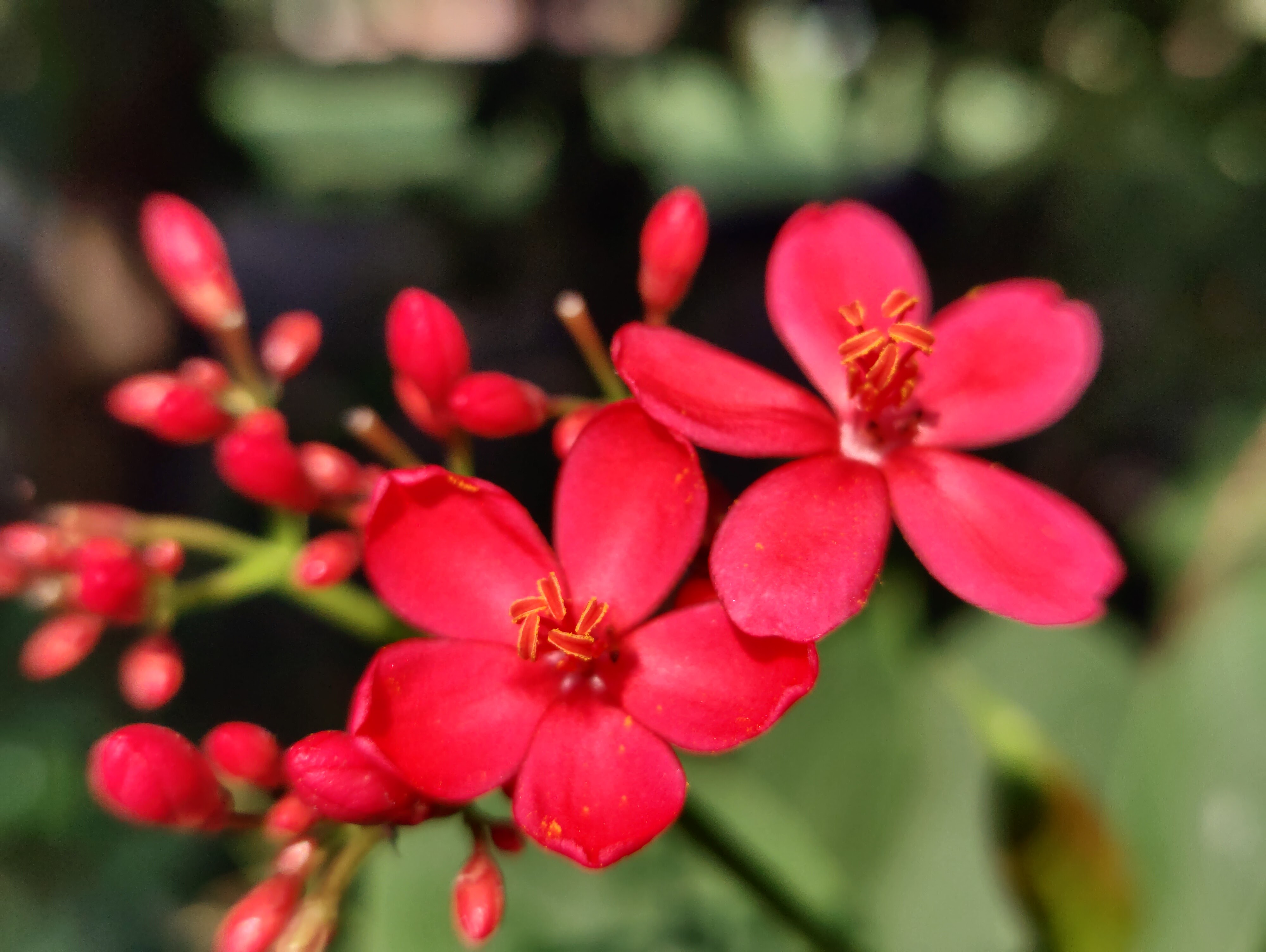
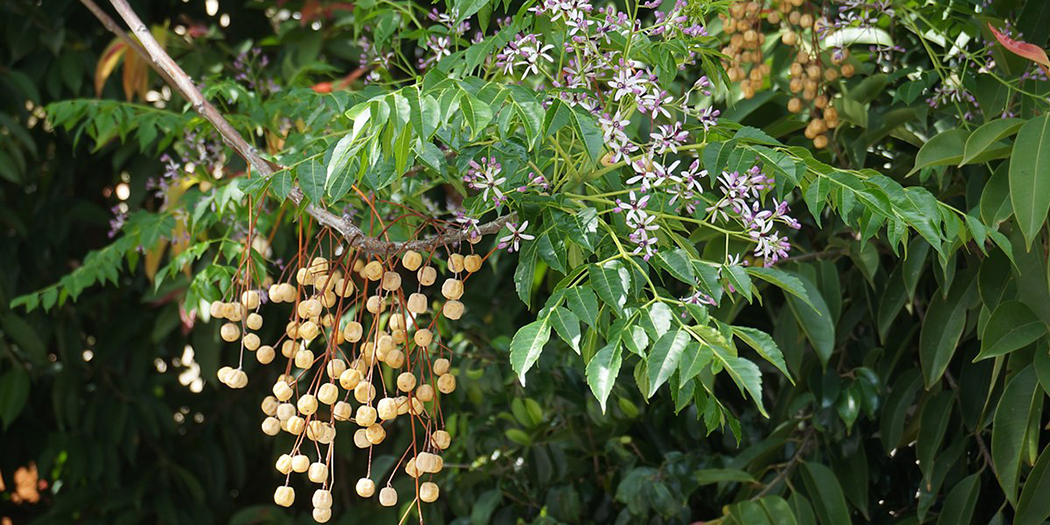
Phyllanthus emblica
Species
Families
Local Names
Genus
Native/Introduced
DNA Barcode
Description
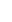
Phyllanthus emblica, also known as emblic, emblic myrobalan, myrobalan, Indian gooseberry, Malacca tree, or amla, from the Sanskrit amalaki, is a deciduous tree of the family Phyllanthaceae. Its native range is tropical and southern Asia.
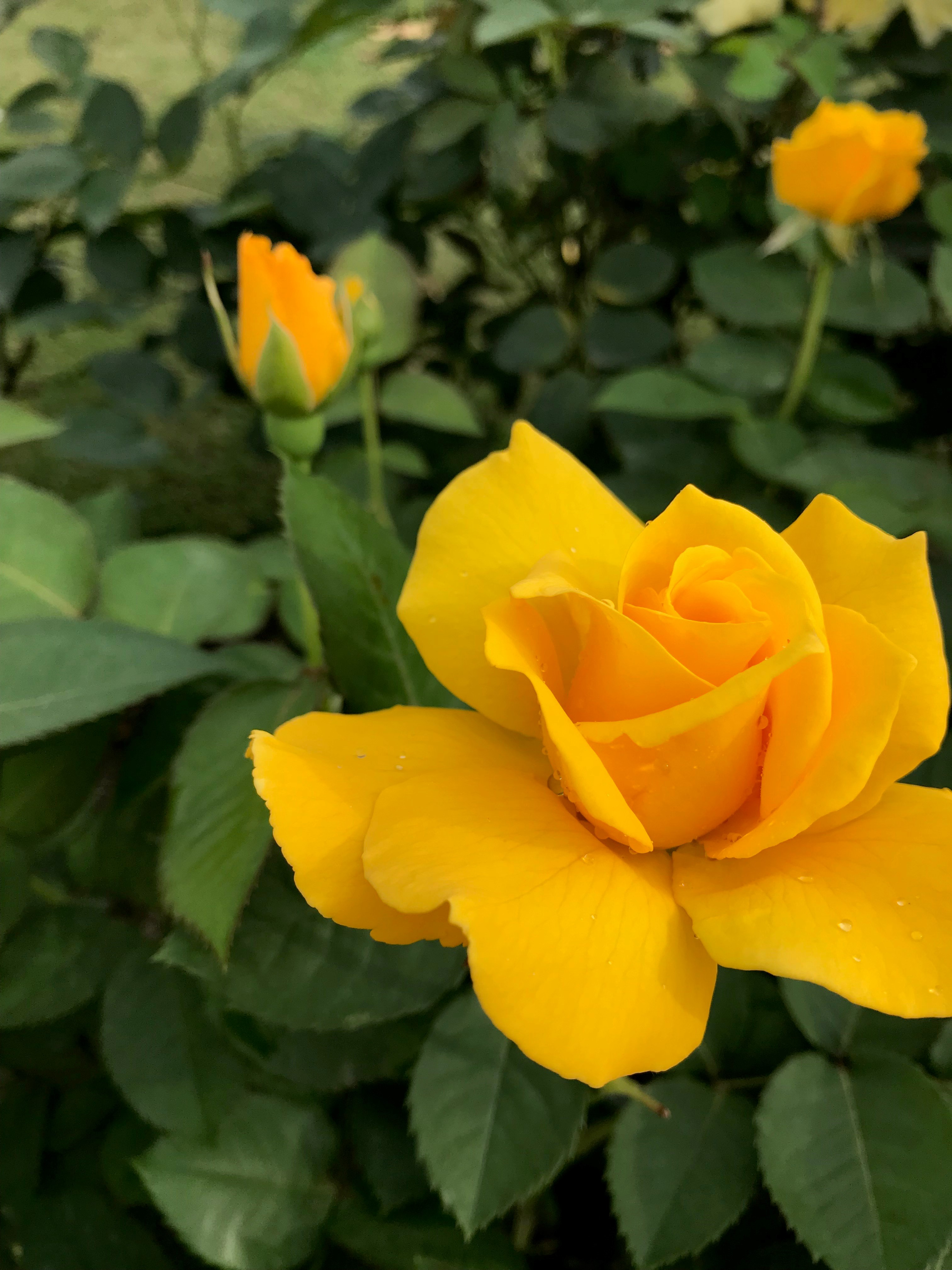
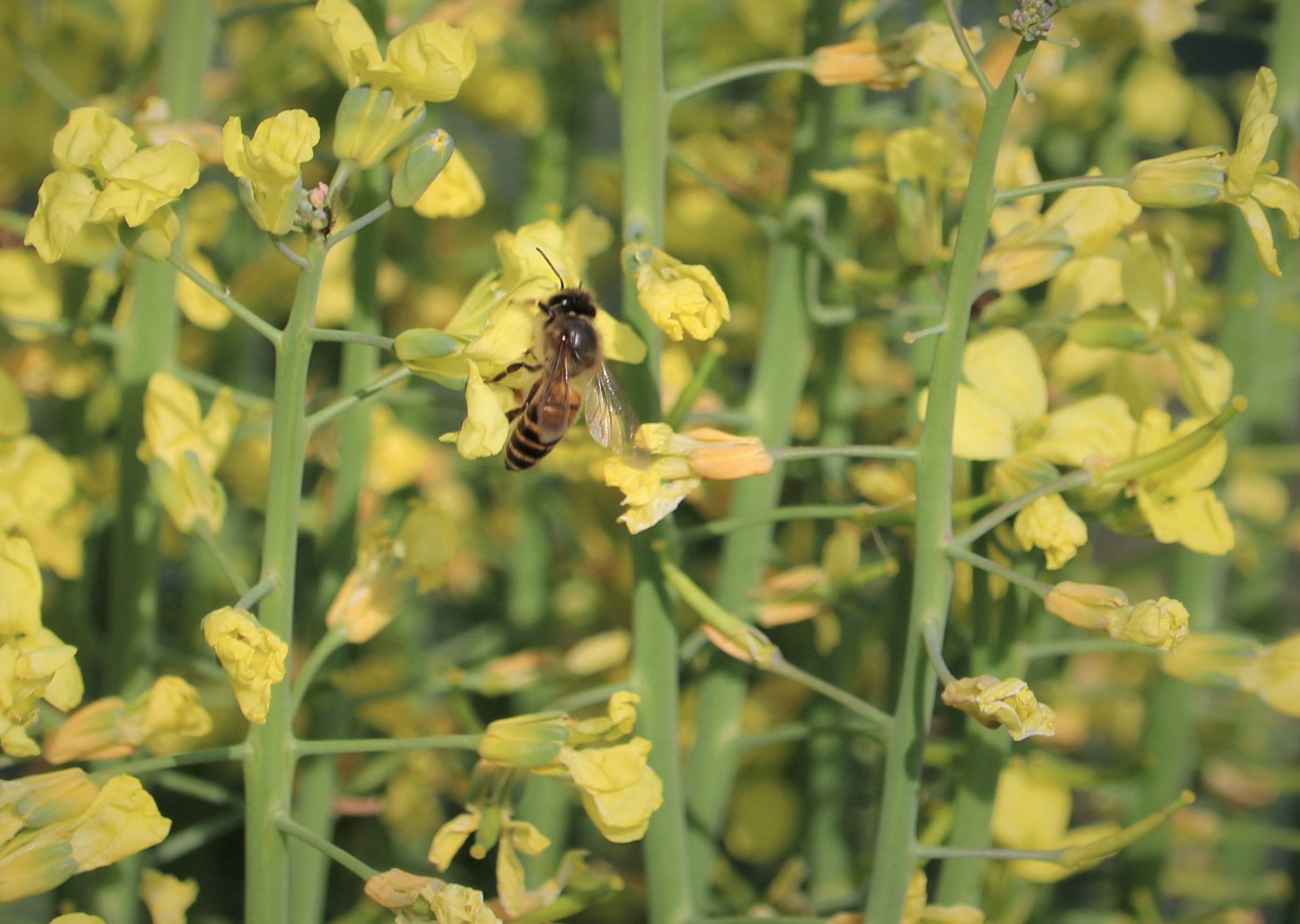
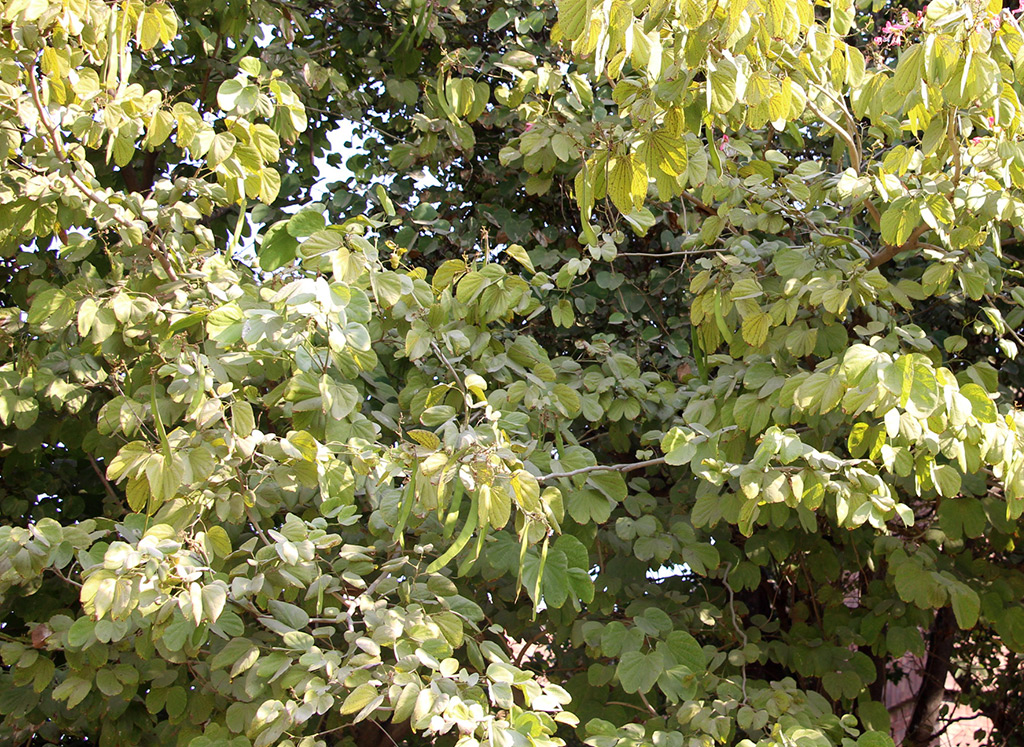
