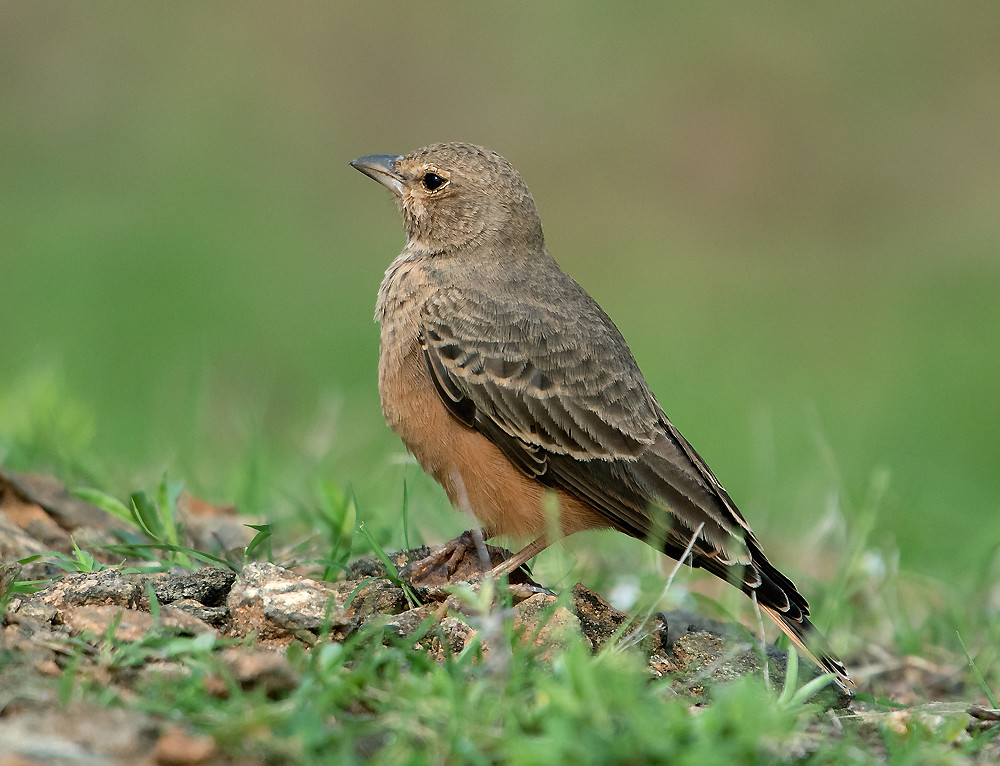
Sequoia (Giant sequoia)
Species
Families
Local Names
Genus
Native/Introduced
DNA Barcode
Description
Sequoiadendron giganteum is the sole living species in the genus Sequoiadendron, and one of three species of coniferous trees known as redwoods, classified in the family Cupressaceae in the subfamily Sequoioideae, together with Sequoia sempervirens and Metasequoia glyptostroboides.
