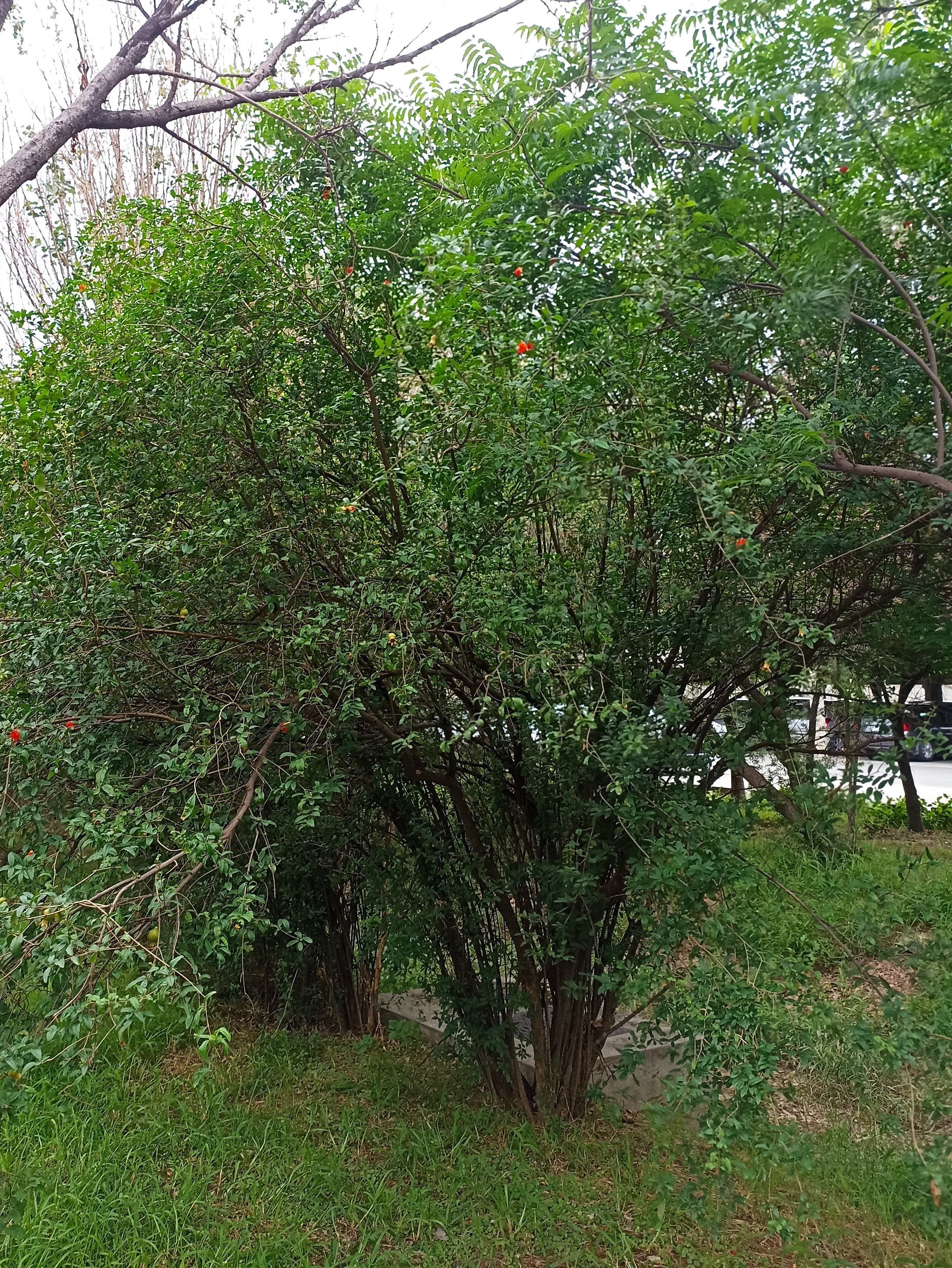
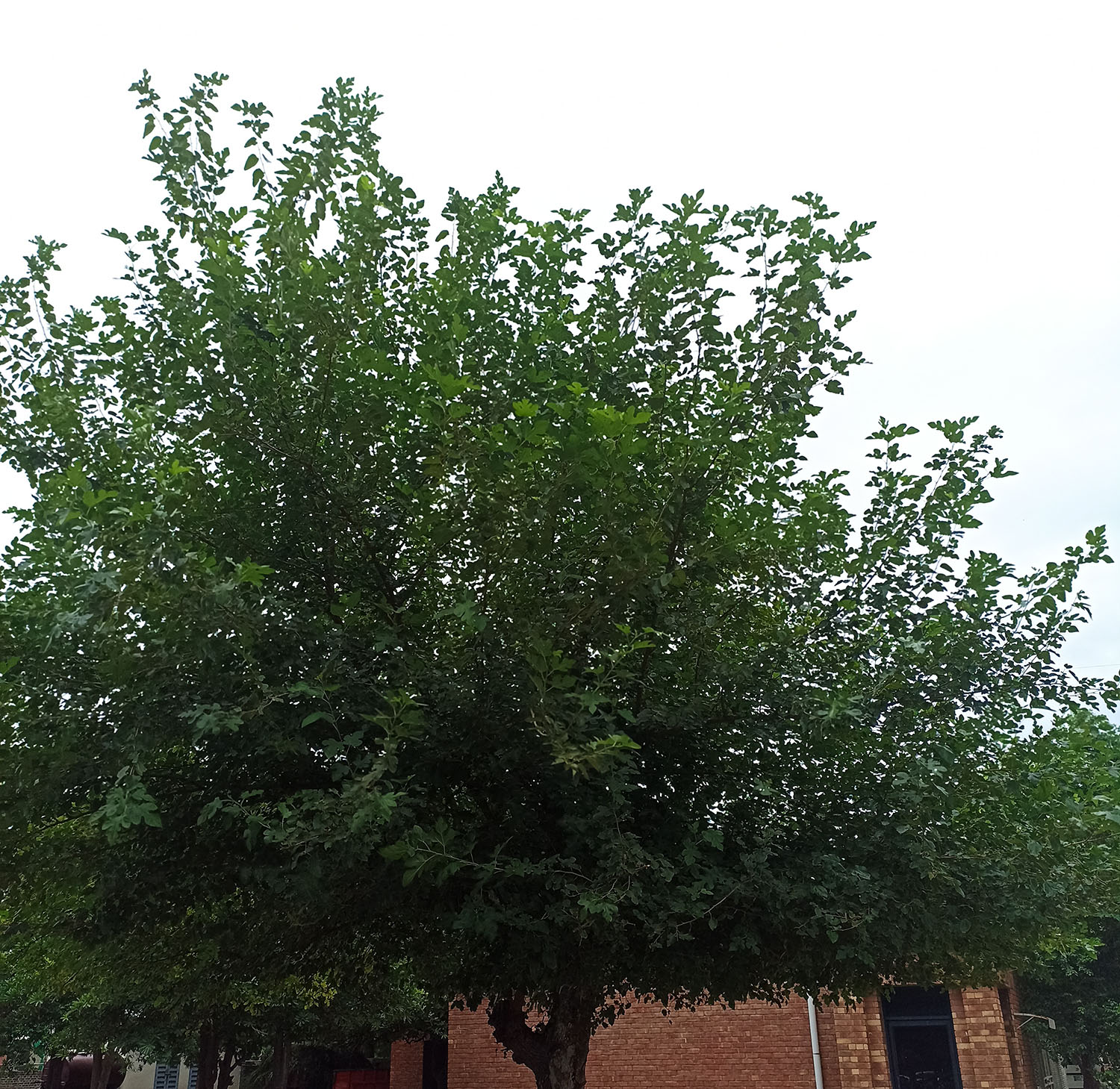
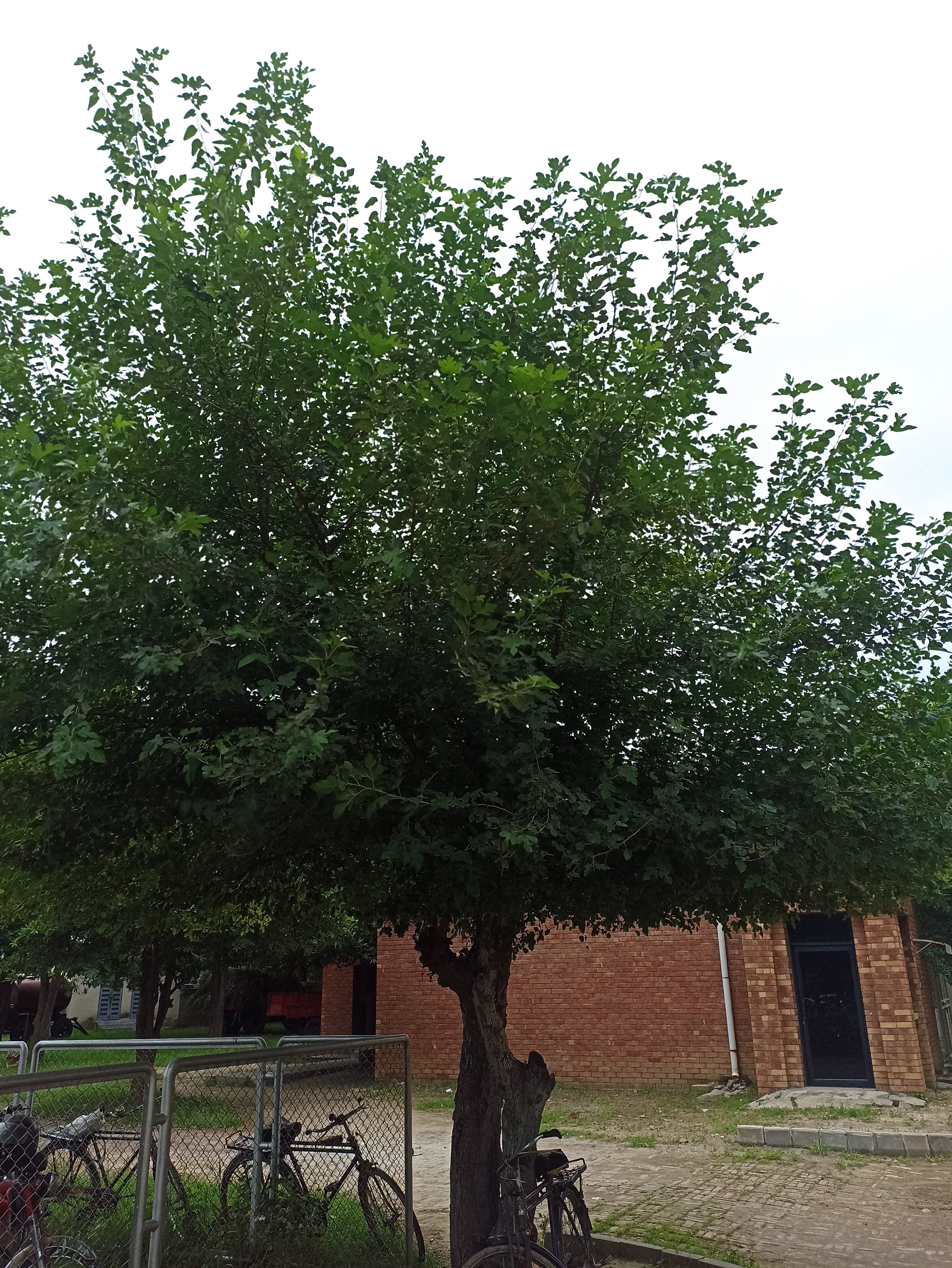
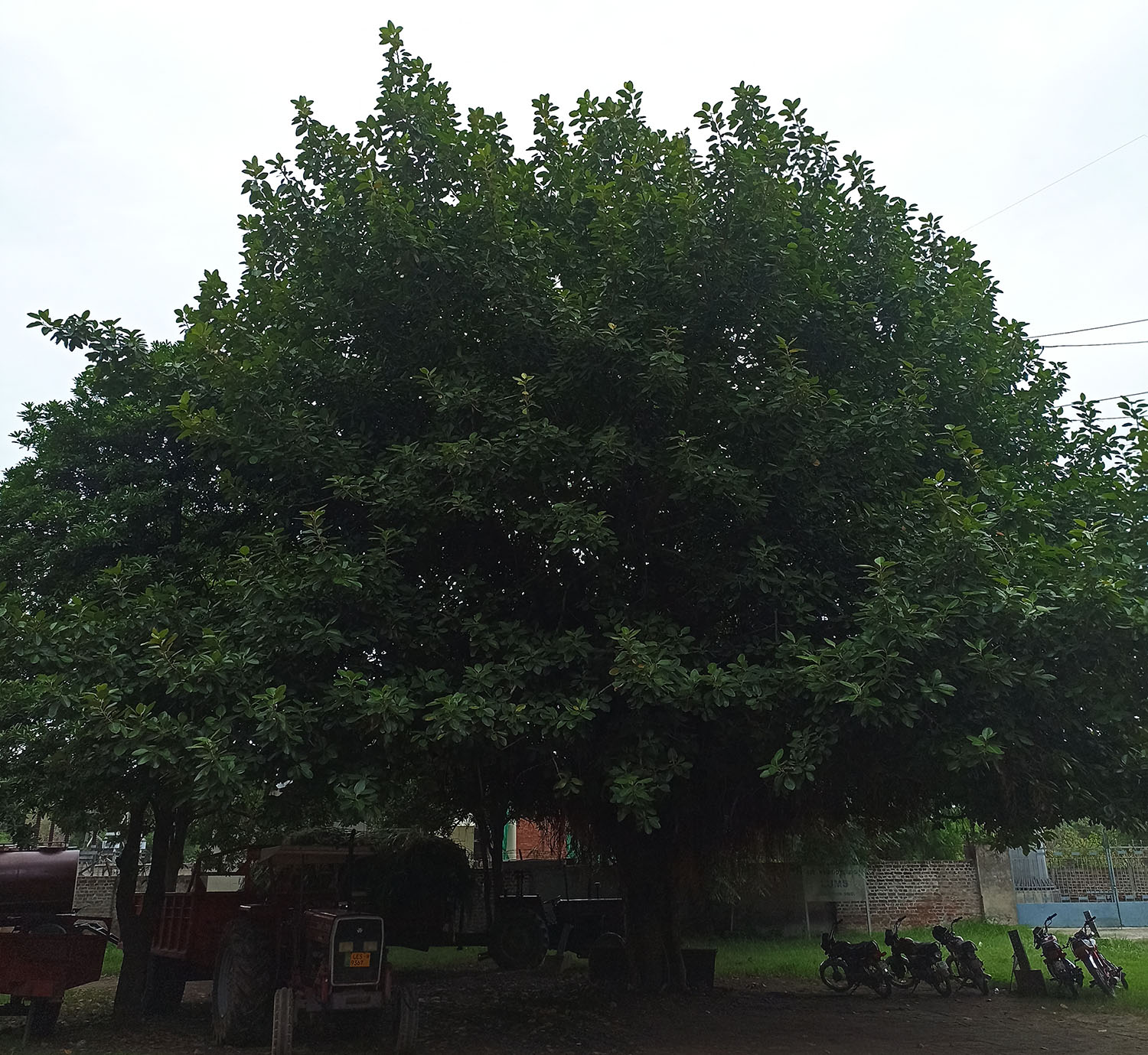
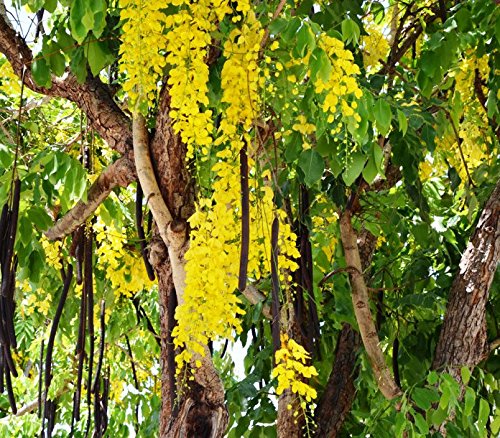
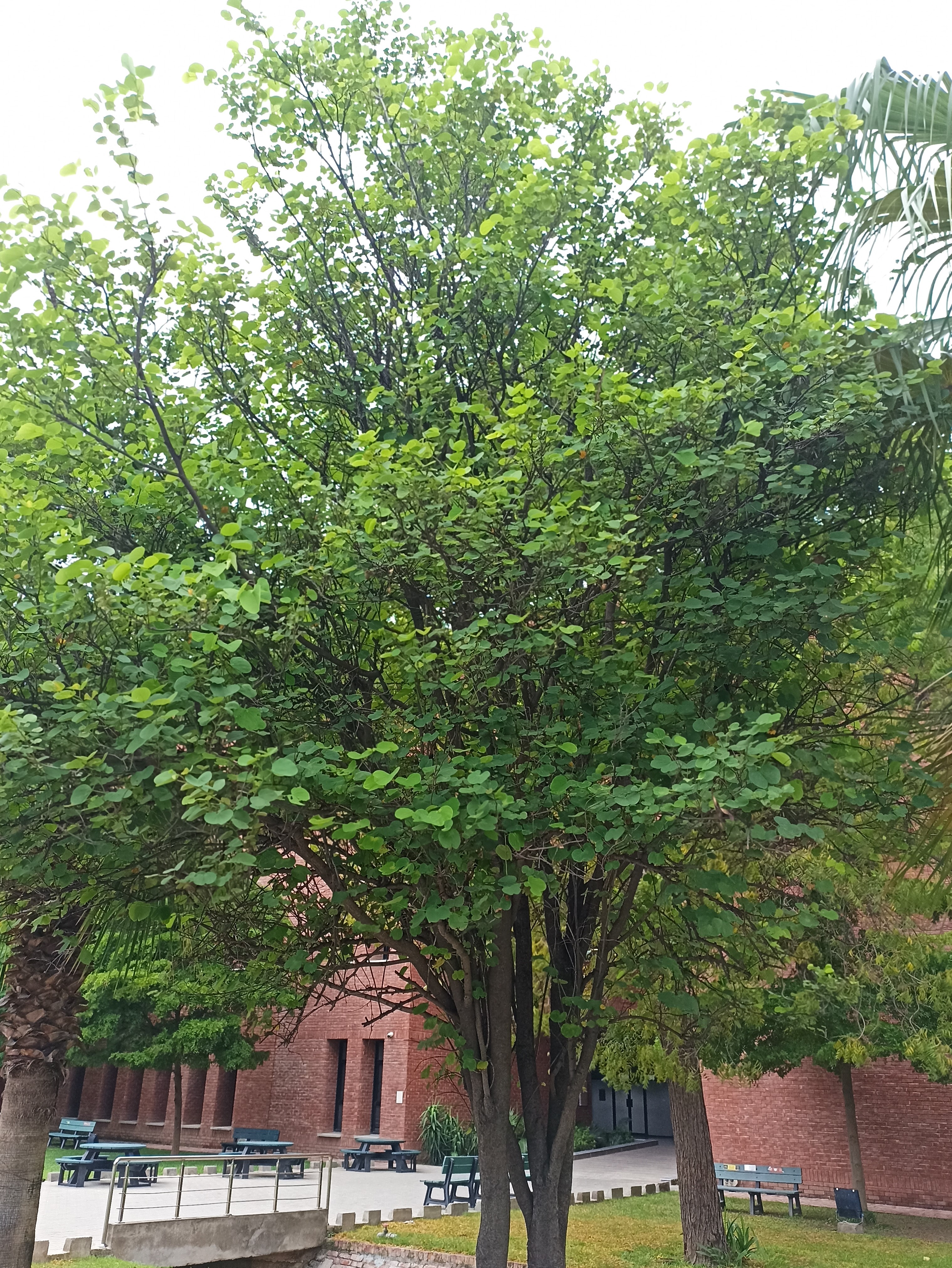
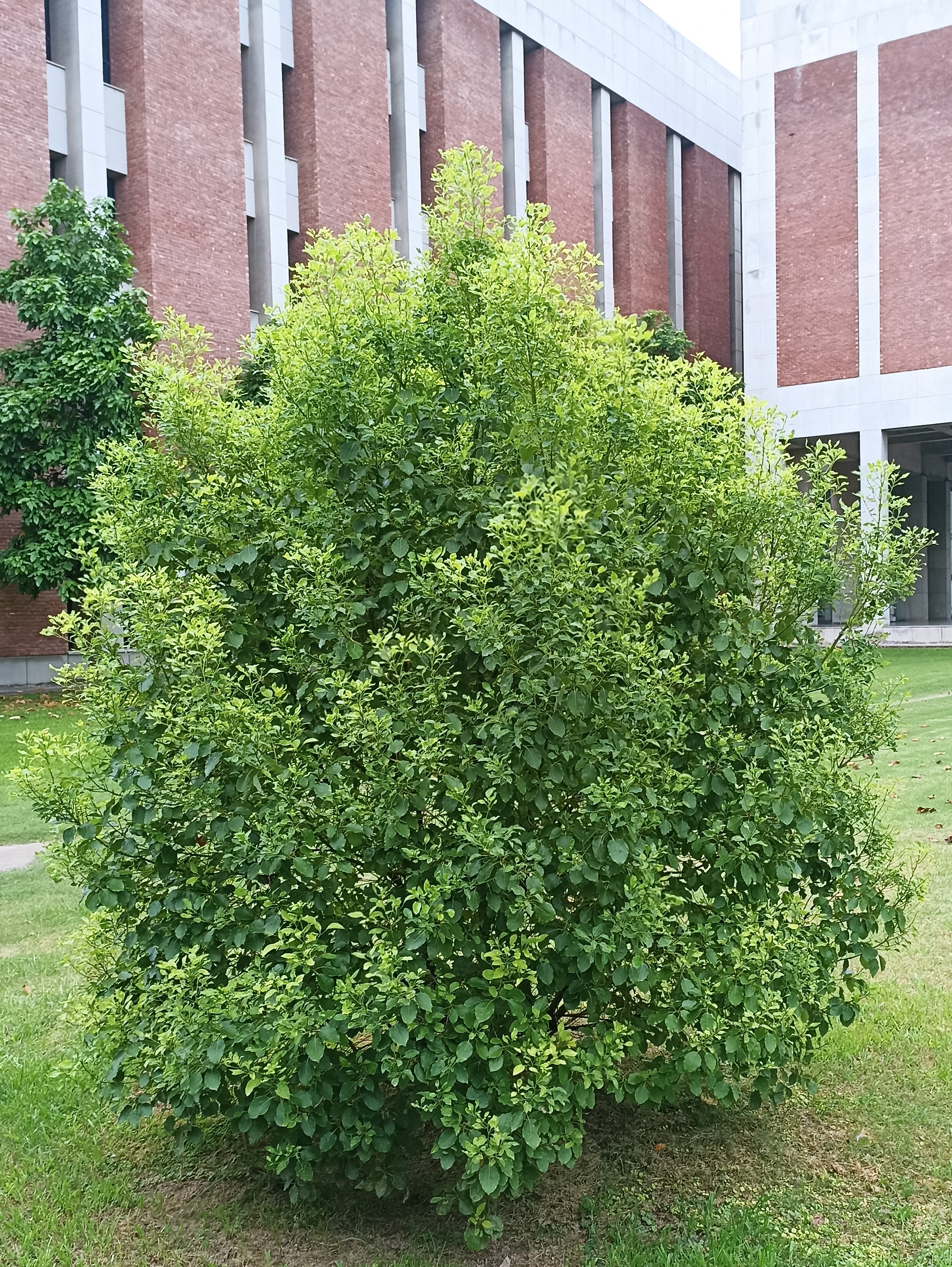
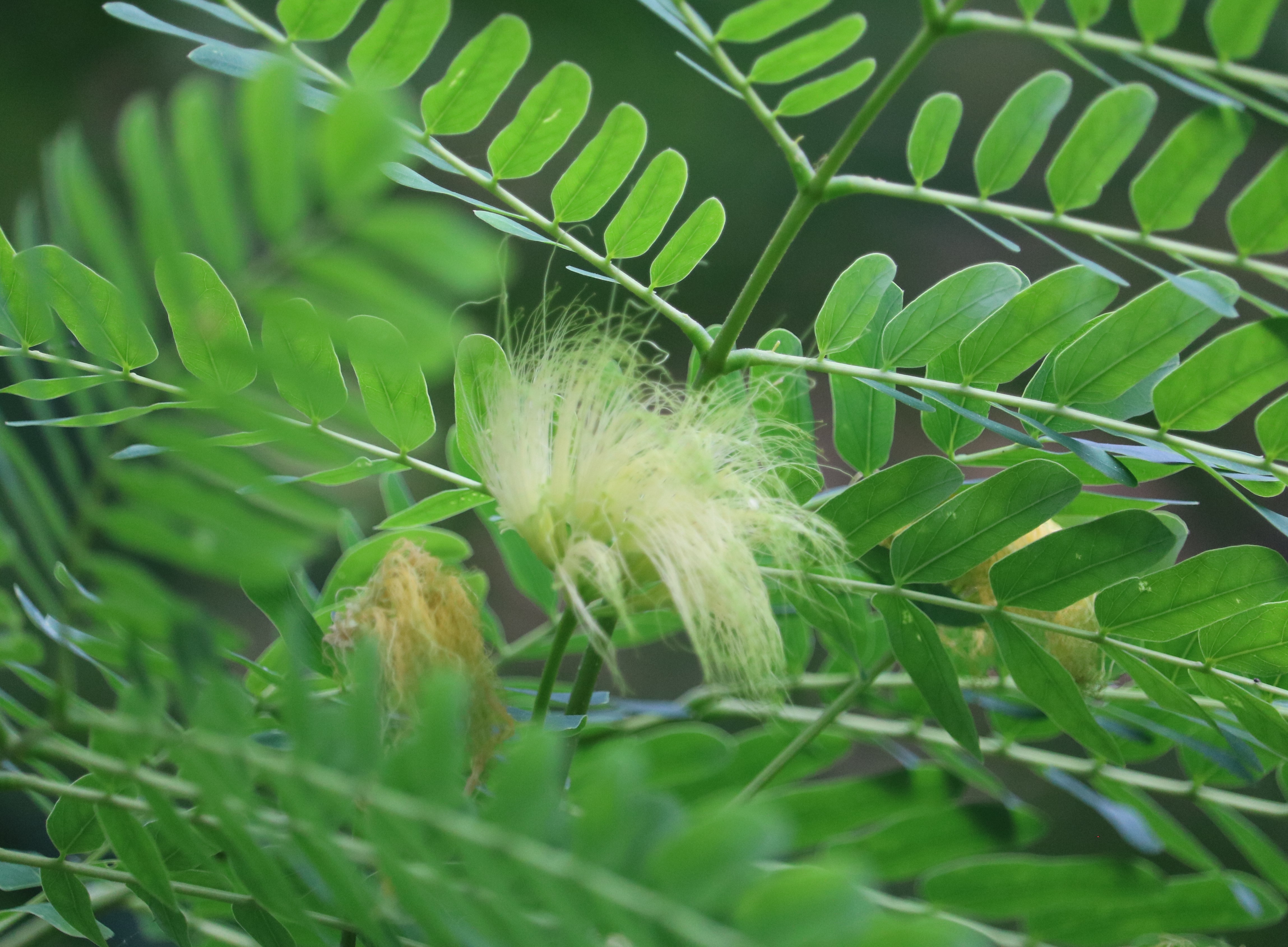
The pomegranate (Punica granatum) is a fruit-bearing deciduous shrub in the family Lythraceae, subfamily Punicoideae, that grows between 5 and 10 m (16 and 33 ft) tall. The pomegranate was originally described throughout the Mediterranean region. It was introduced into Spanish America in the late 16th century and into California by Spanish settlers in 1769. The fruit is typically in season in the Northern Hemisphere from October to February and in the Southern Hemisphere from March to May. As intact sarcotestas or juice, pomegranates are used in baking, cooking, juice blends, meal garnishes, smoothies, and alcoholic beverages, such as cocktails and wine.