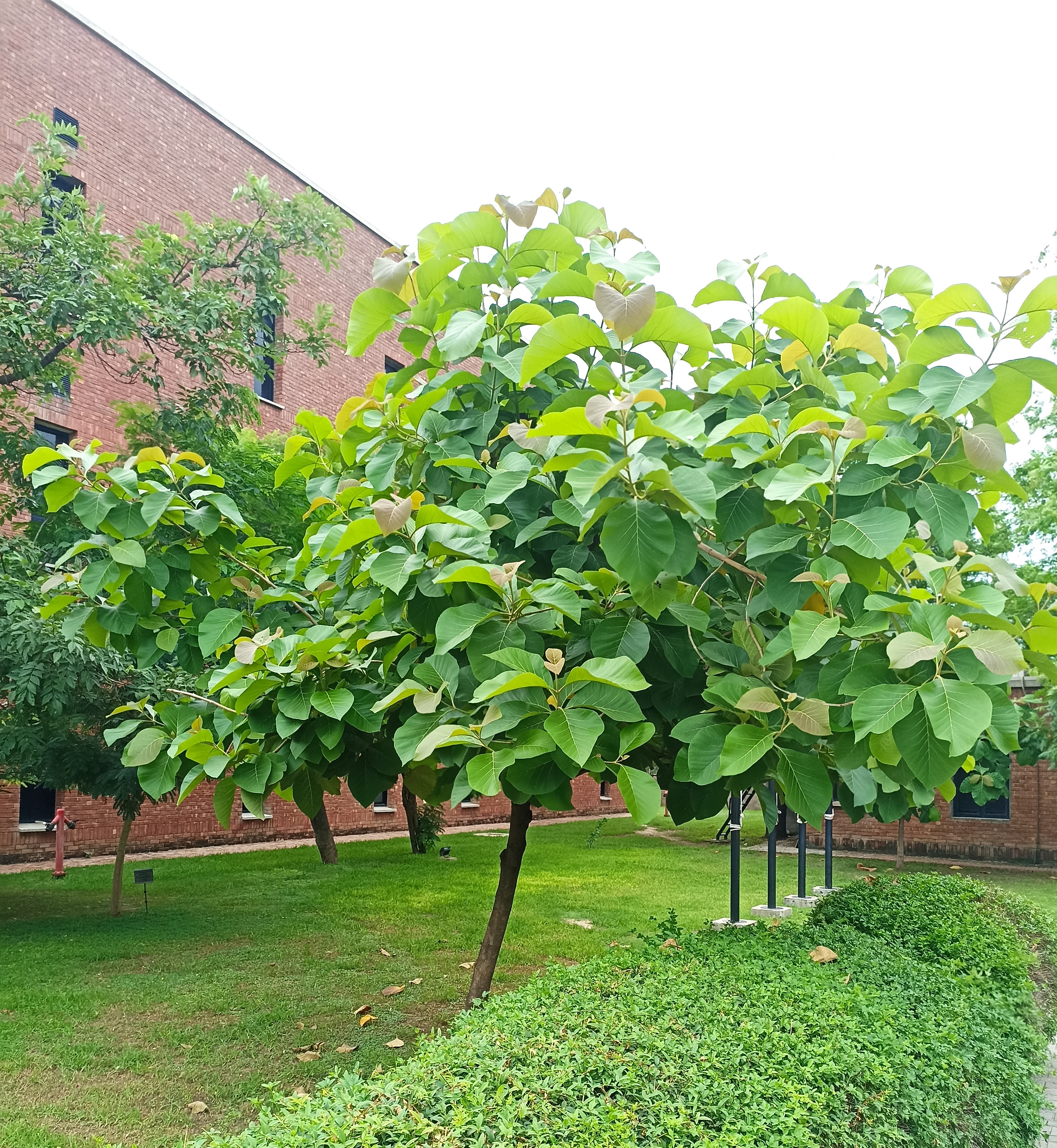
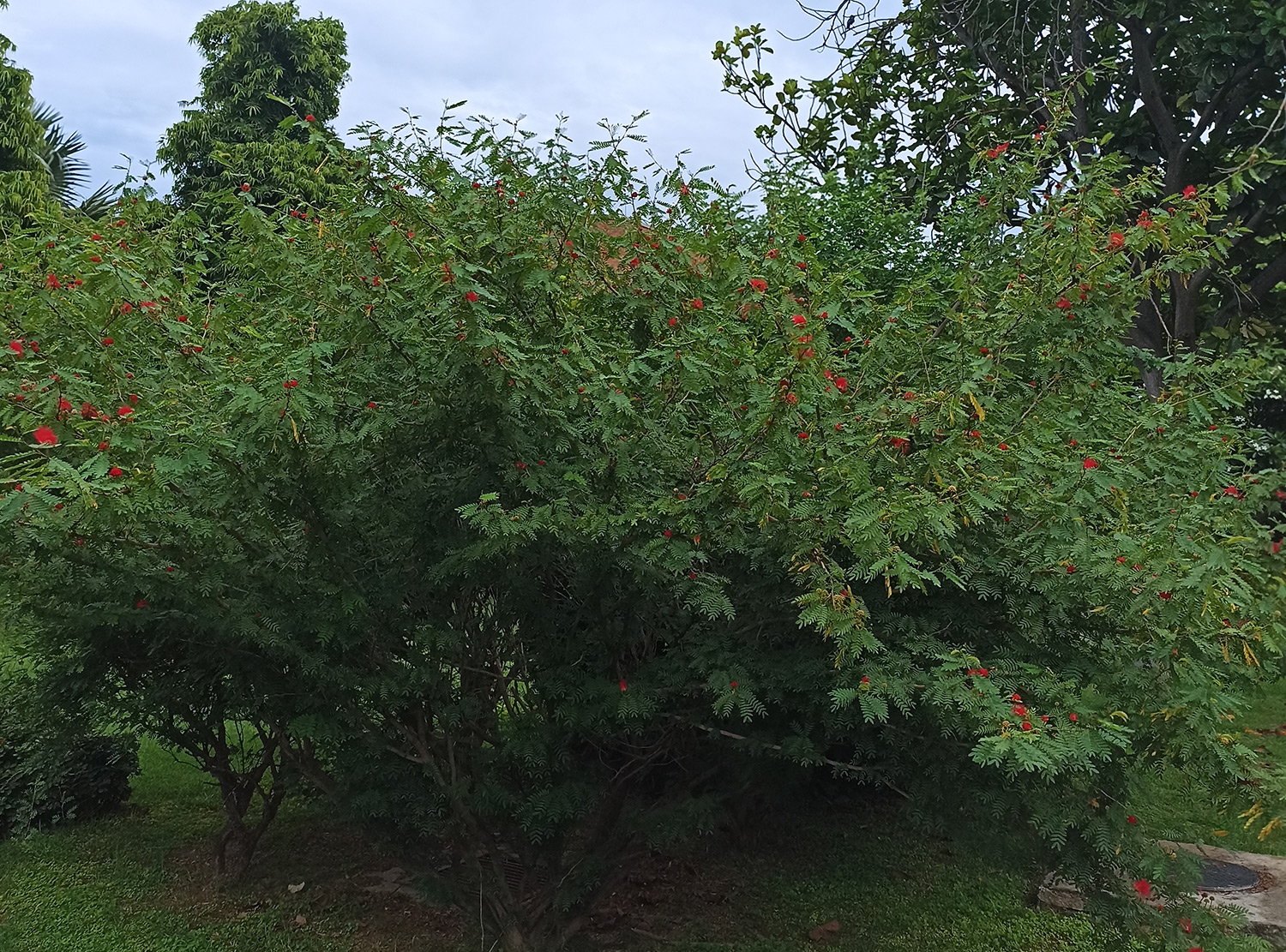
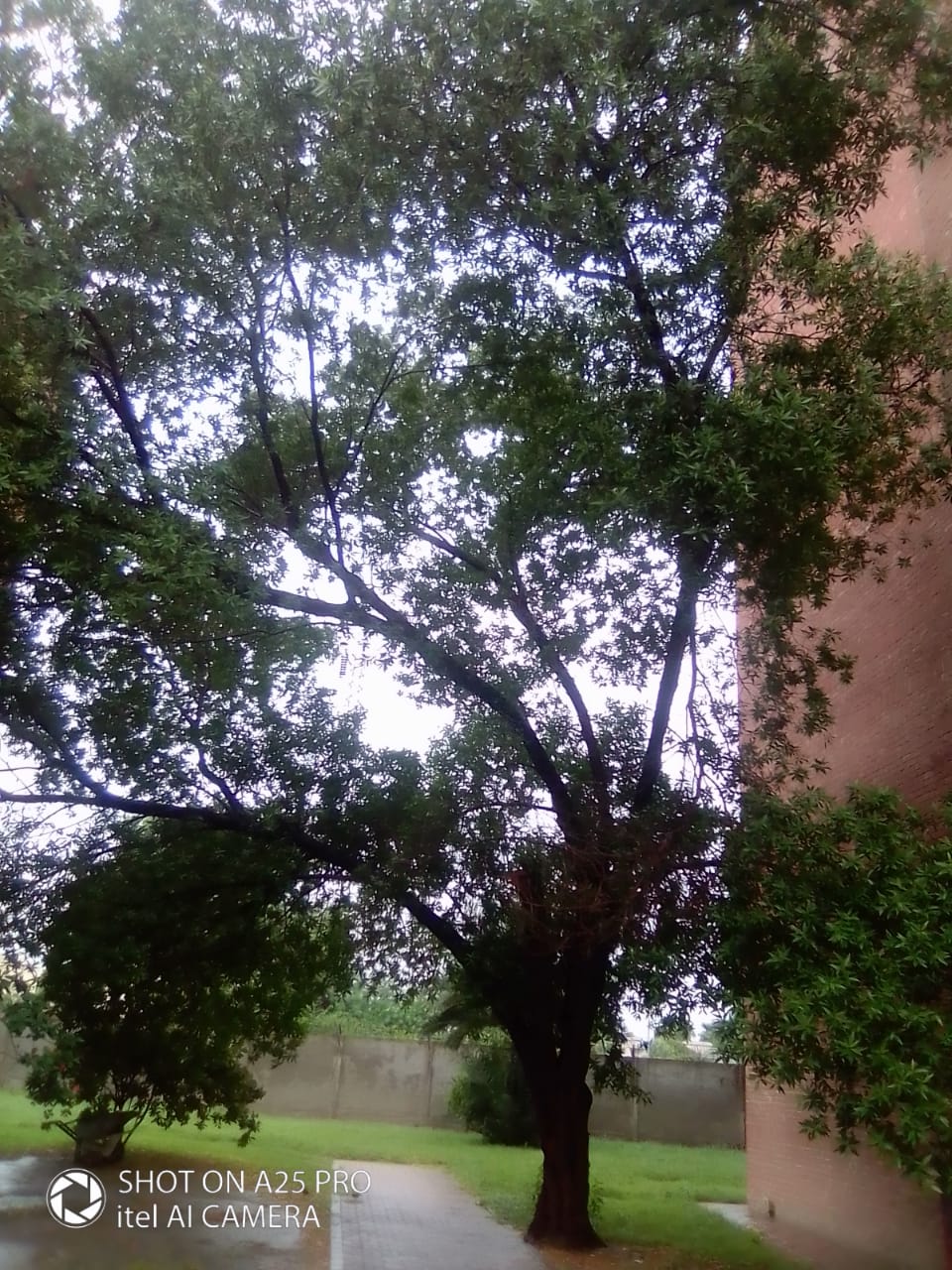
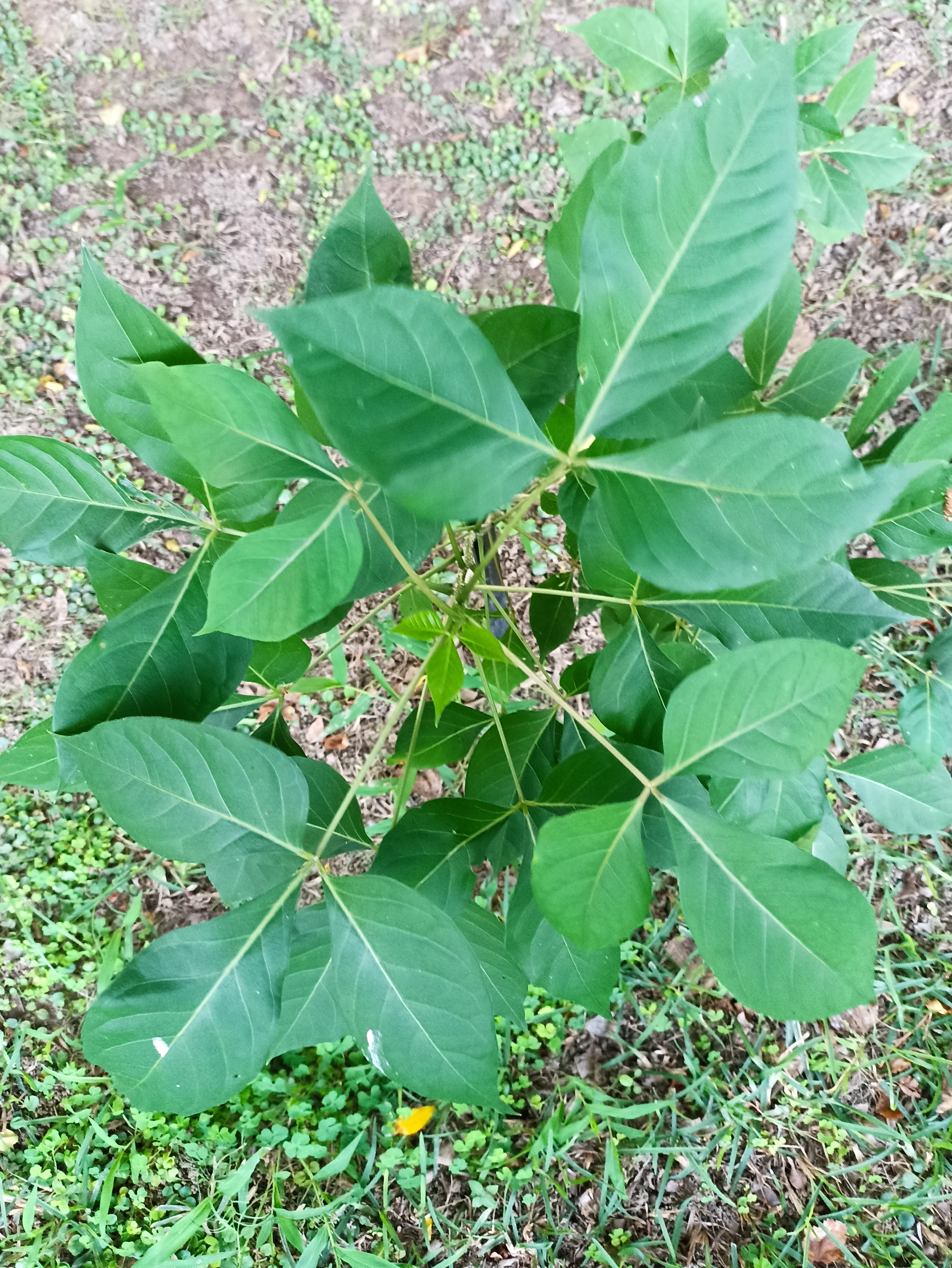
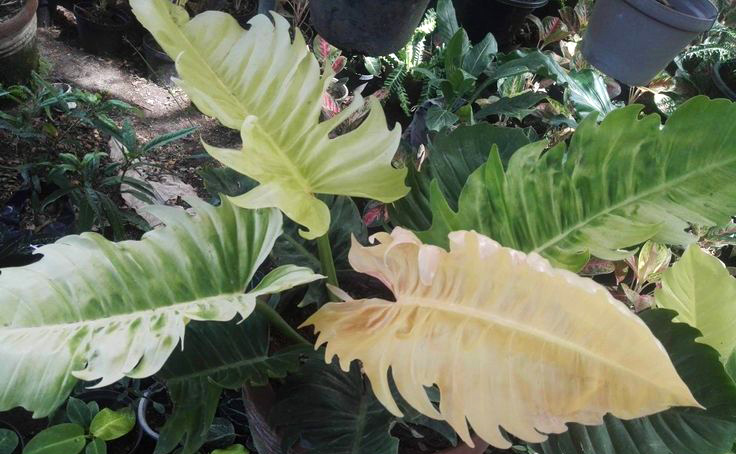
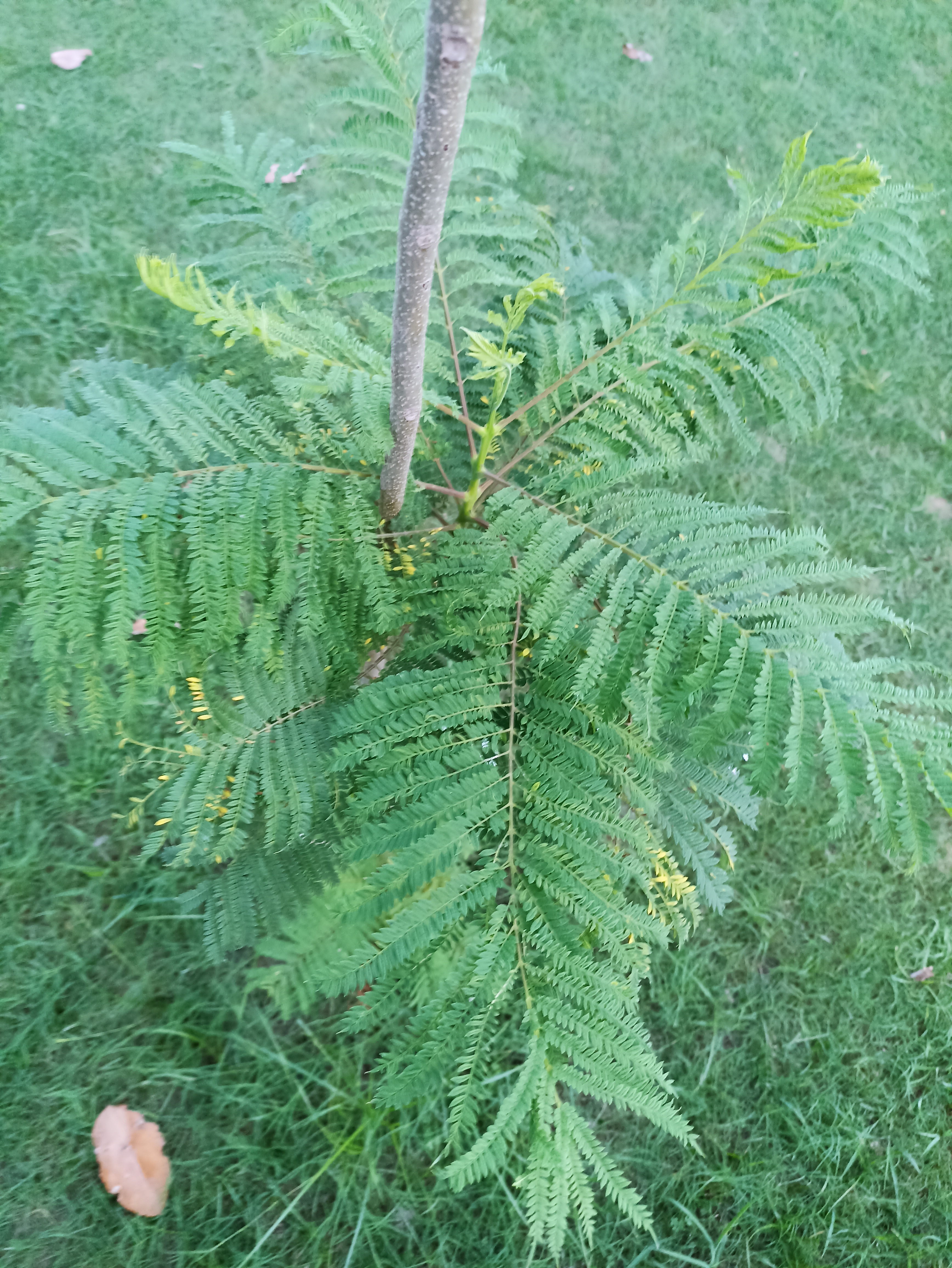
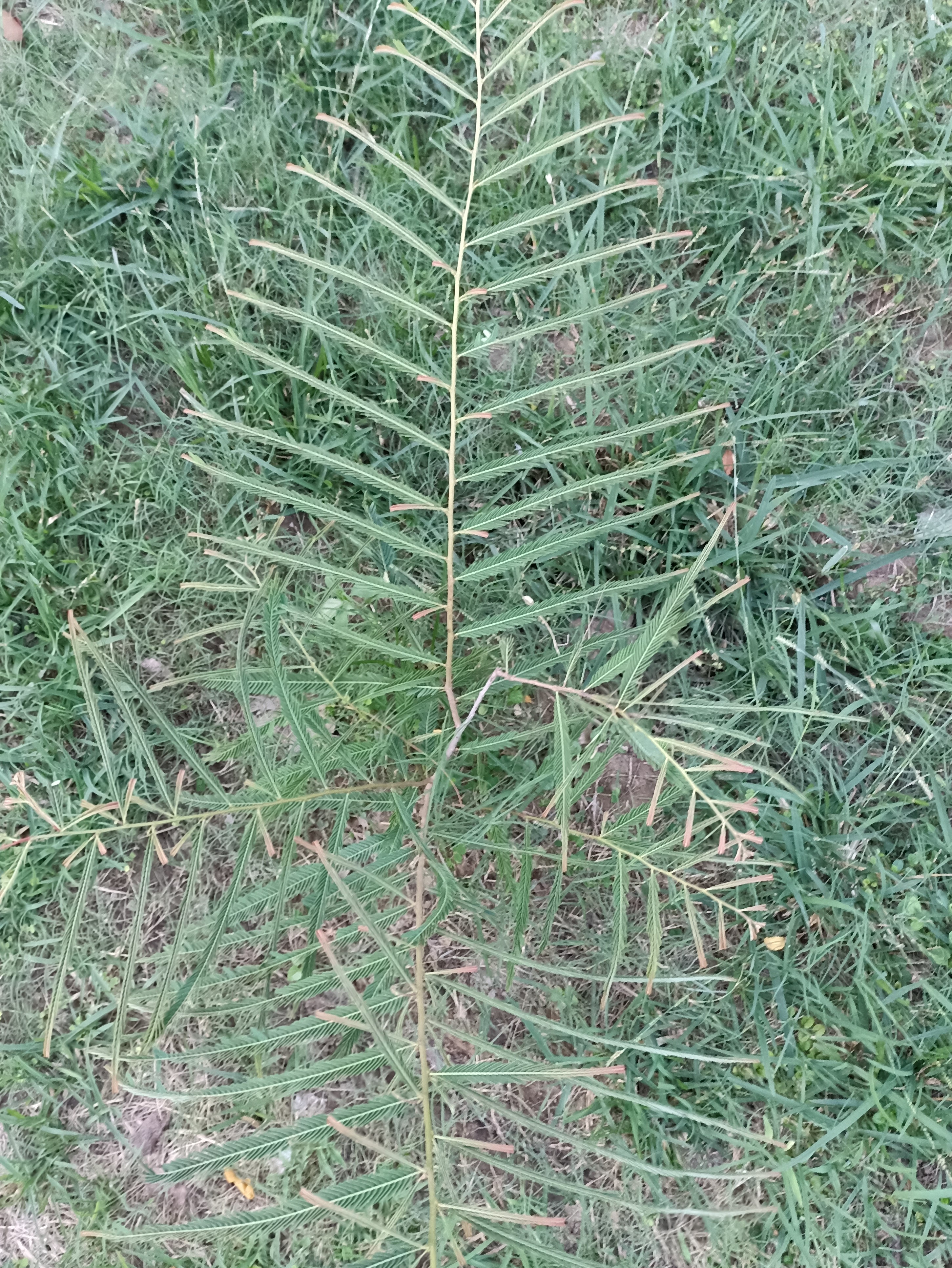
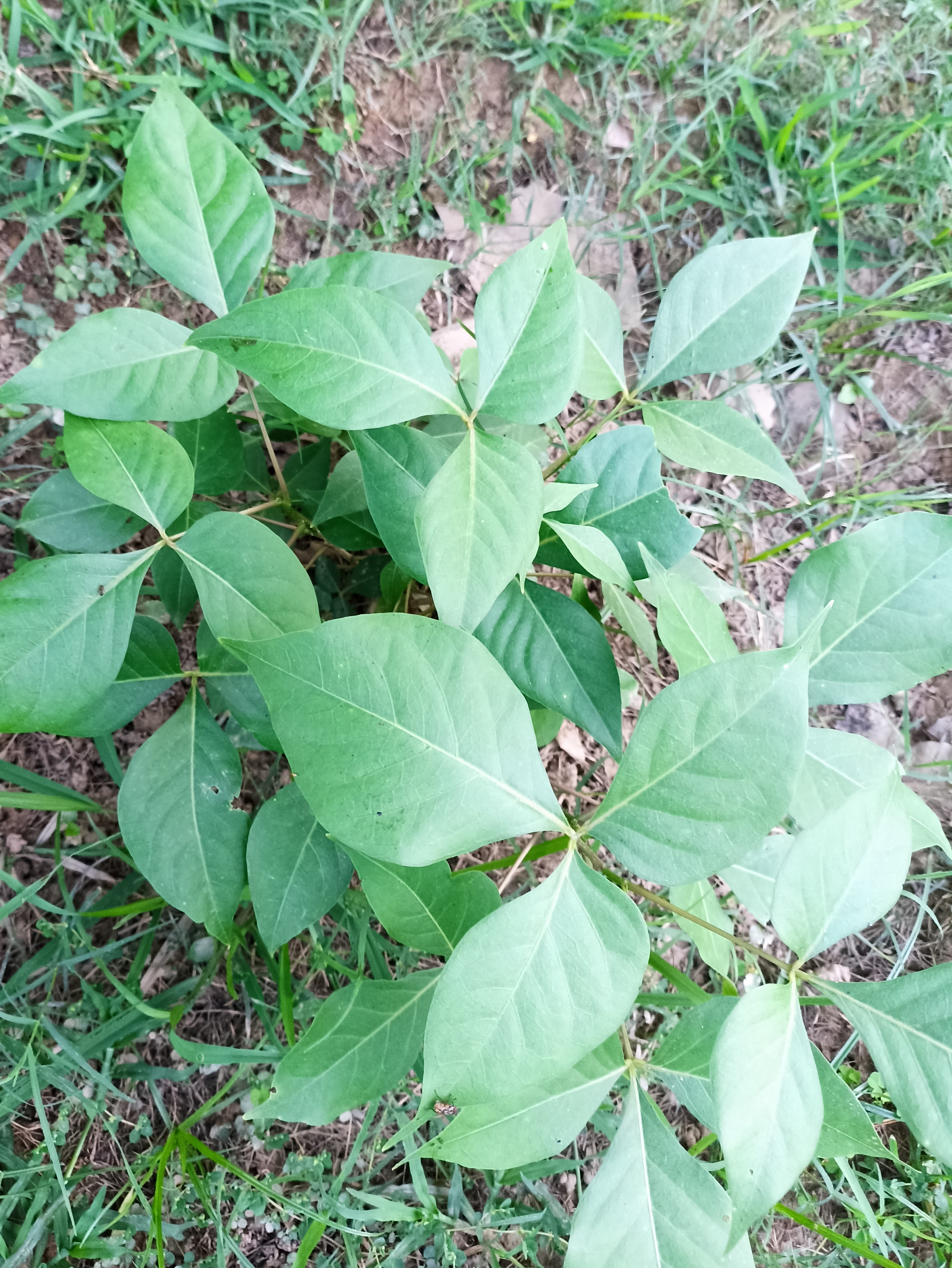
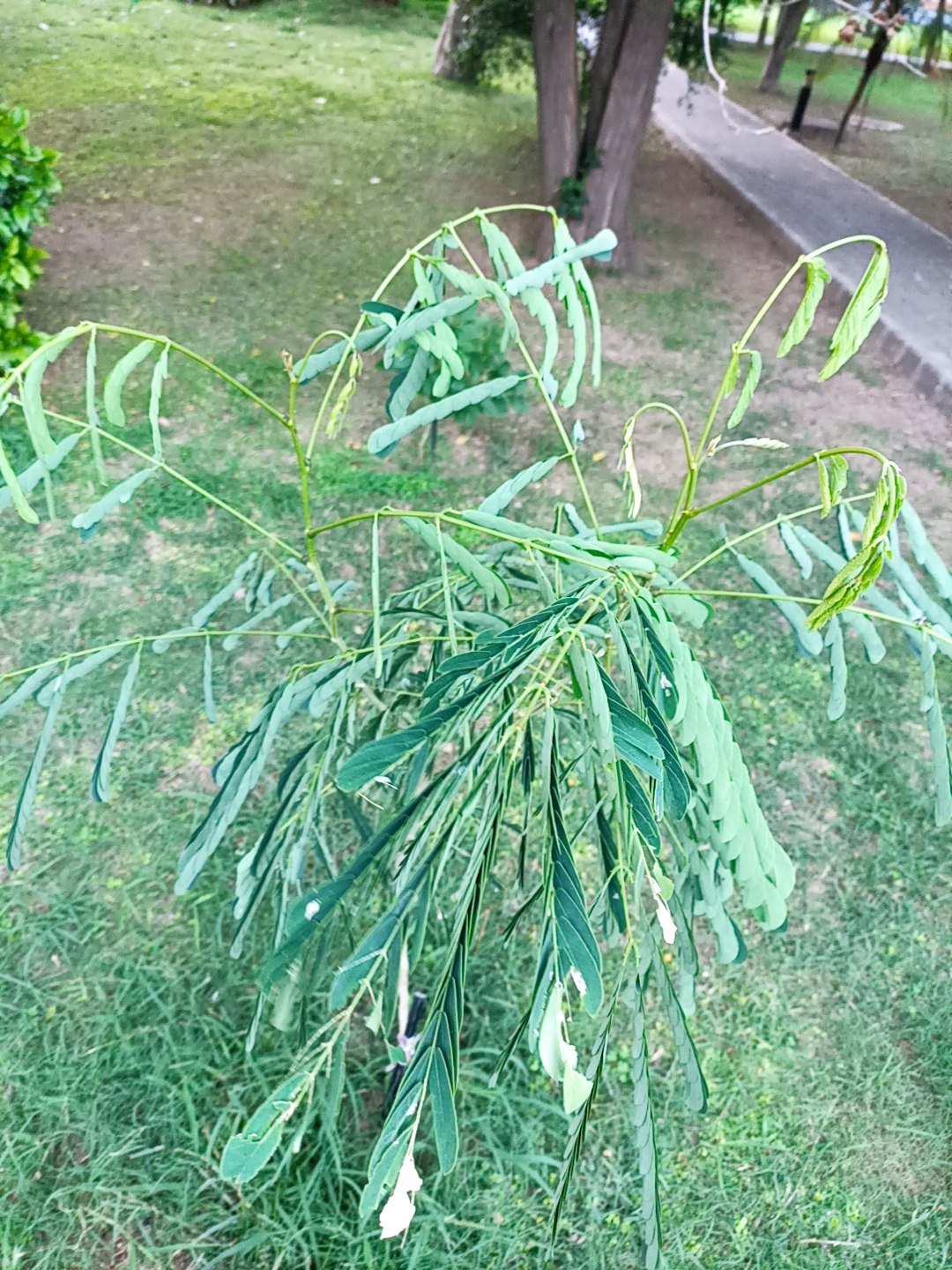
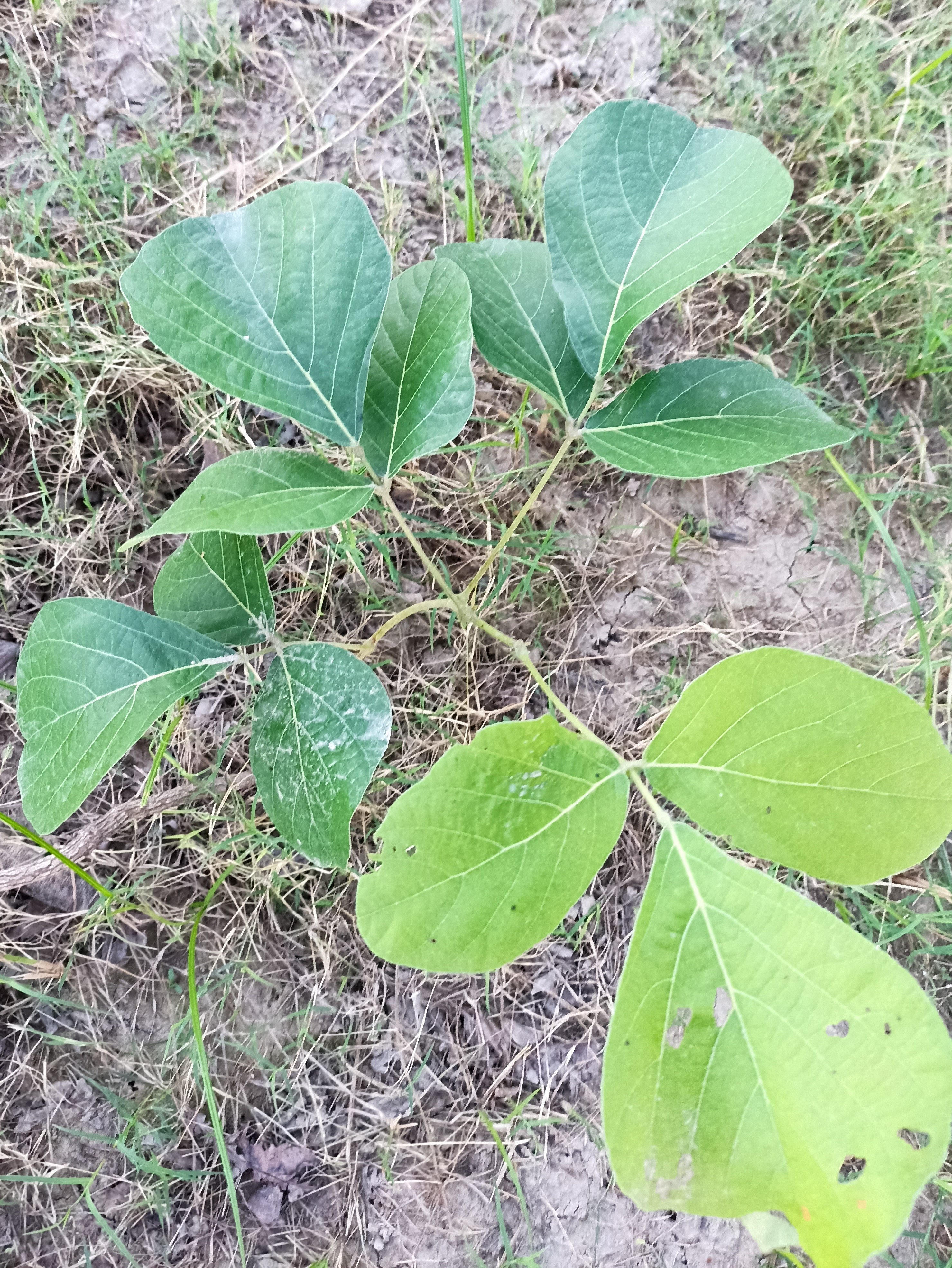
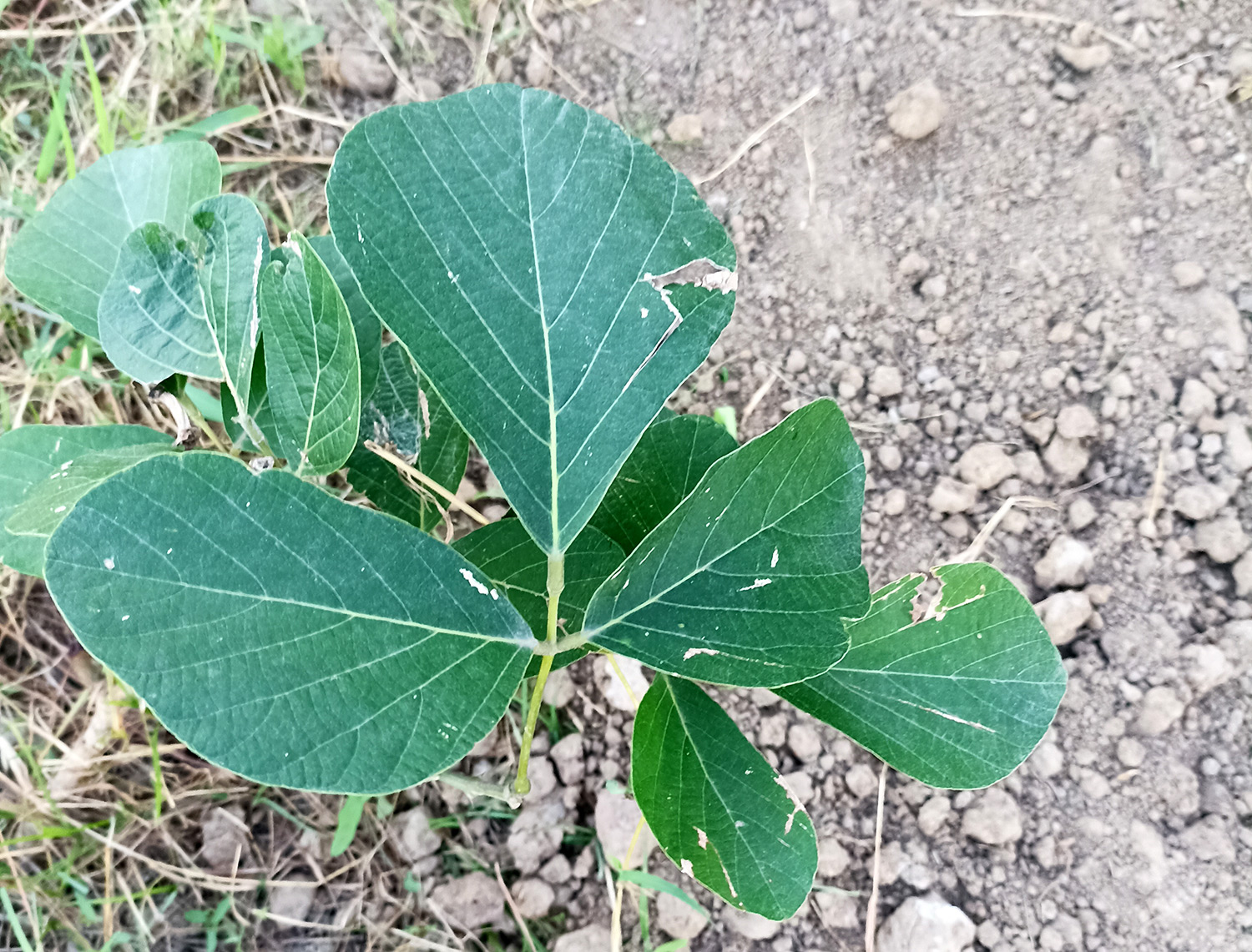
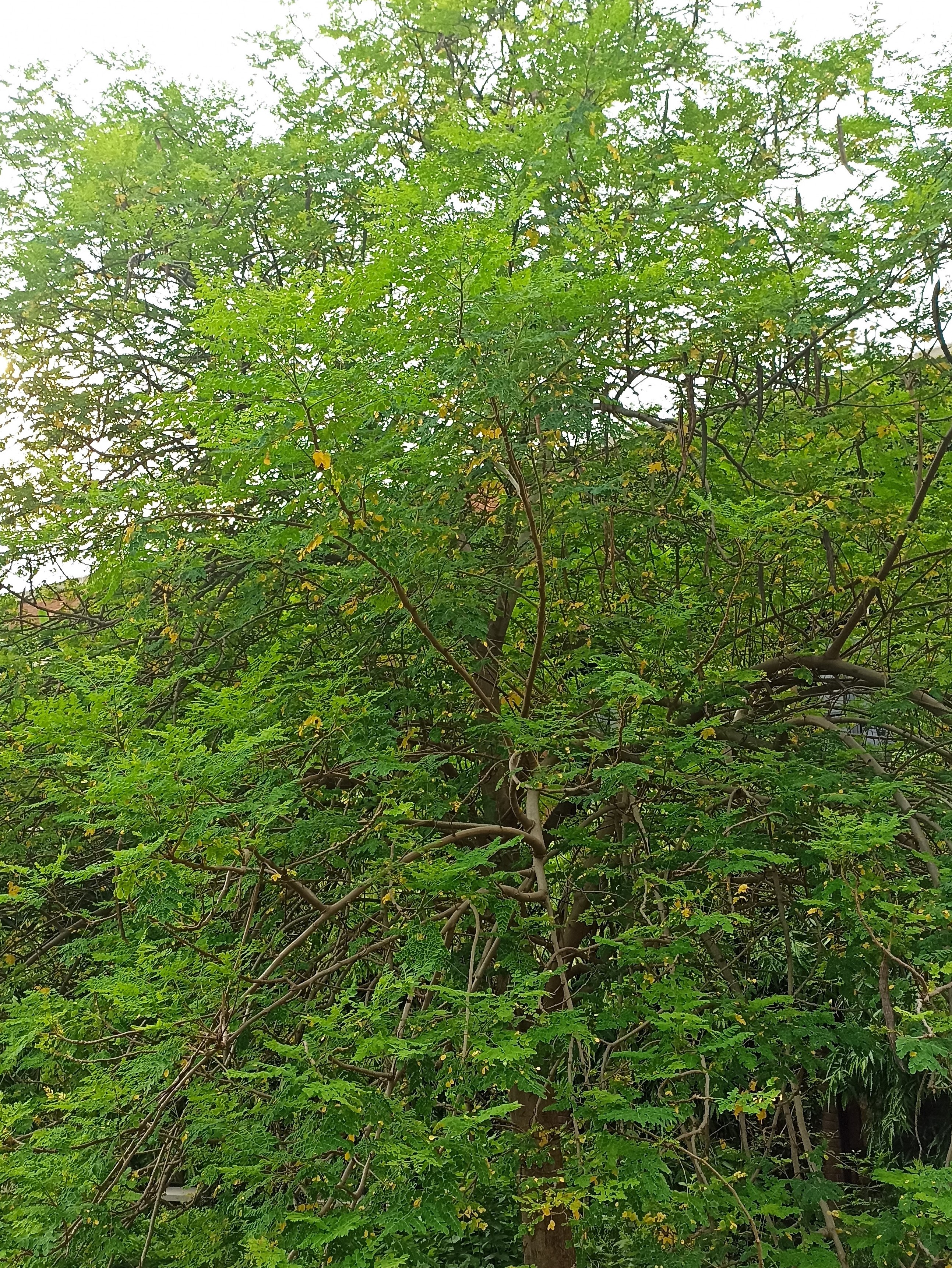
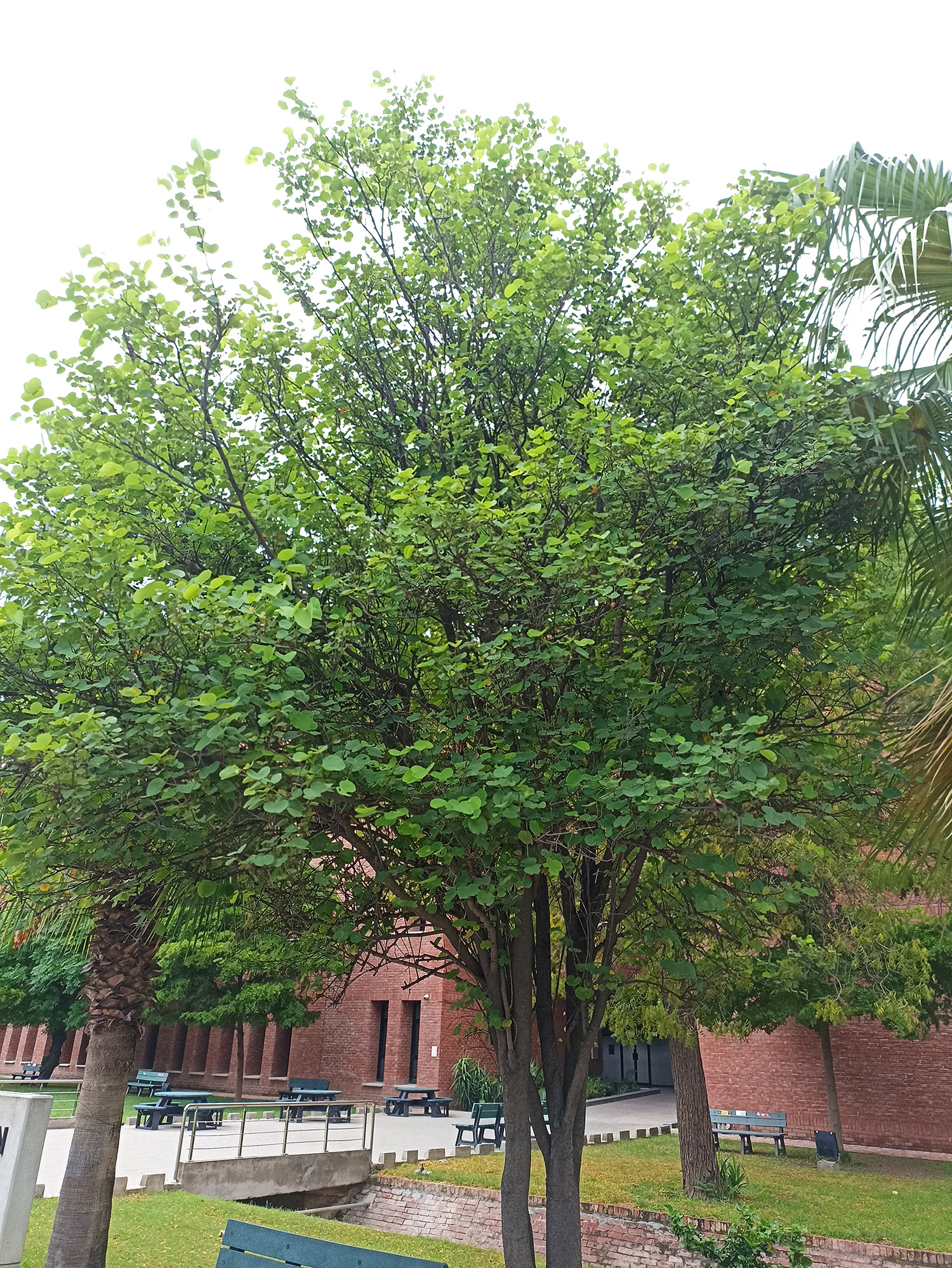
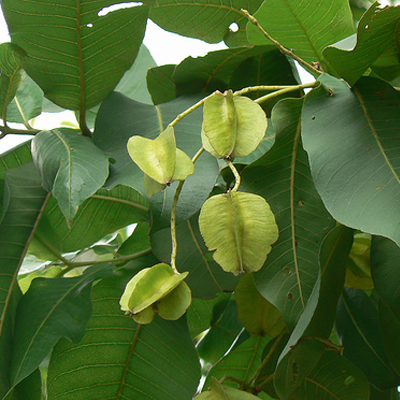
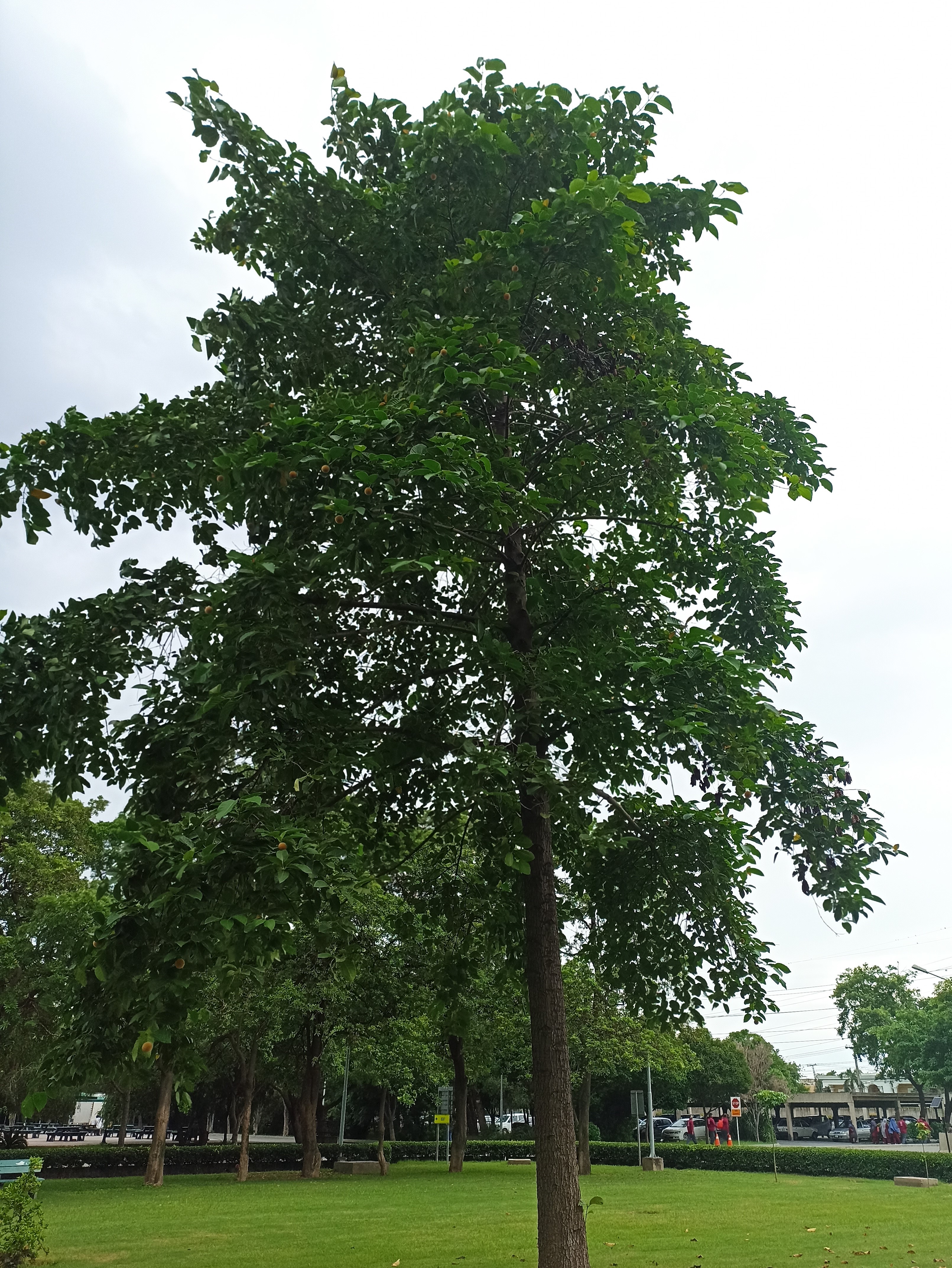
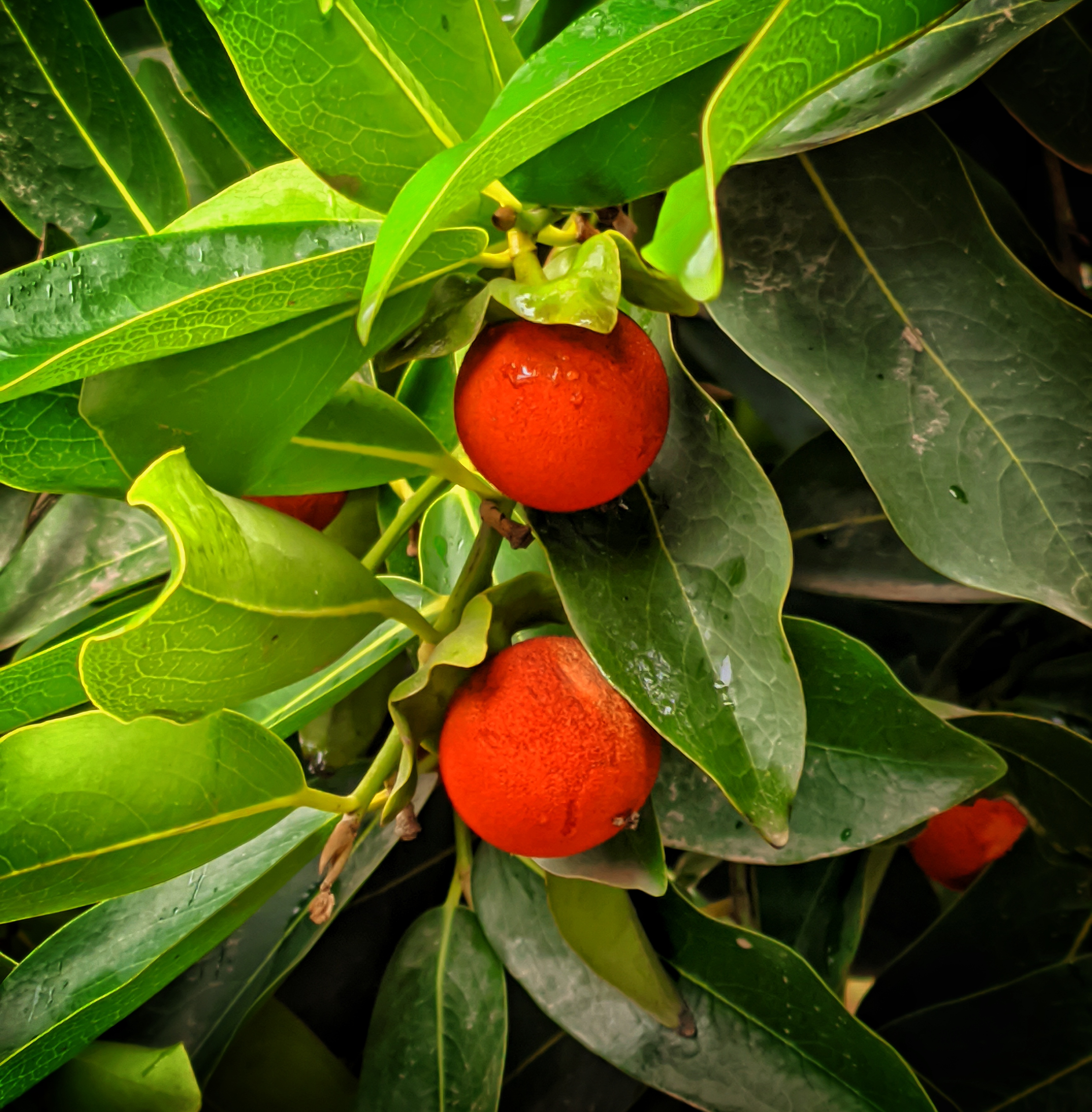
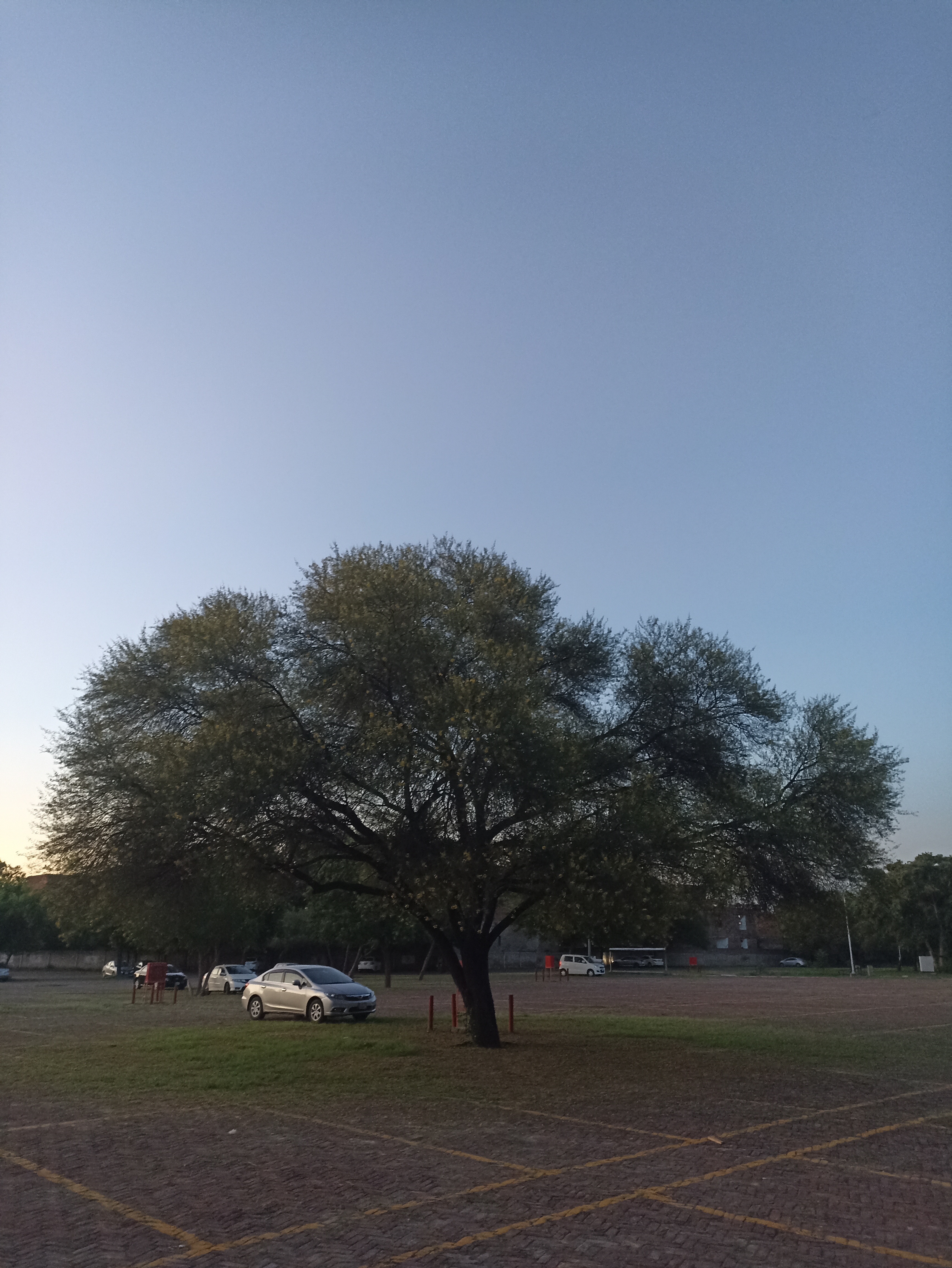
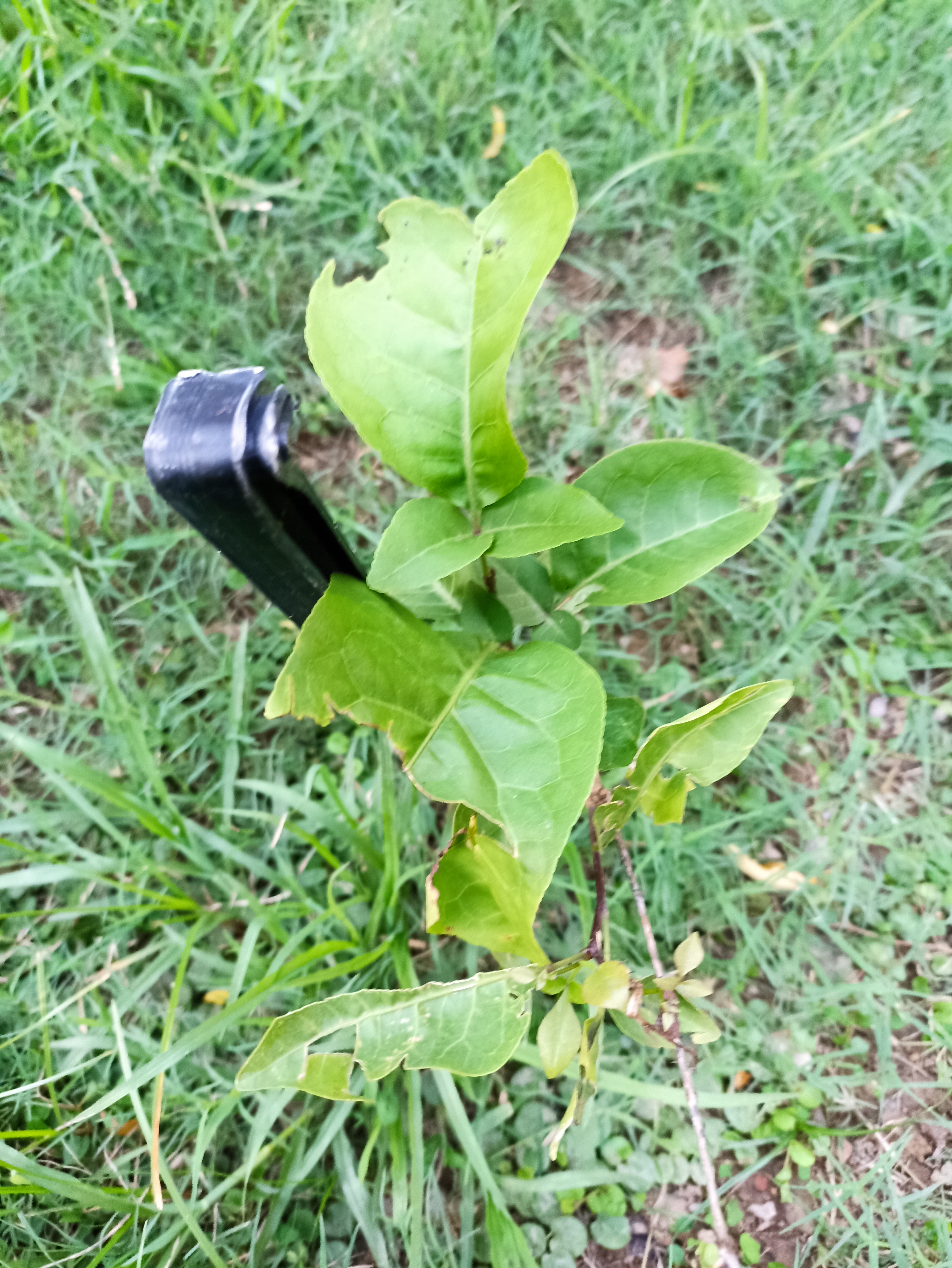
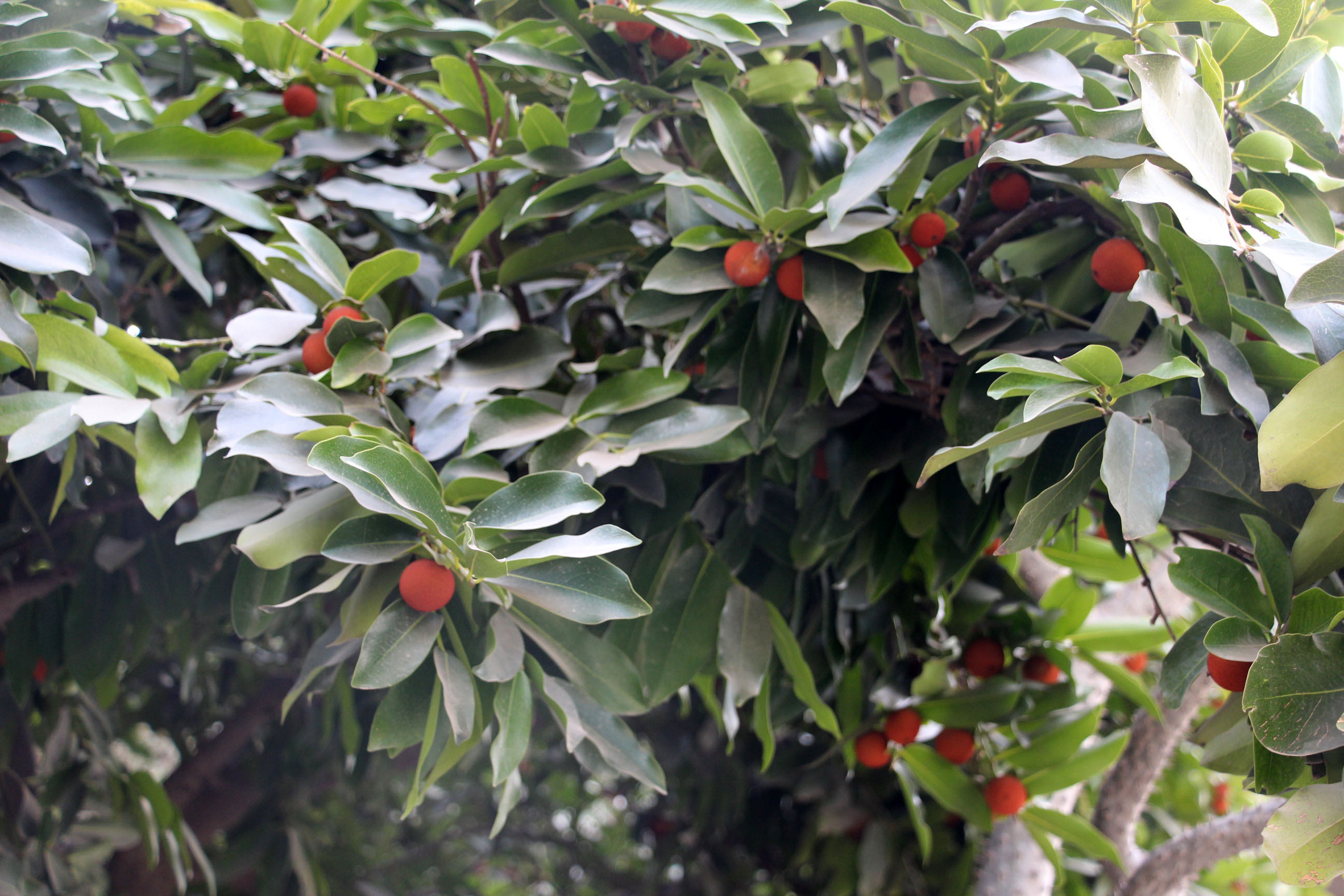
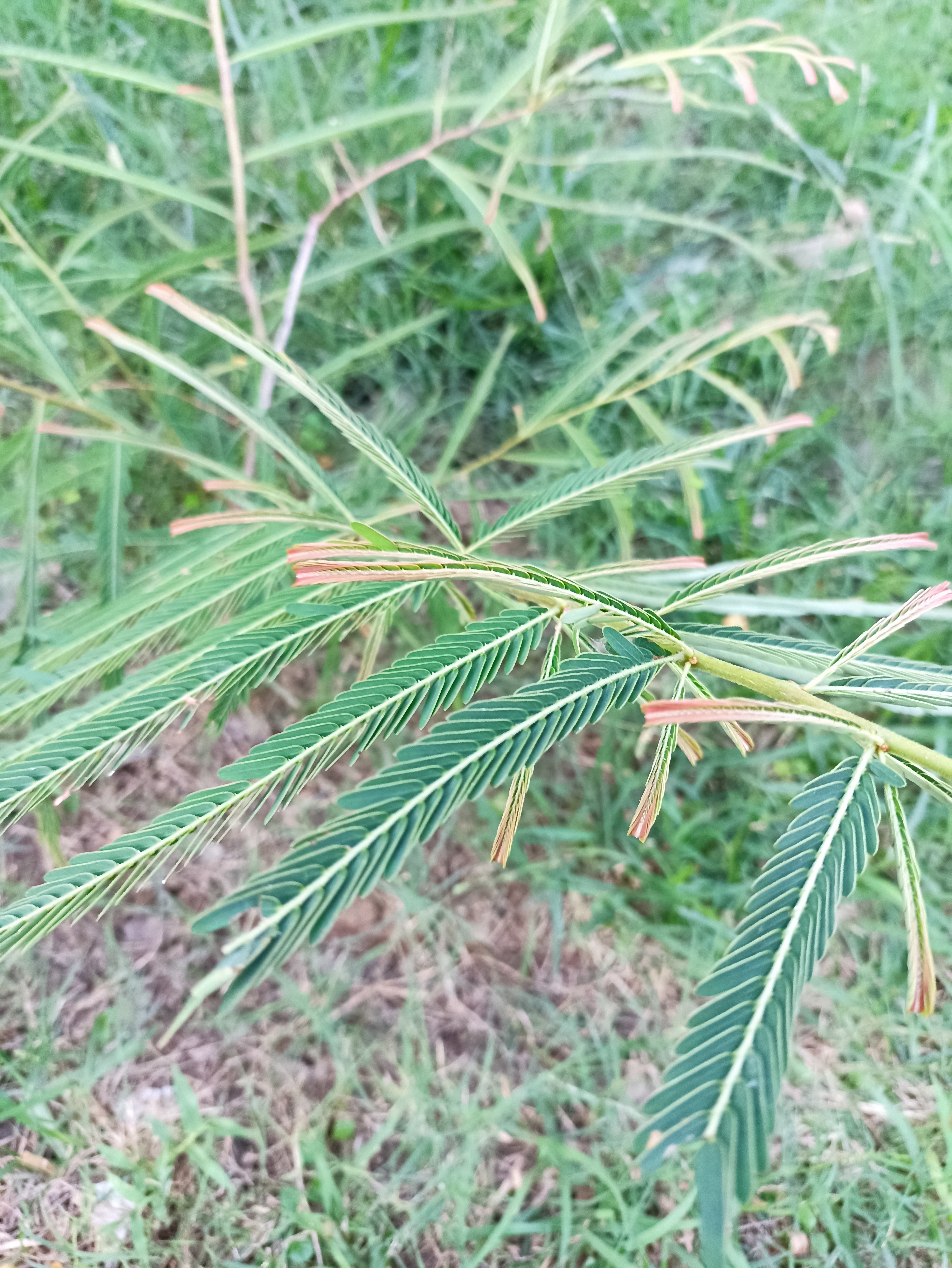
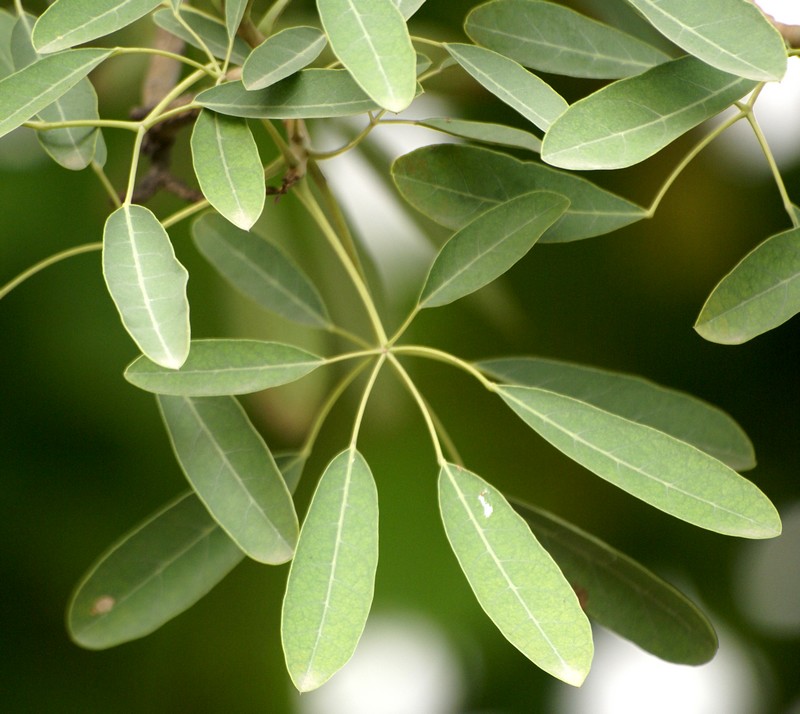
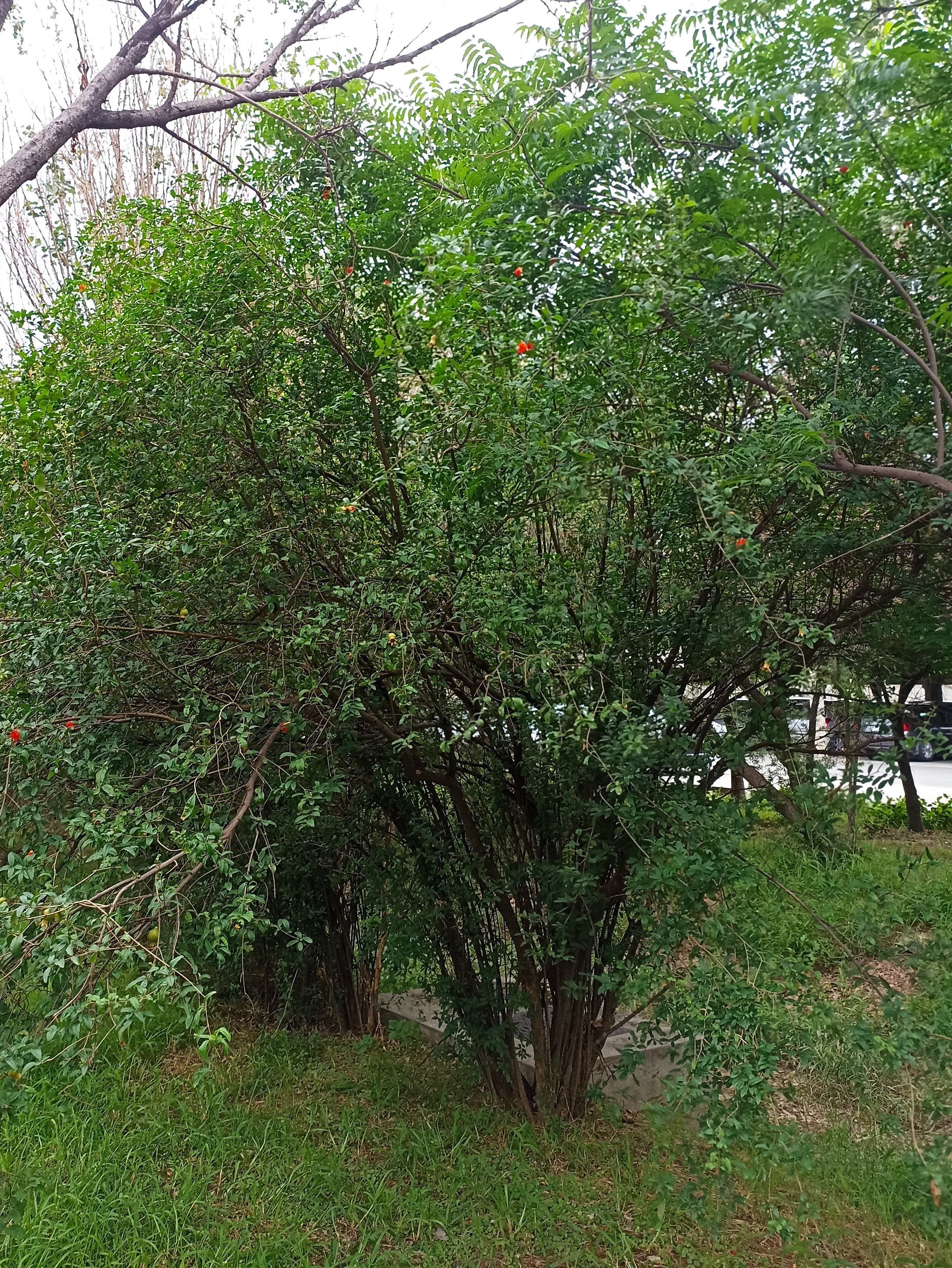
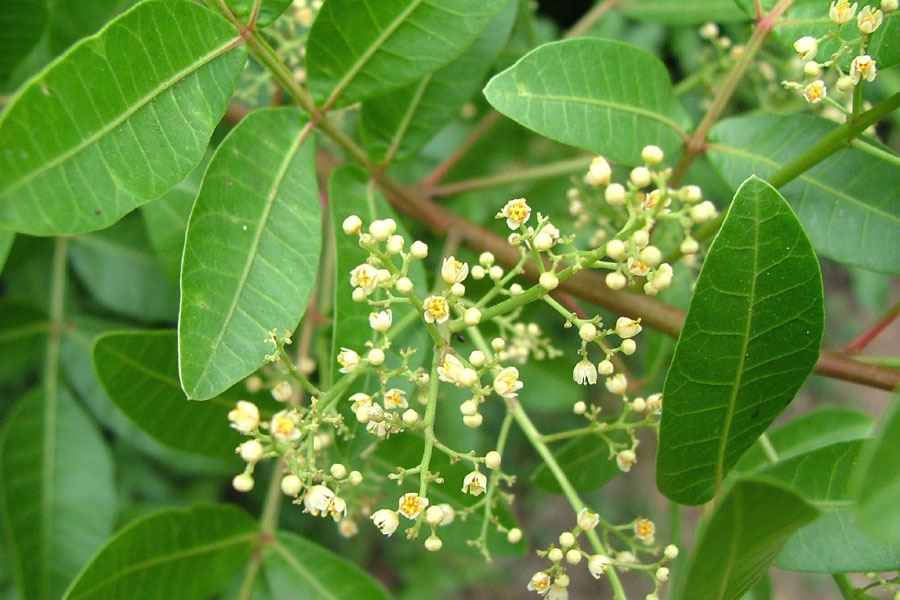
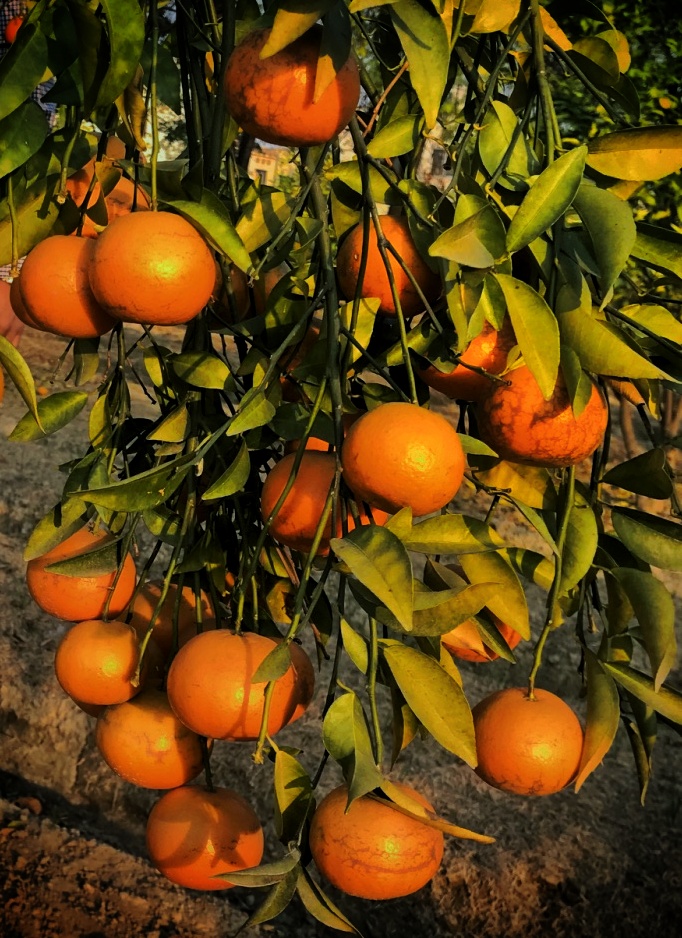
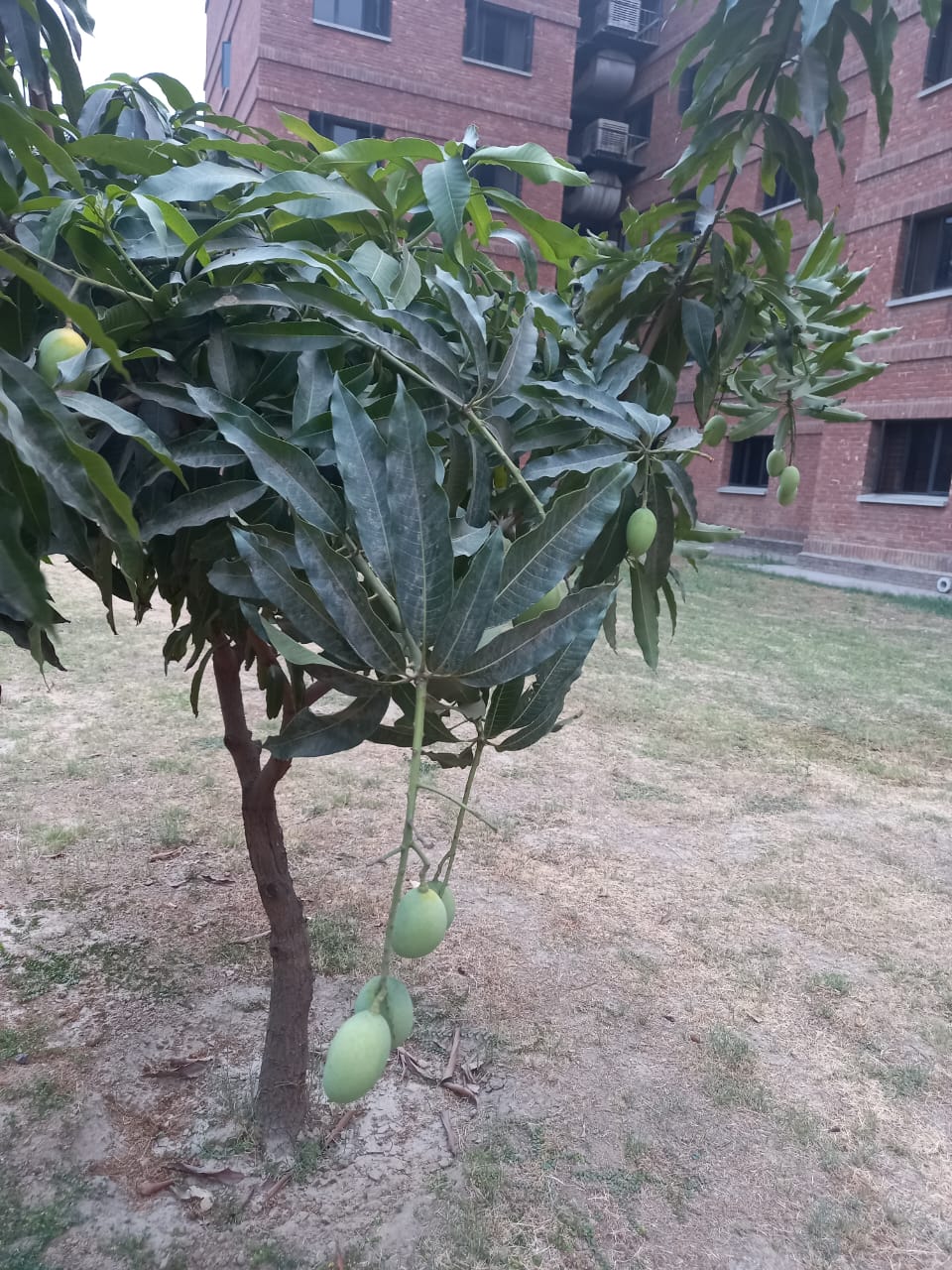
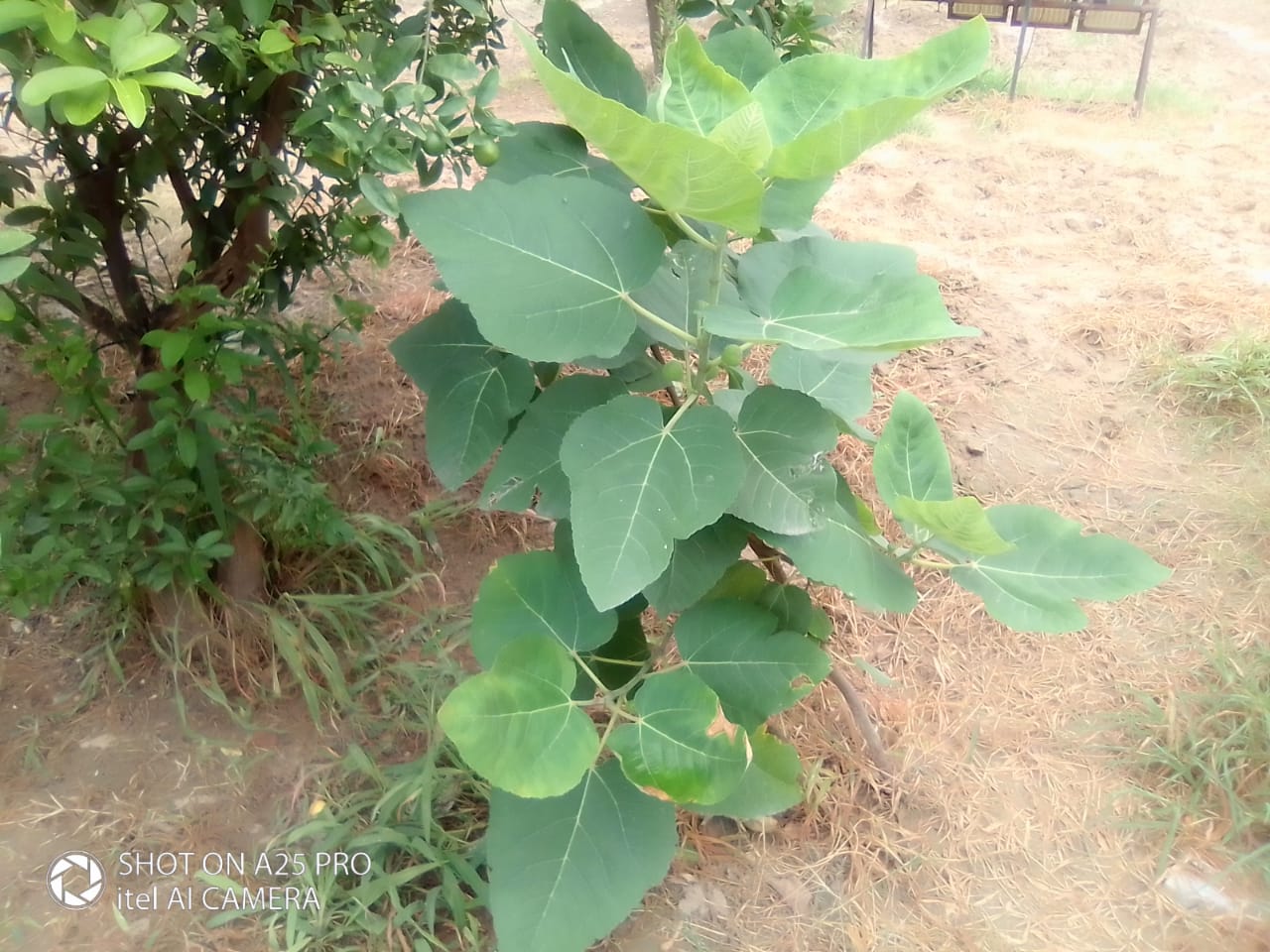
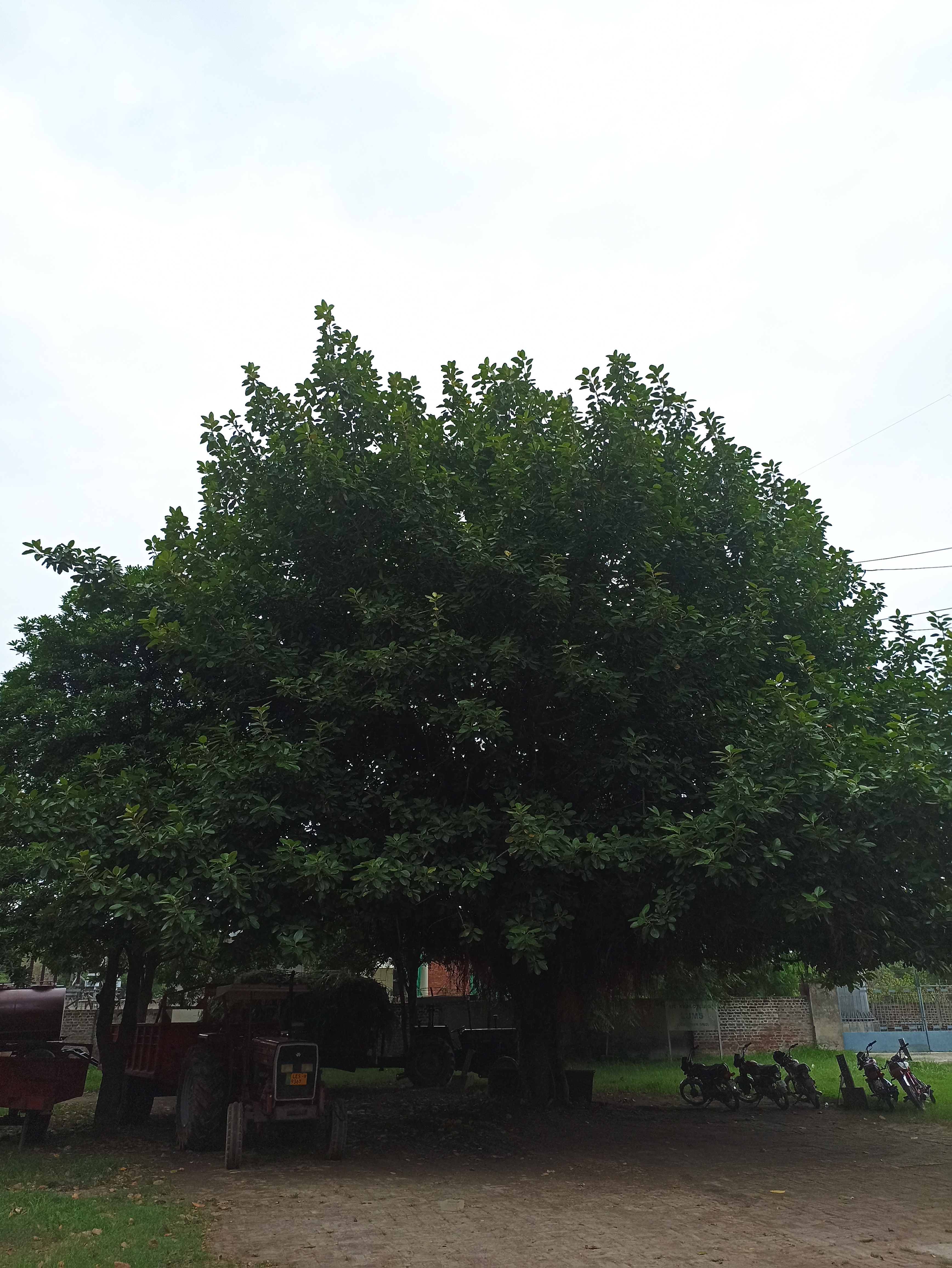