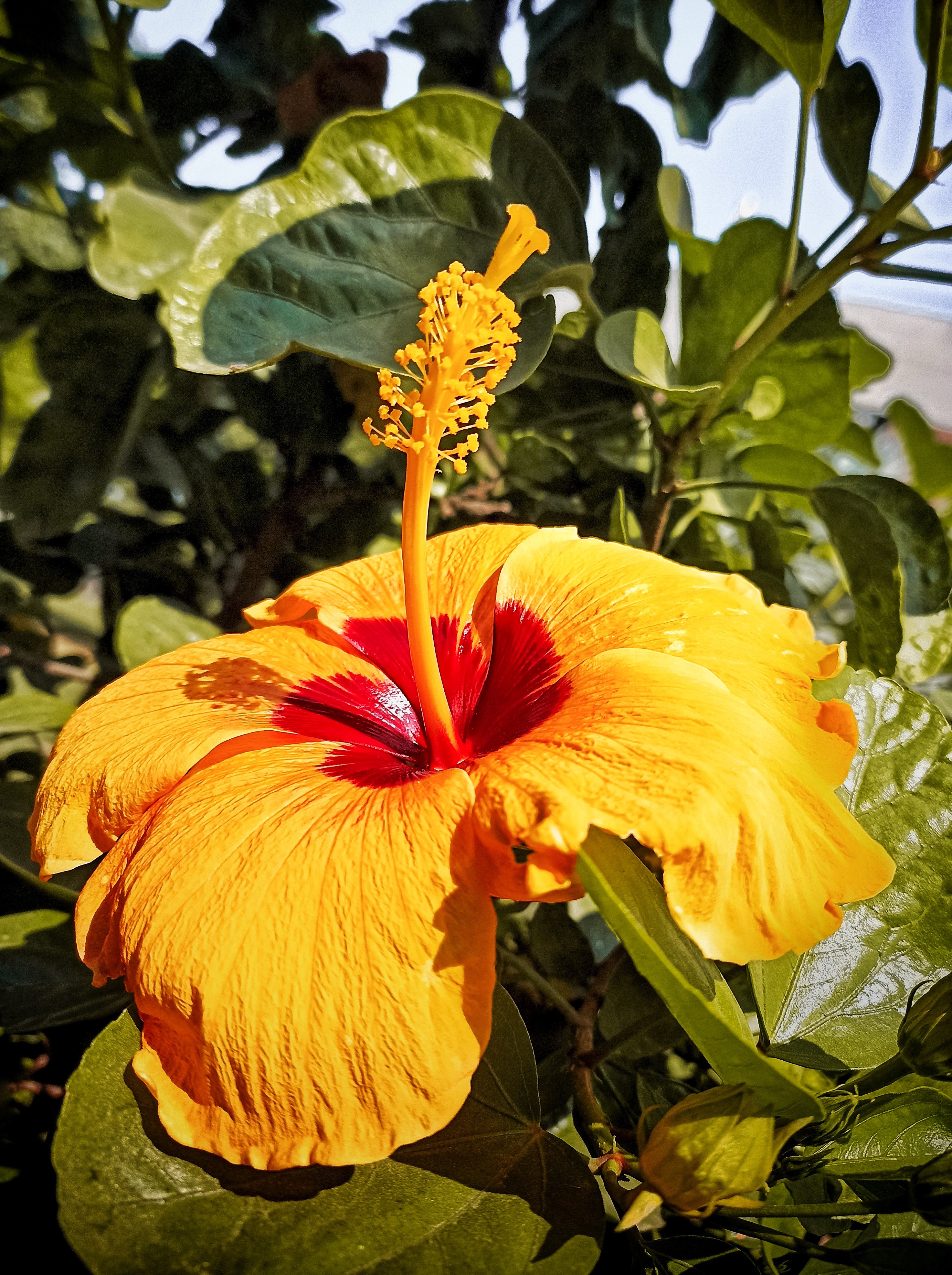
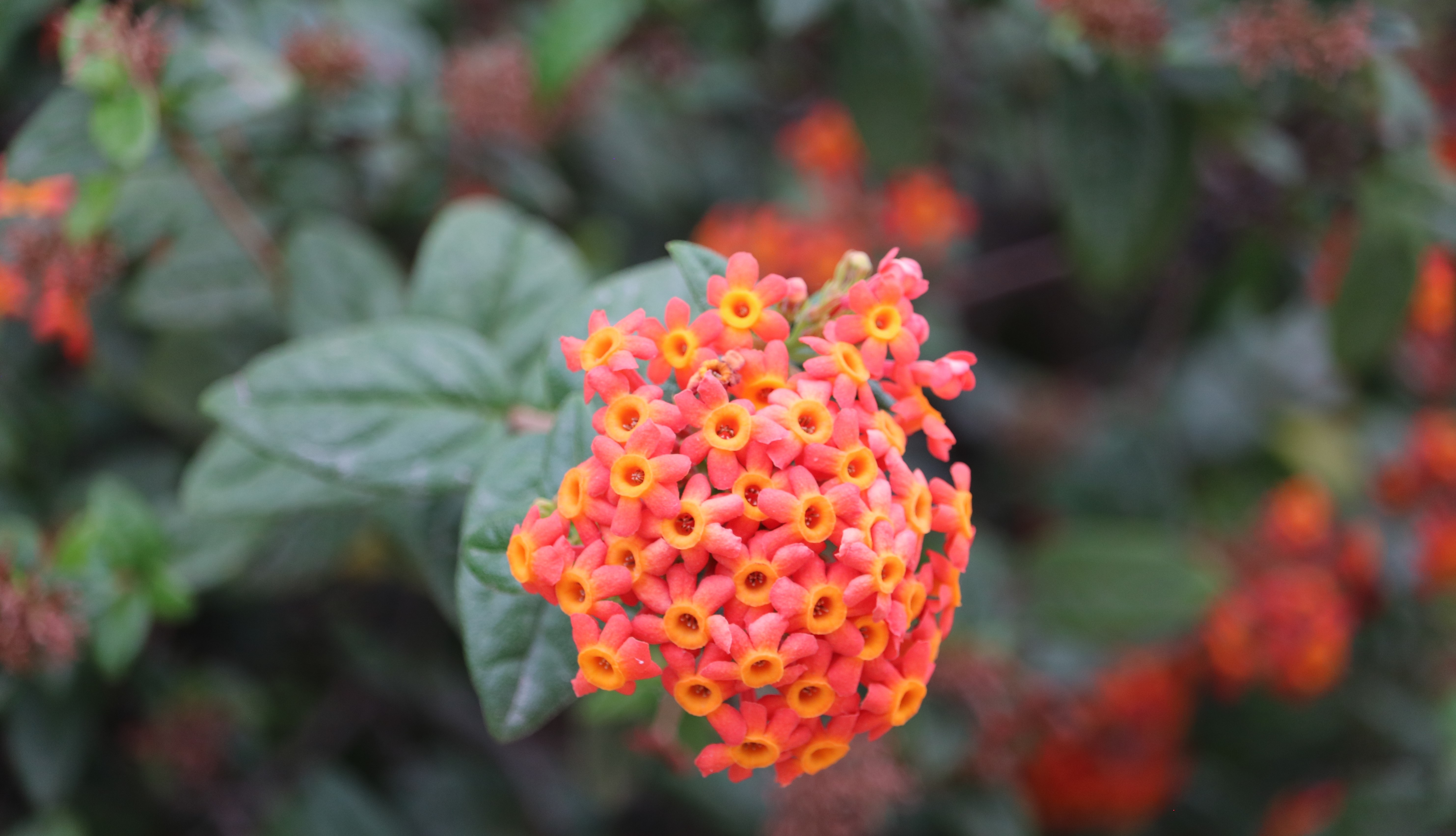
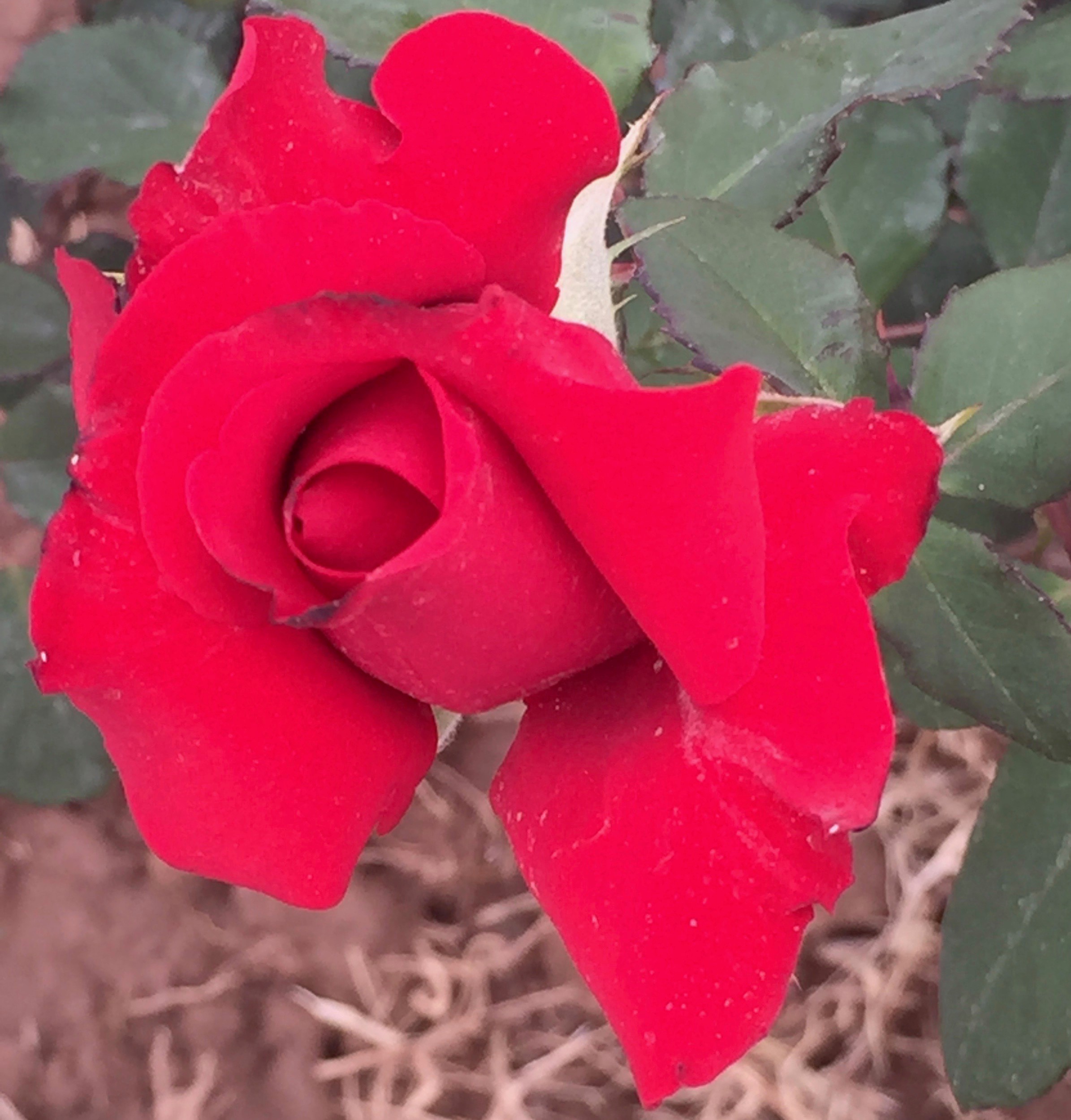
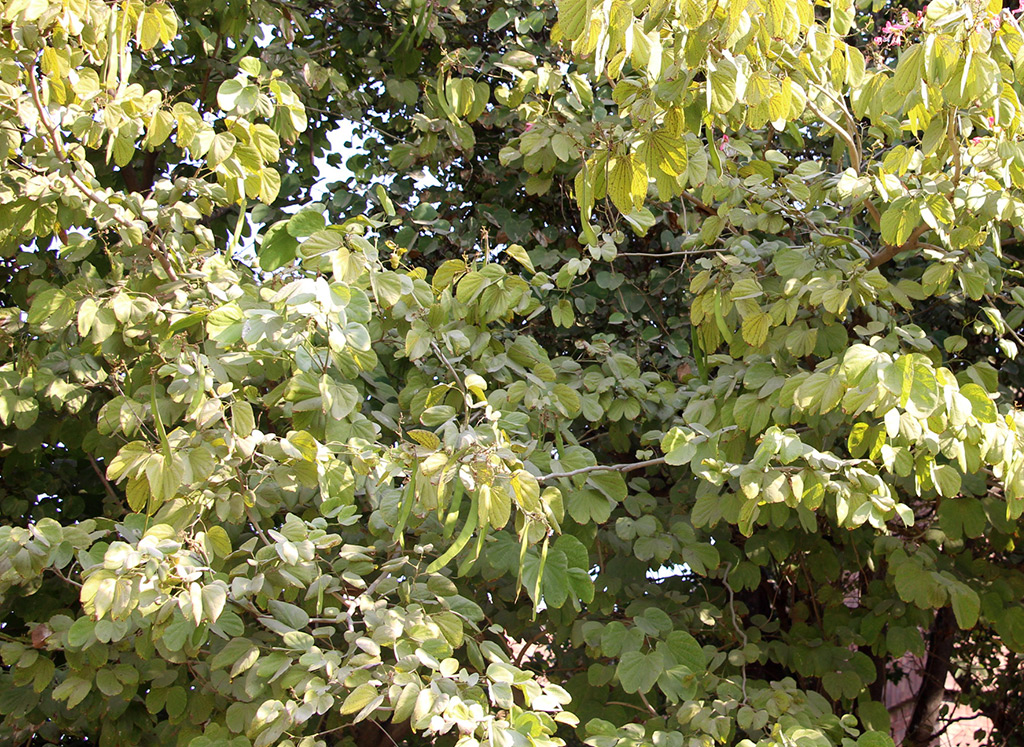
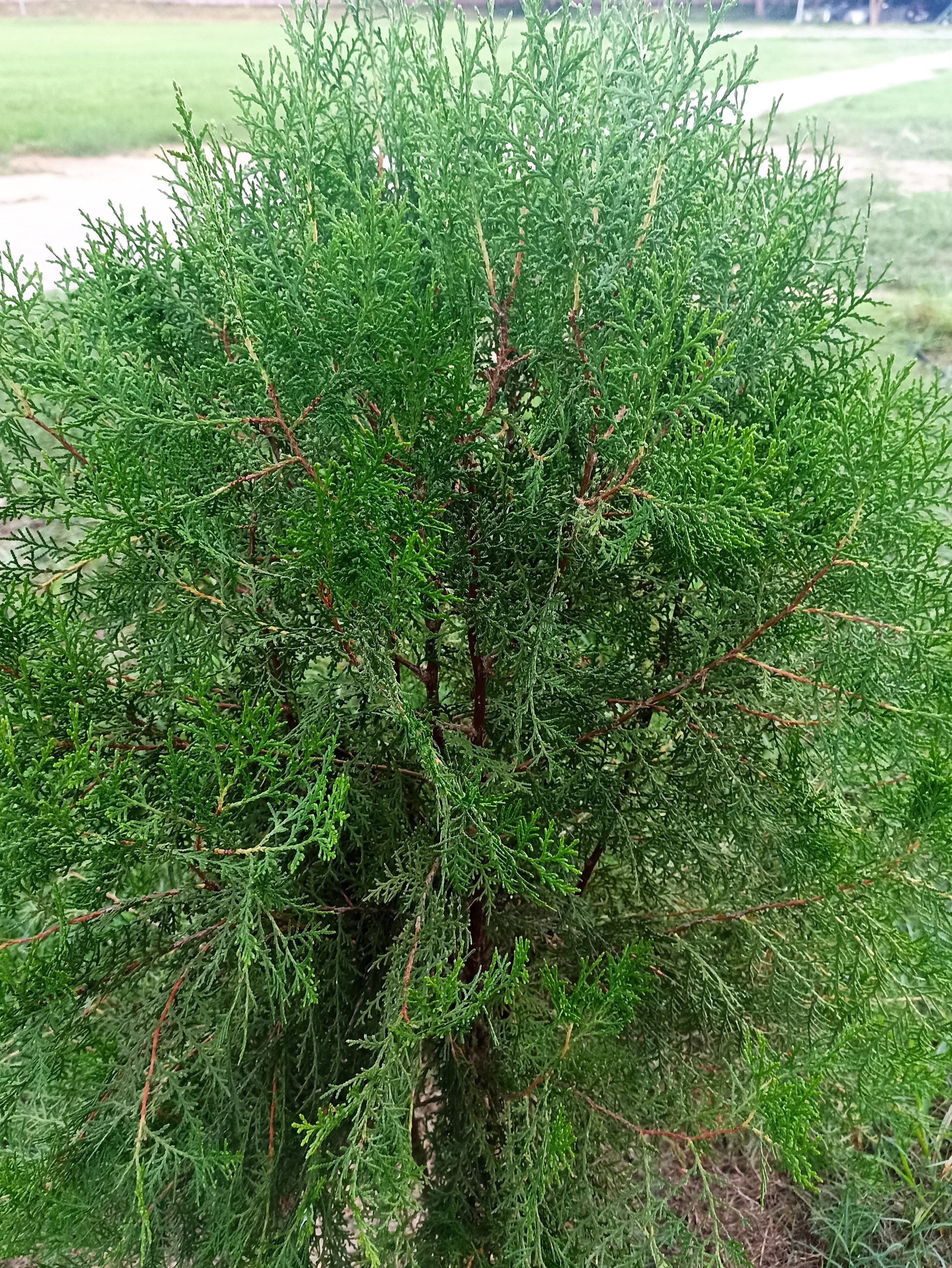
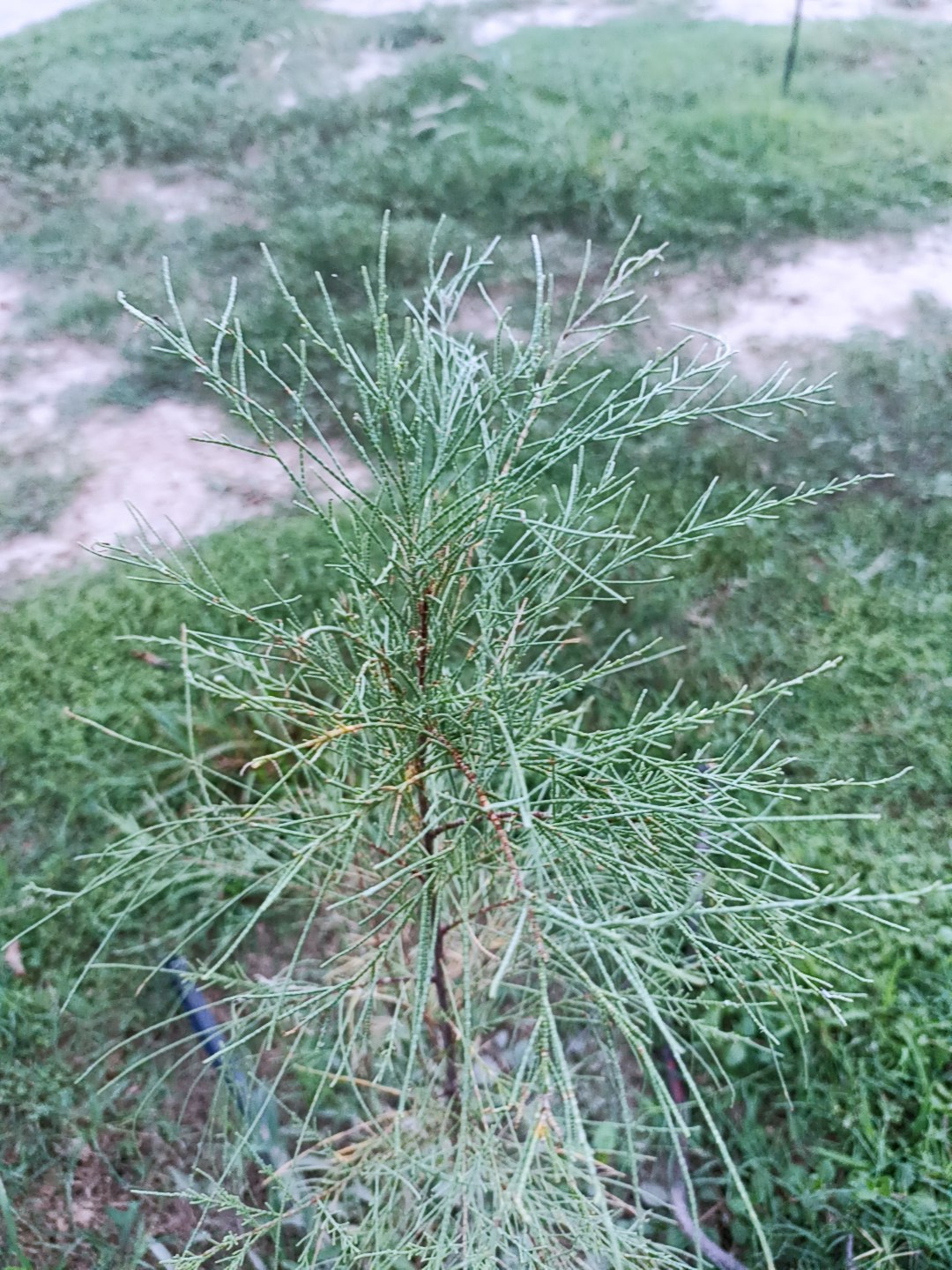