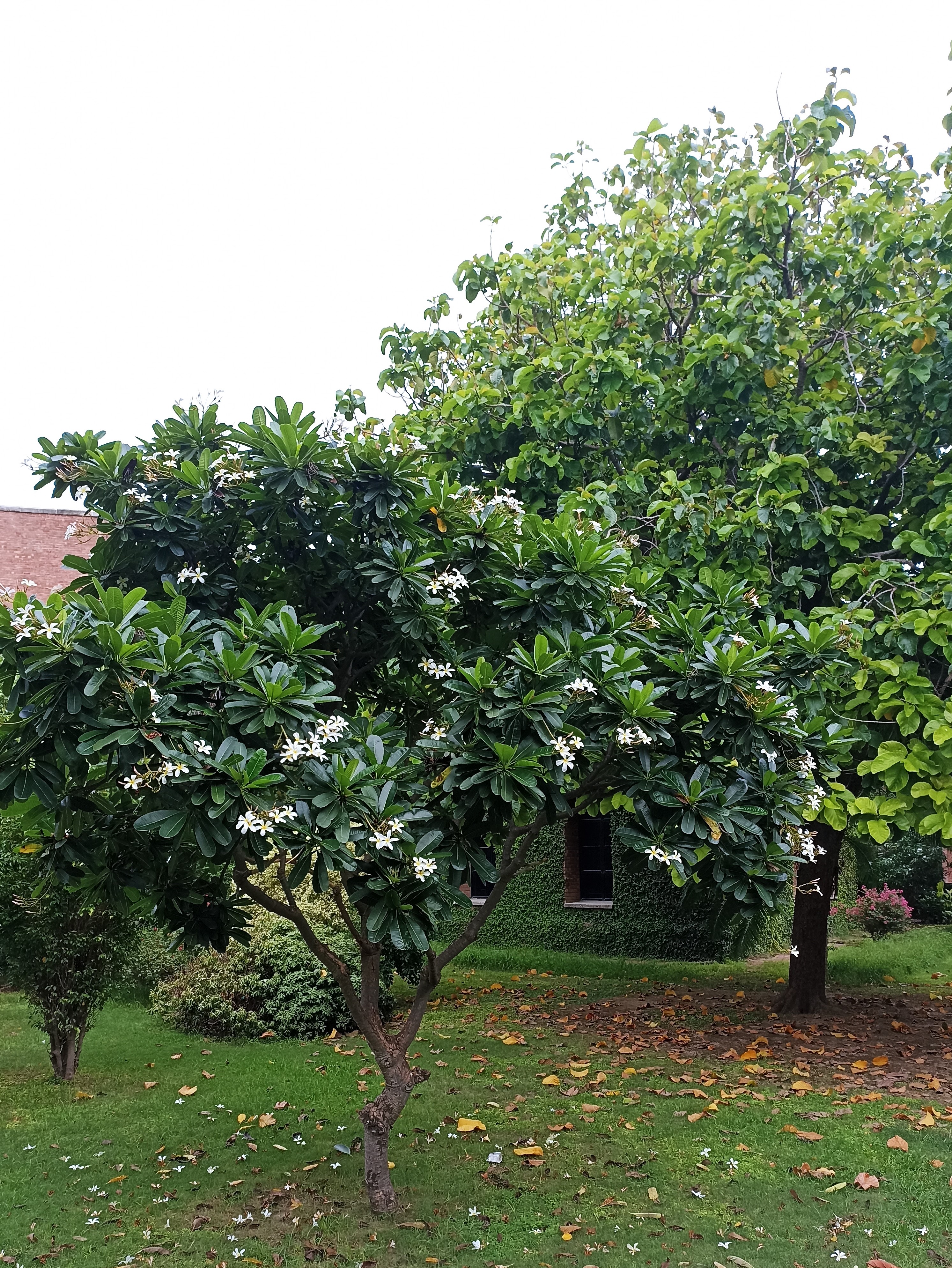
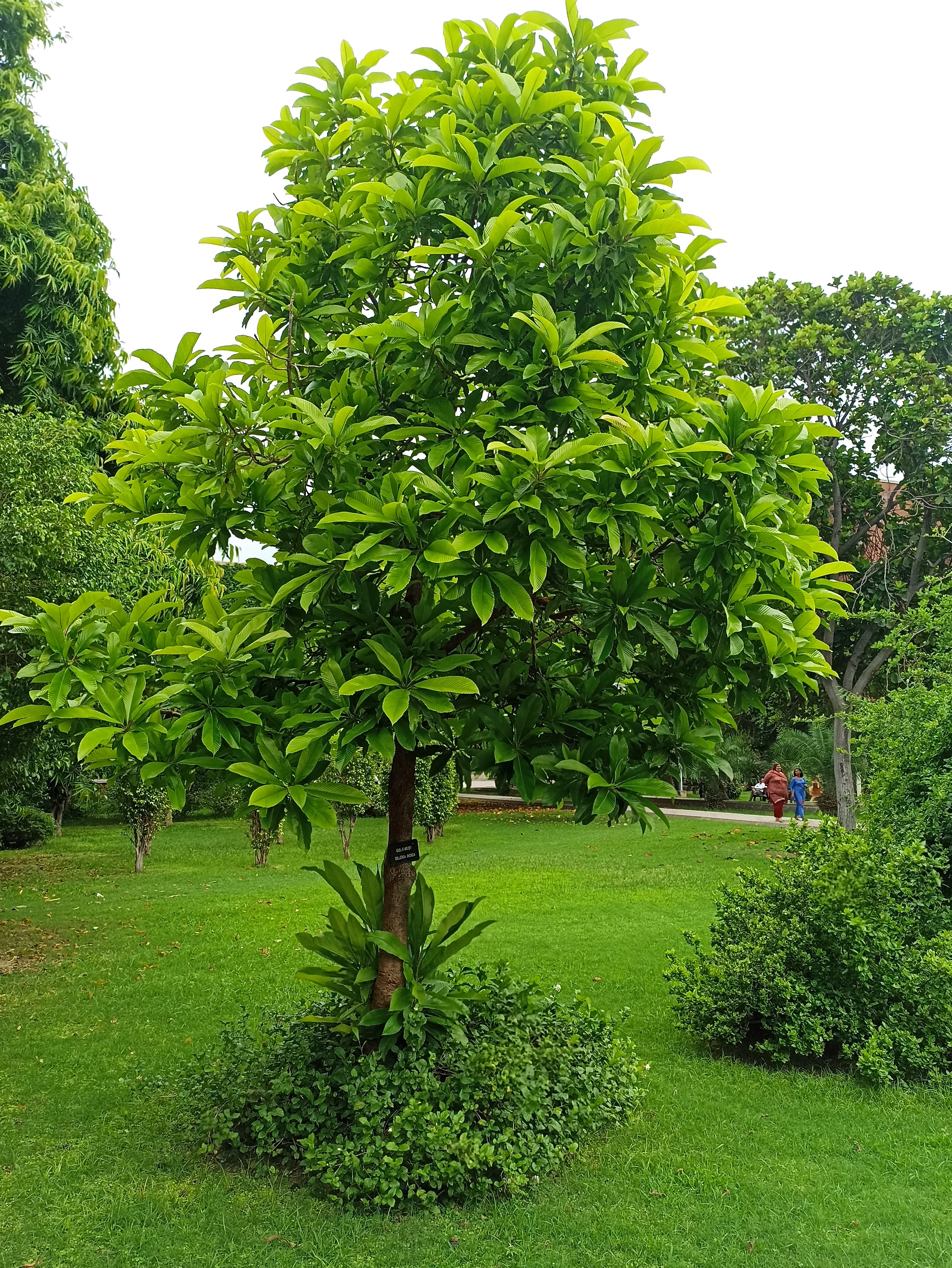
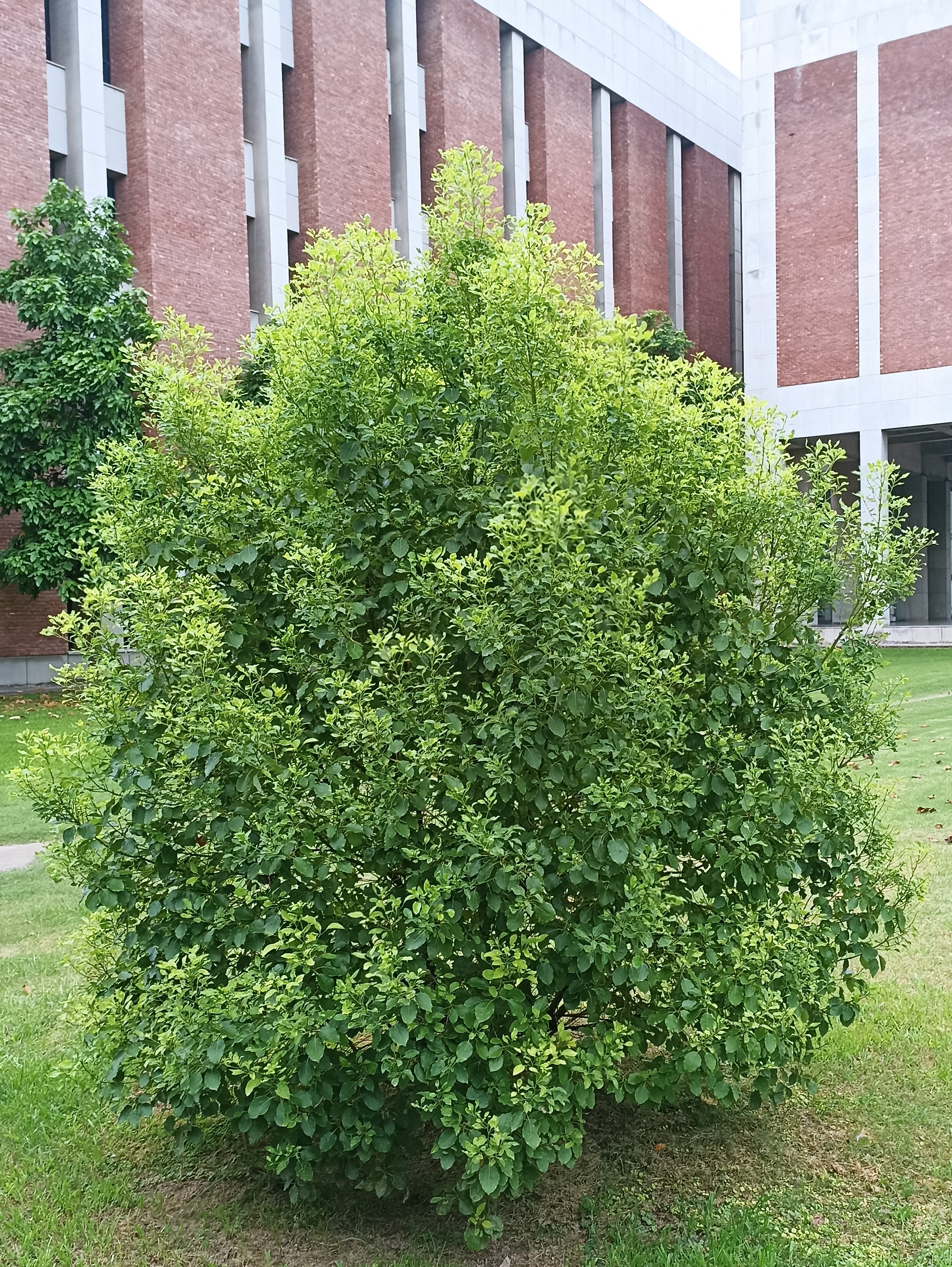
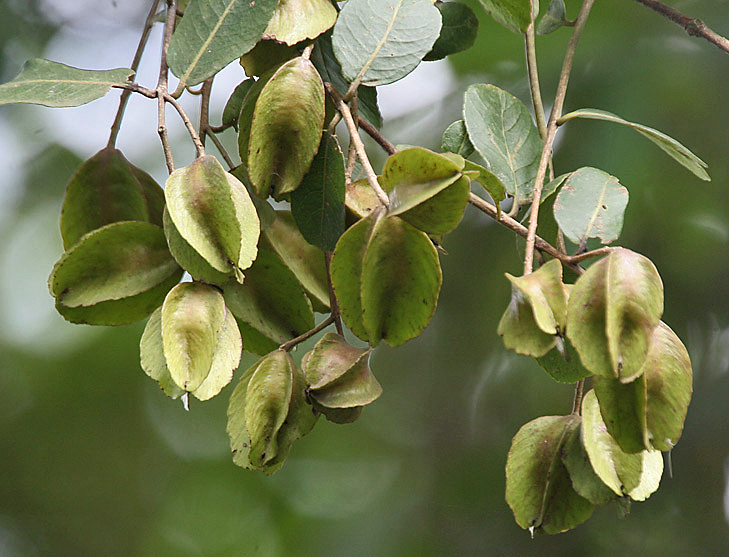
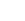
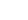
The tree is small to medium in size, reaching 1–8 m (3 ft 3 in – 26 ft 3 in) in height. The branchlets are not glabrous or finely pubescent, 10–20 cm (3.9–7.9 in) long, usually deciduous; the leaves are simple, subsessile and closely set along branchlets, light green, resembling pinnate leaves. The flowers are greenish-yellow. The fruit is nearly spherical, light greenish-yellow, quite smooth and hard on appearance, with six vertical stripes or furrows. The fruit is up to 26 mm (1.0 in) in diameter, and, while the fruit of wild plants weigh approximately 5.5 g (0.19 oz), cultivated fruits average 28.4 g (1.00 oz) to 56 g (2.0 oz).
Ripening in autumn, the berries are harvested by hand after climbing to upper branches bearing the fruits. The taste of Indian emblic is sour, bitter and astringent, and it is quite fibrous.
Buddhist symbolism
In the Buddhist tradition there are many references to the fruit of the emblic myrobalan. In Buddha’s knowledge is described in a poetic simile: “O Bhagavan, the entire origination of all types of phenomena throughout time is within the range of your mind, like an ambalan fruit in the palm of your hand”
Half an amalaka fruit was the final gift to the Buddhist sangha by the great Indian emperor Ashoka. This is illustrated in the Ashokavadana in the following verses: "A great donor, the lord of men, the eminent Maurya Ashoka, has gone from being lord of Jambudvipa [the continent] to being lord of half a myrobalan". In Theravada Buddhism, this plant is said to have been used as the tree for achieving enlightenment, or Bodhi, by the twenty first Buddha, named Phussa Buddha.
Traditional uses
Indian gooseberry pickle
The amla fruit is eaten raw or cooked into various dishes, such as dal (a lentil preparation) and amle ka murabbah, a sweet dish made by soaking the berries in sugar syrup until they are candied. It is traditionally consumed after meals.
In the Batak area of Sumatra, Indonesia, the inner bark is used to impart an astringent, bitter taste to the broth of a traditional fish soup known as holat.
Traditional medicine
In Ayurveda, dried and fresh fruits of the plant are used as a common constituent.
Chemical constituents
These fruits contain high amounts of ascorbic acid (vitamin C) and have a bitter taste that may derive from a high density of ellagitannins, such as emblicanin A (37%), emblicanin B (33%), punigluconin (12%), and pedunculagin (14%). Amla also contains punicafolin and phyllanemblinin A, phyllanemblin other polyphenols, such as flavonoids, kaempferol, ellagic acid, and gallic acid.