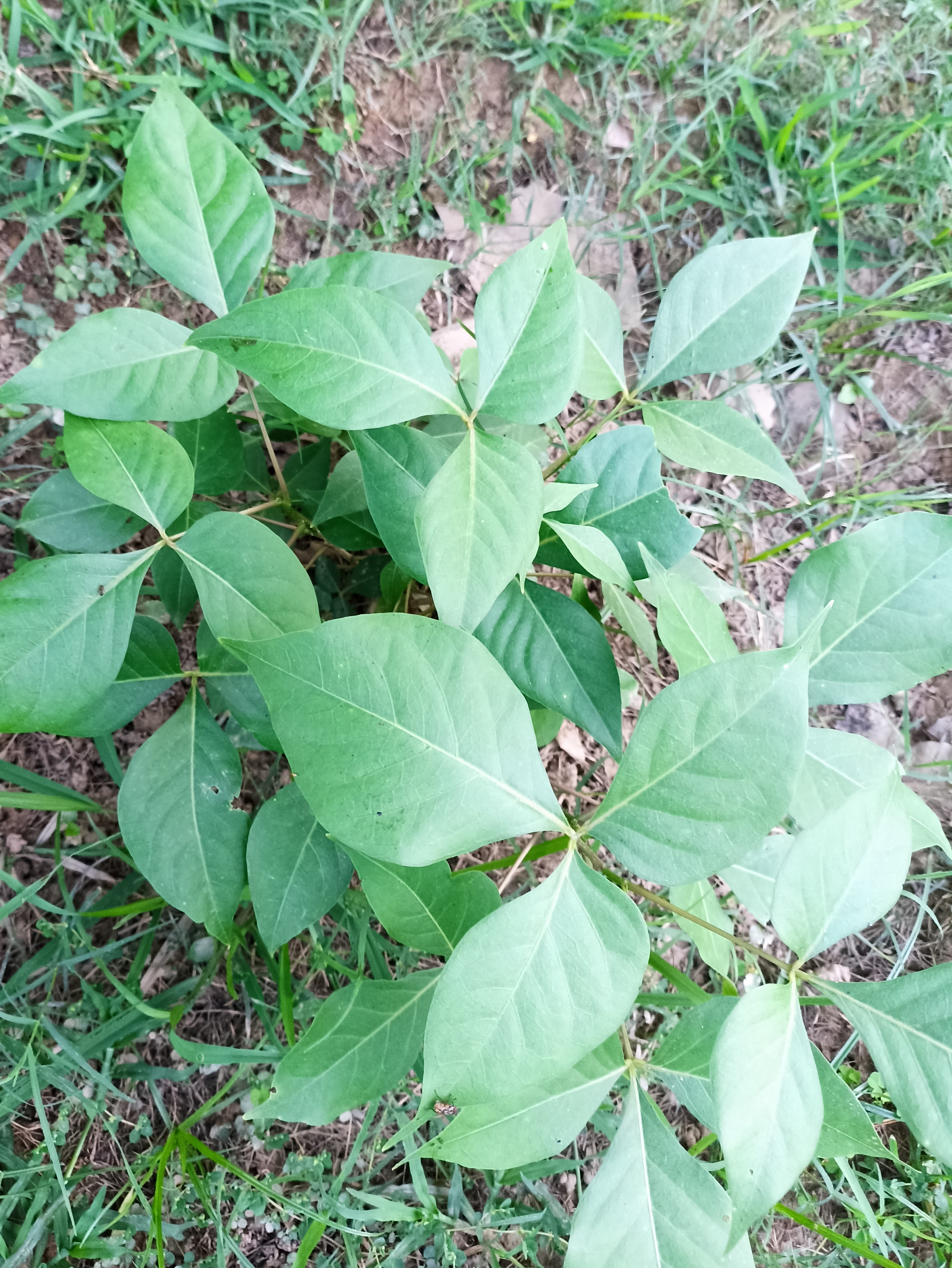
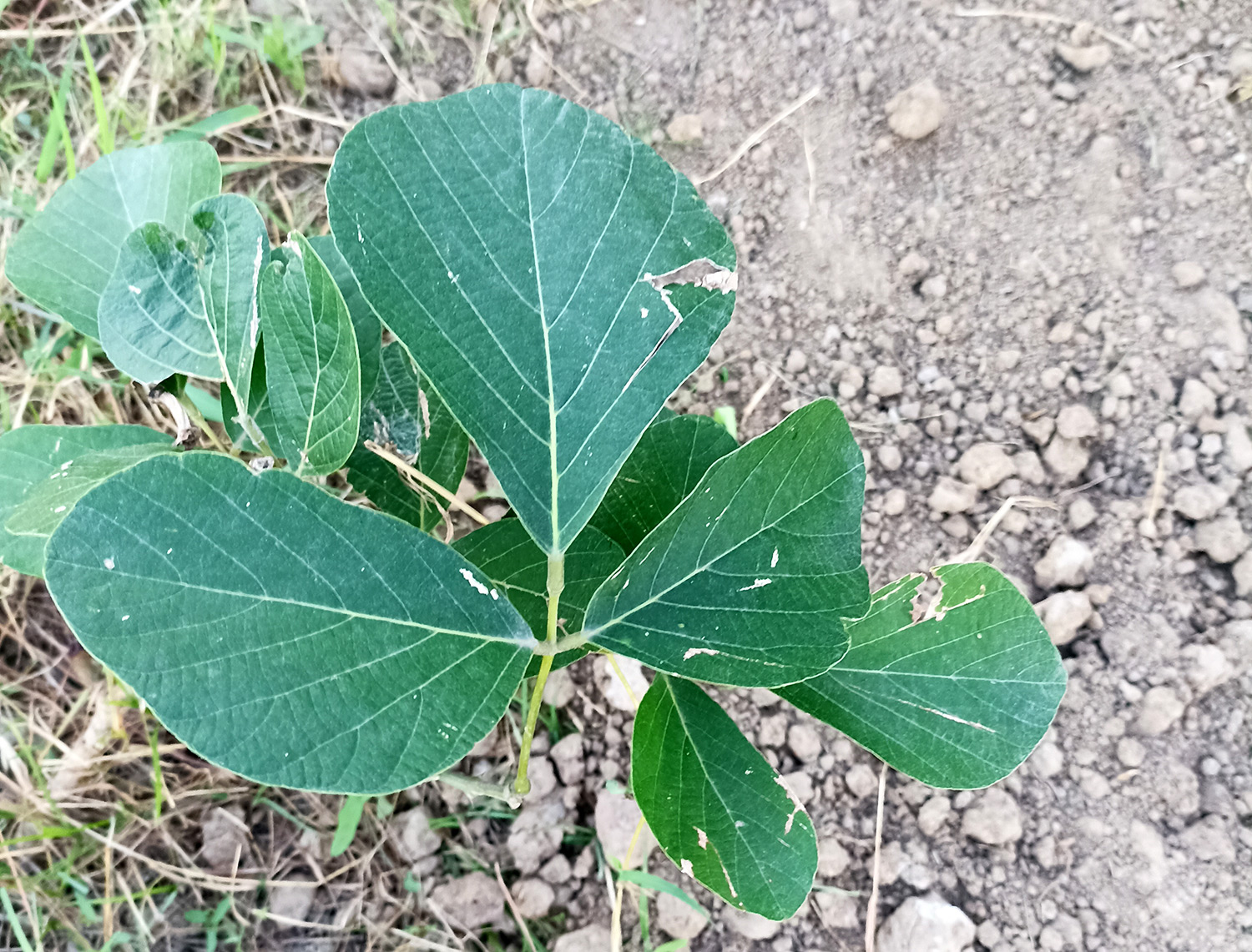
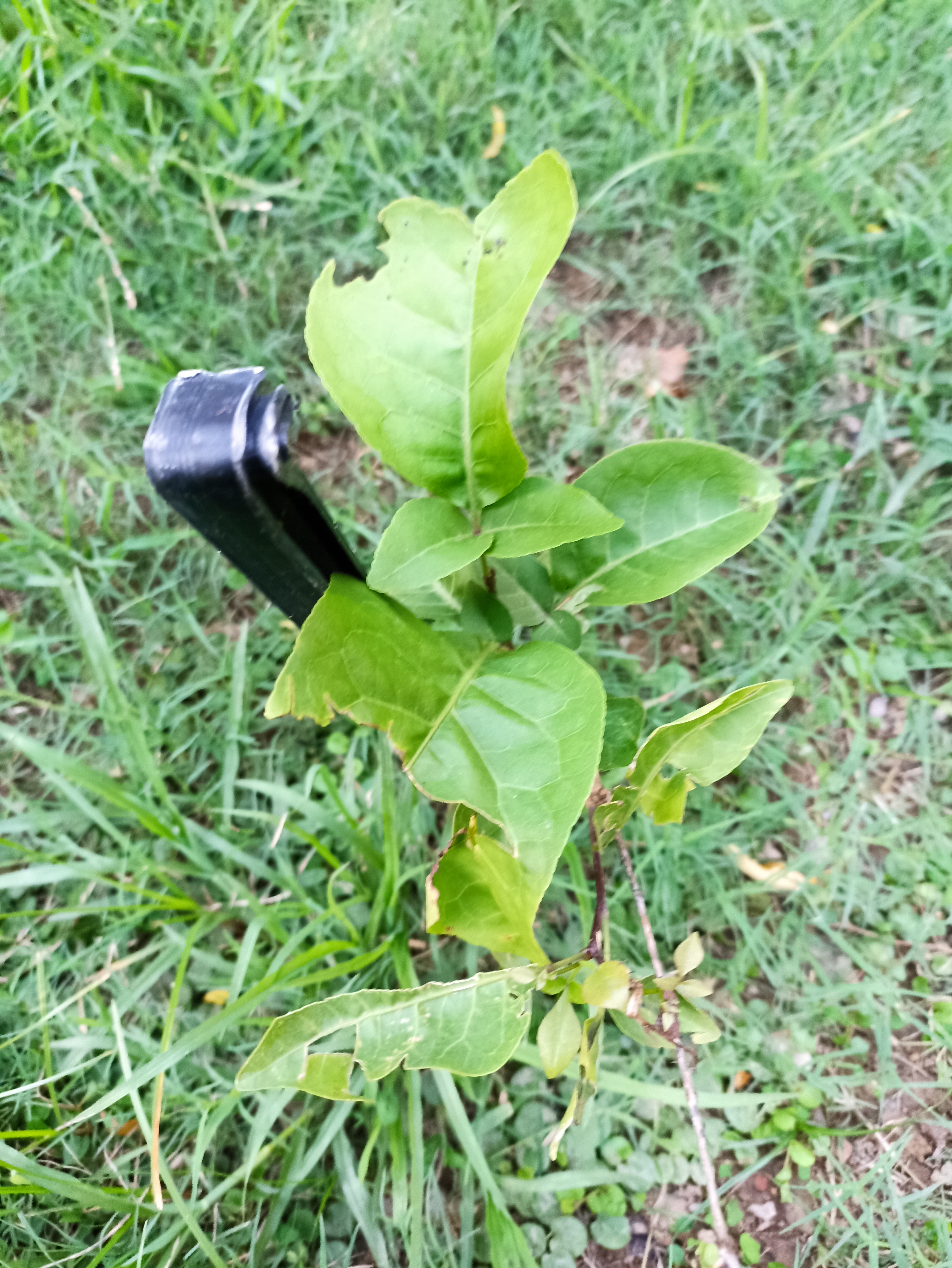
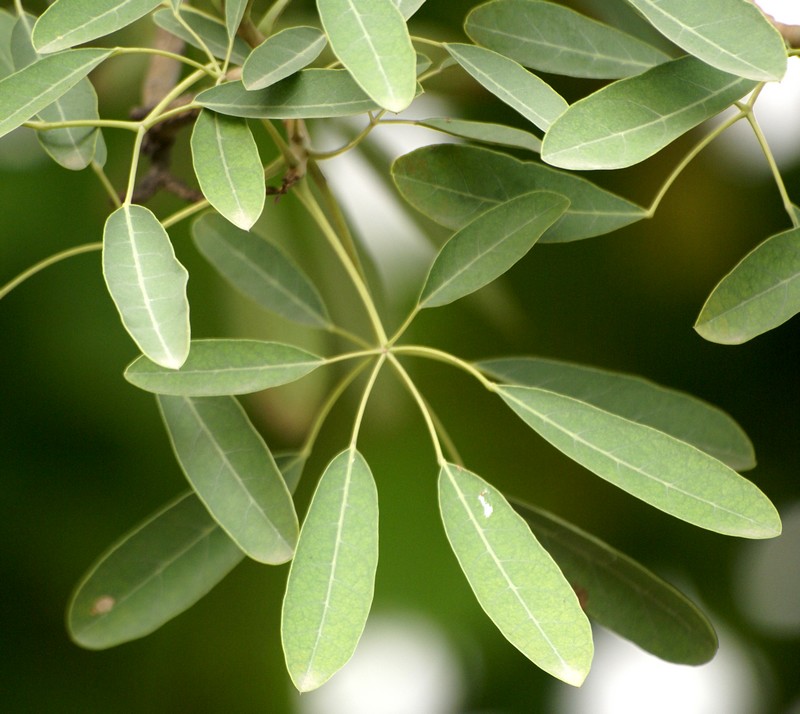
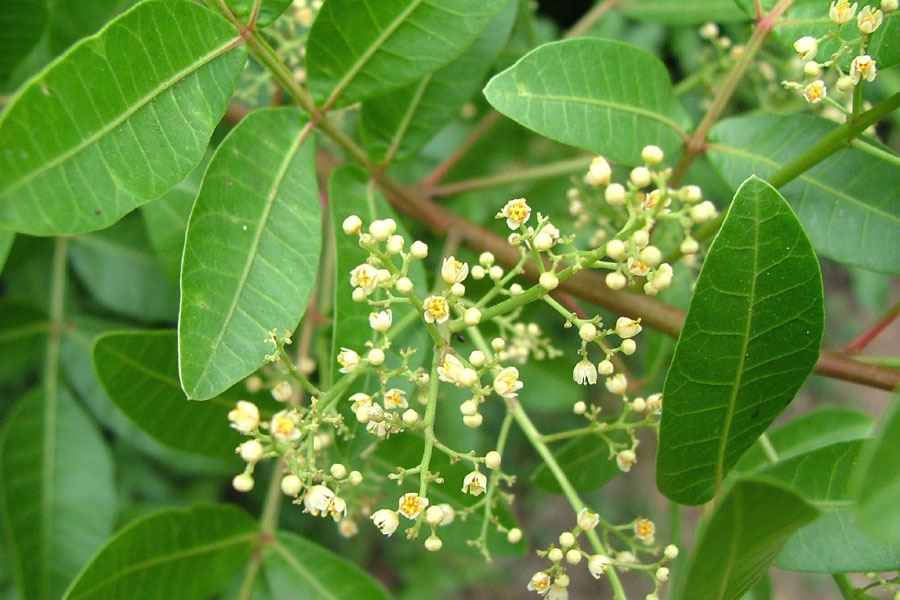
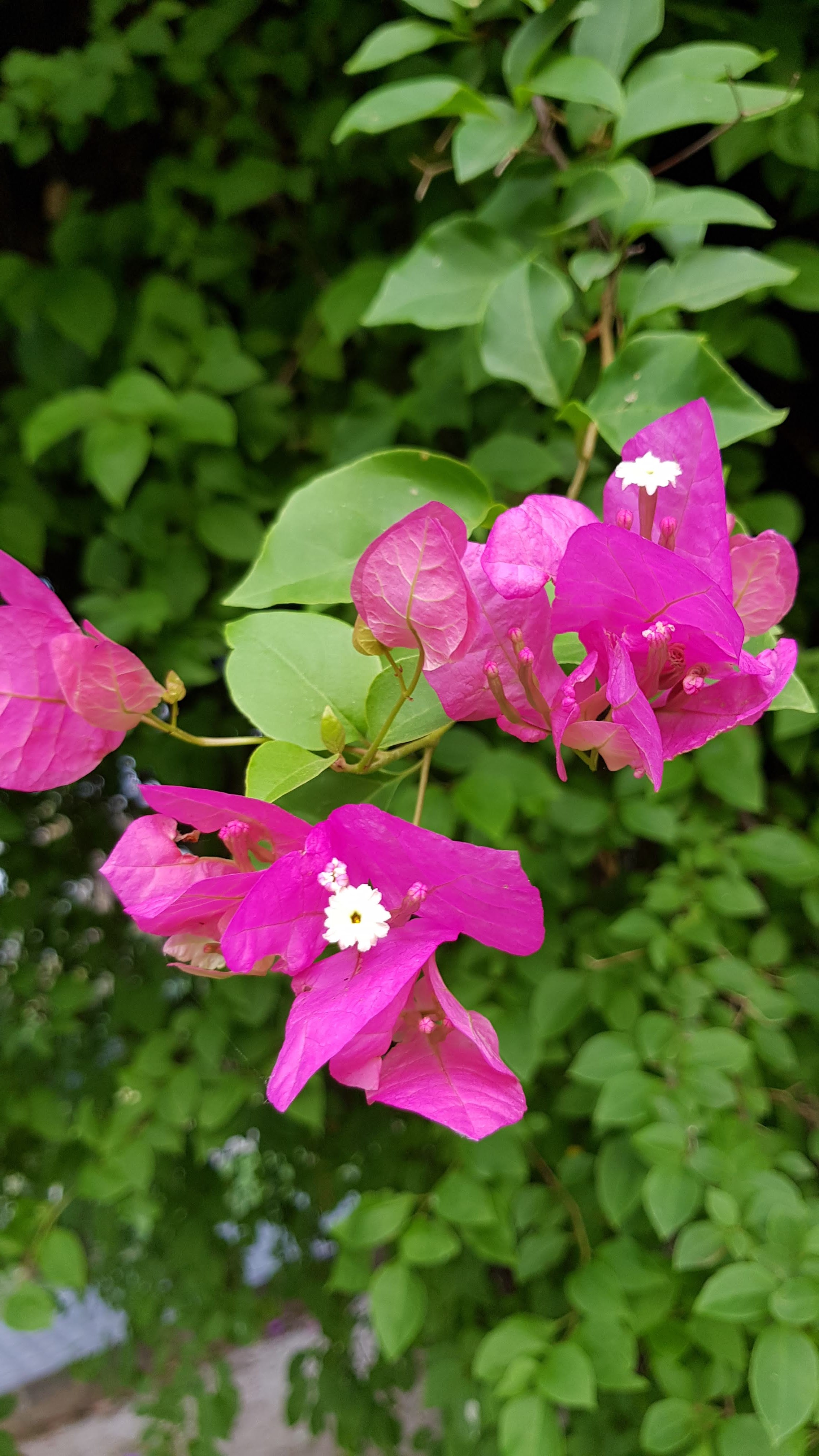
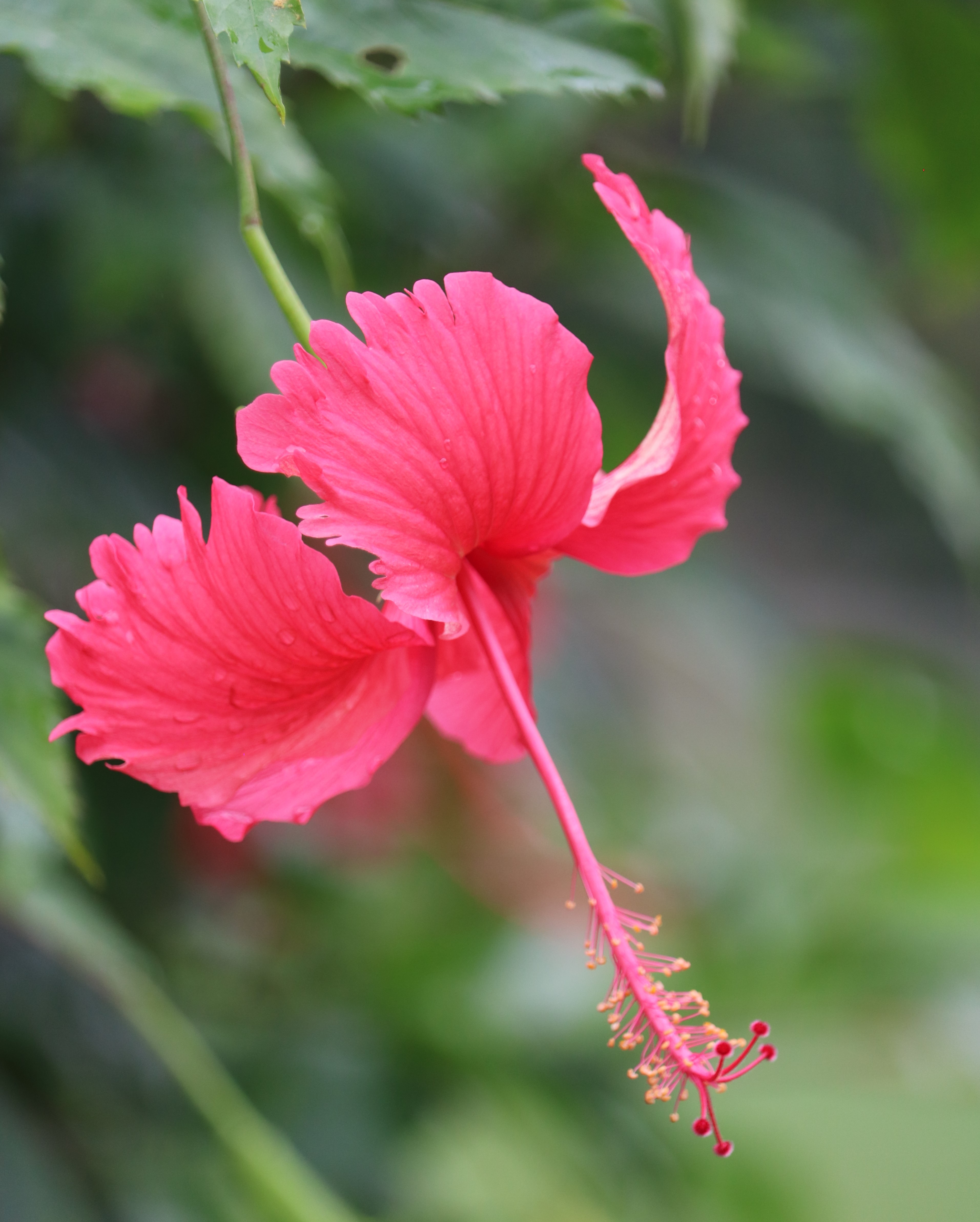
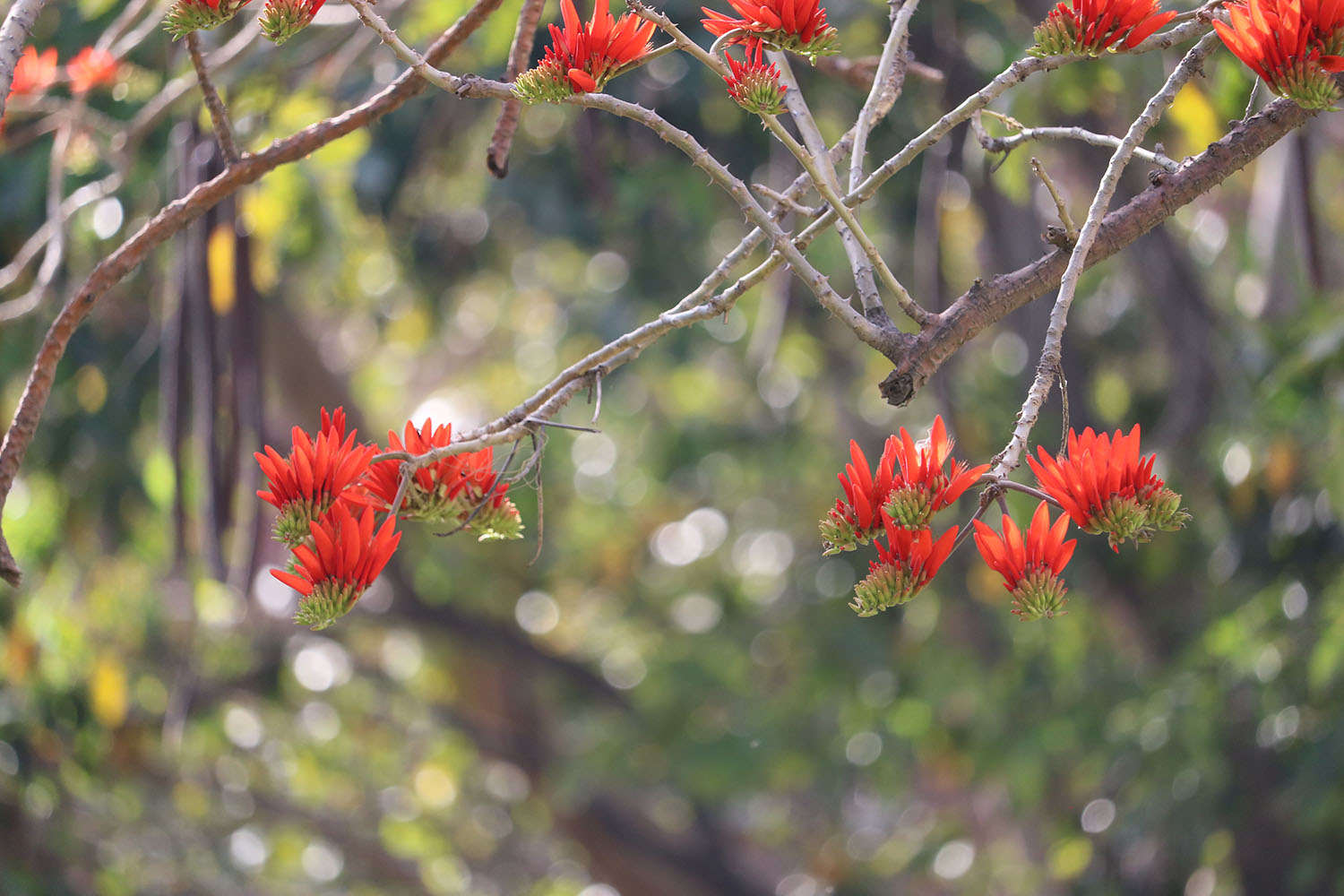
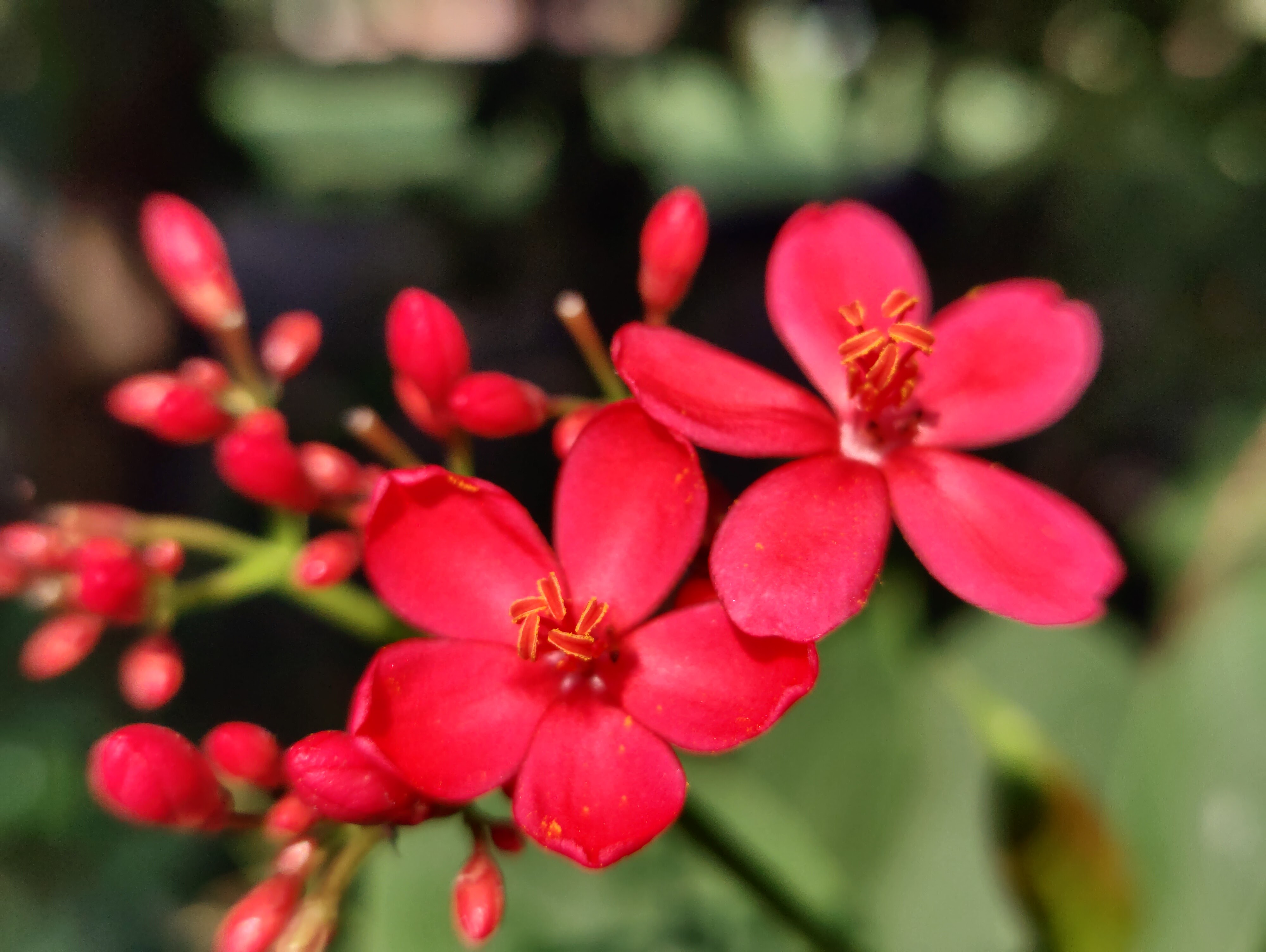
Pomegranates are widely cultivated throughout the Middle East and Caucasus region, north and tropical Africa, Iran, Armenia, the Indian subcontinent, Central Asia, the drier parts of Southeast Asia, and the Mediterranean Basin. A shrub or small tree growing 5 to 10 m (16 to 33 ft) high, the pomegranate has multiple spiny branches and is long-lived, with some specimens in France surviving for 200 years. P. granatum leaves are opposite or subopposite, glossy, narrow oblong, entire, 3–7 cm (1+1⁄4–2+3⁄4 in) long and 2 cm (3⁄4 in) broad. The flowers are bright red and 3 cm (1+1⁄4 in) in diameter, with three to seven petals. Some fruitless varieties are grown for the flowers alone.