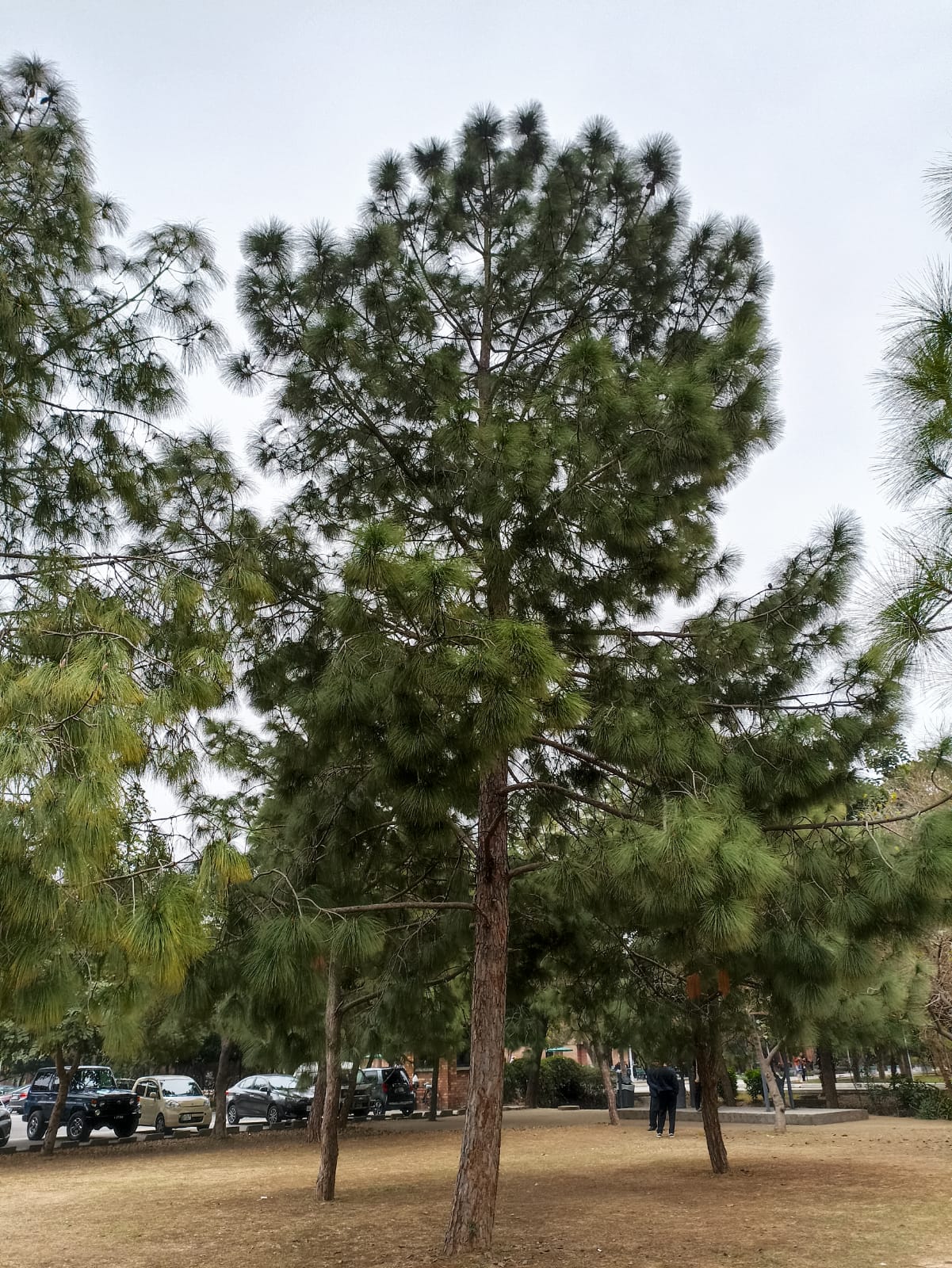
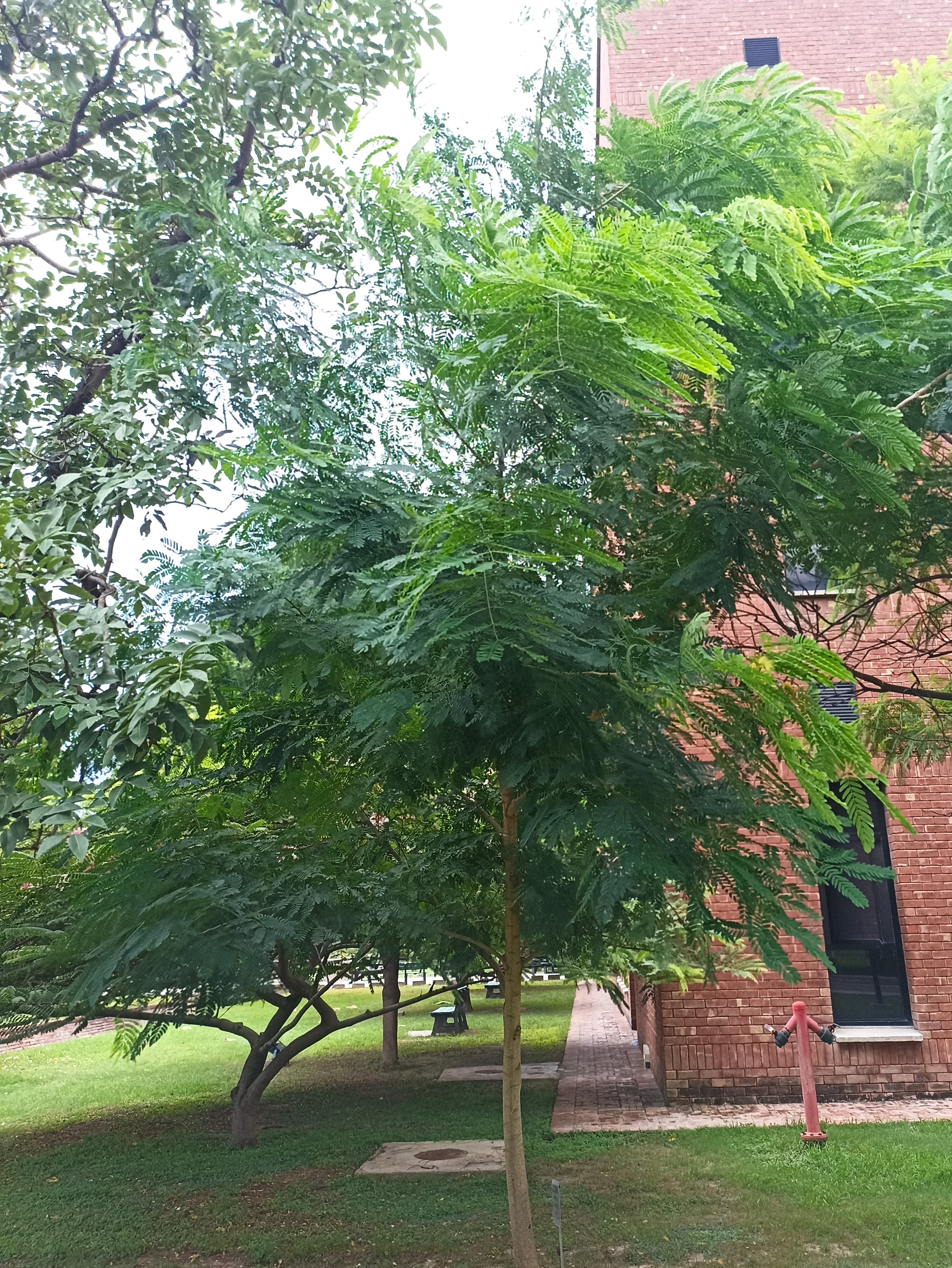
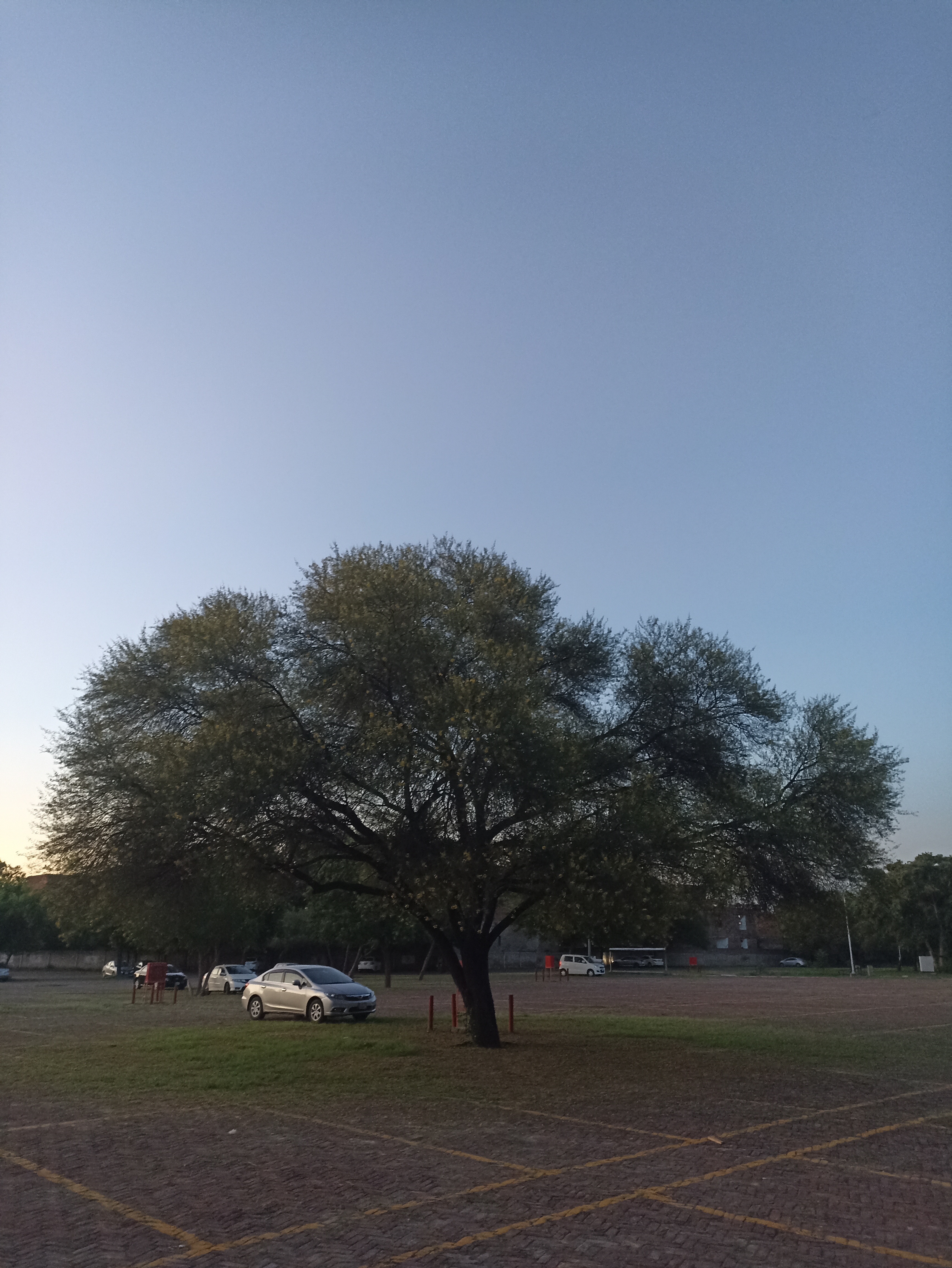
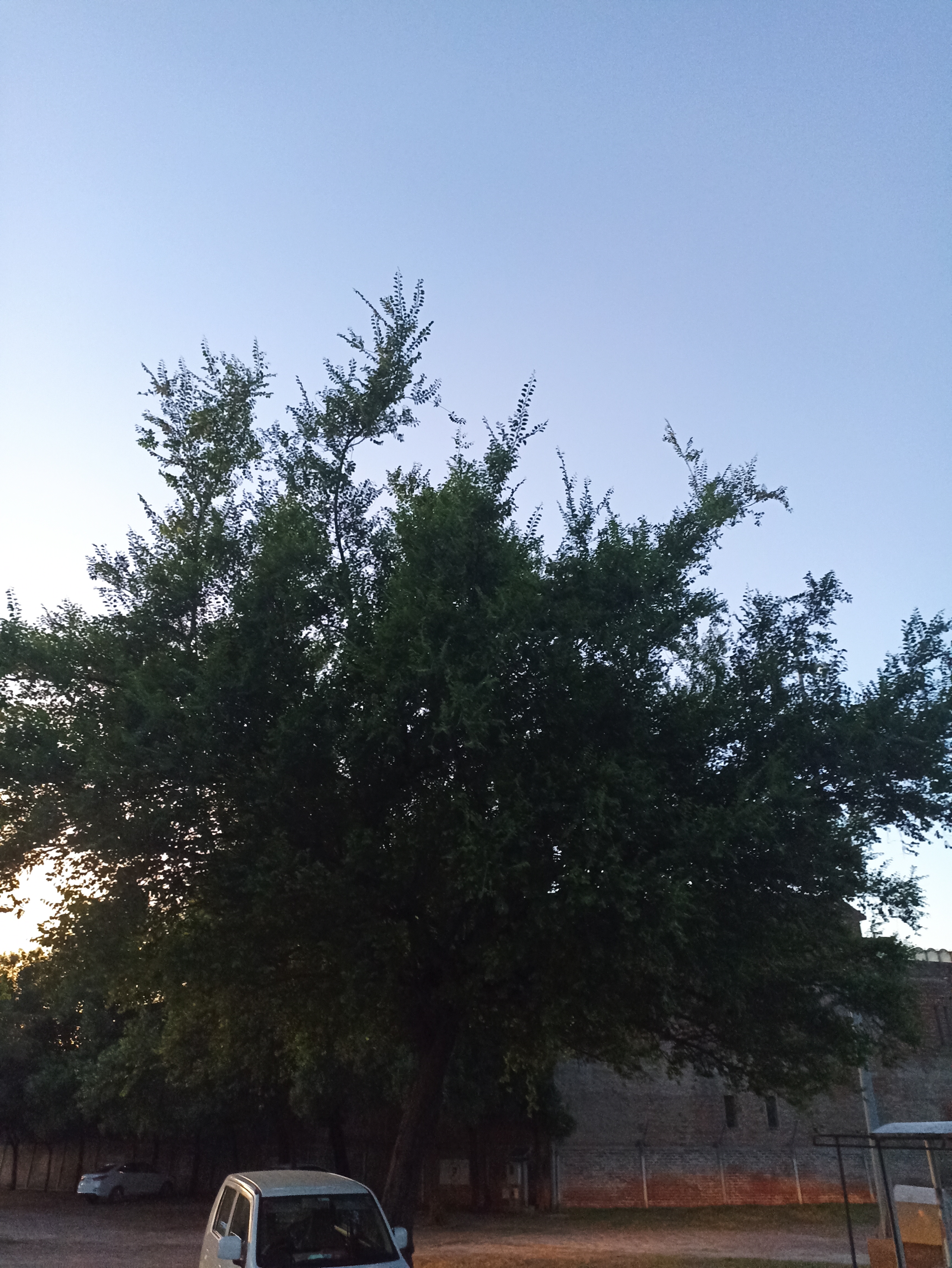
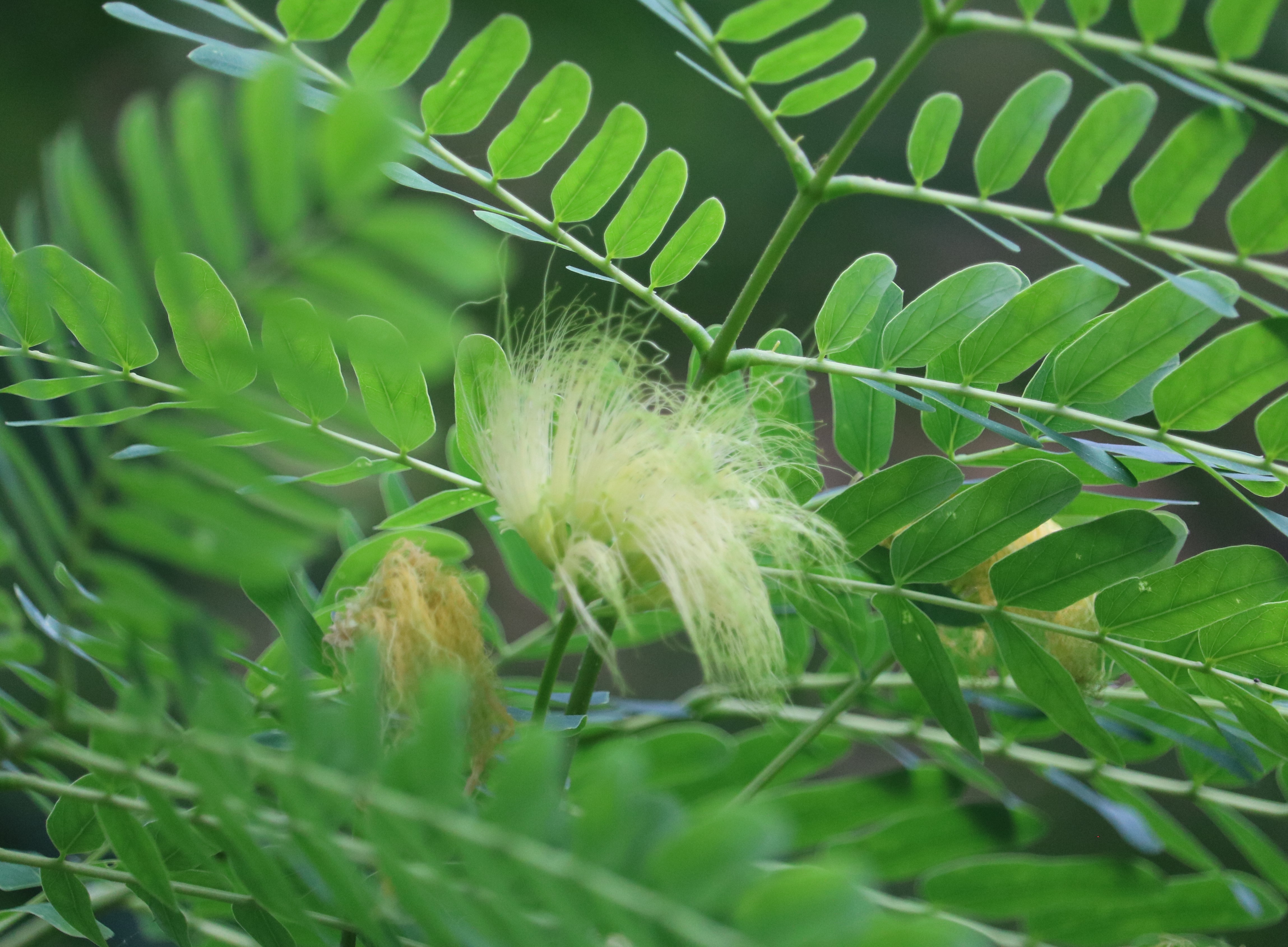
Sequoiadendron giganteum (giant sequoia; also known as giant redwood, Sierra redwood, Sierran redwood, Wellingtonia or simply big tree—a nickname also used by John Muir) is the sole living species in the genus Sequoiadendron, and one of three species of coniferous trees known as redwoods, classified in the family Cupressaceae in the subfamily Sequoioideae, together with Sequoia sempervirens (coast redwood) and Metasequoia glyptostroboides (dawn redwood). Giant sequoia specimens are the most massive trees on Earth. The common use of the name sequoia usually refers to Sequoiadendron giganteum, which occurs naturally only in groves on the western slopes of the Sierra Nevada mountain range of California.
The giant sequoia is listed as an endangered species by the IUCN, with fewer than 80,000 trees remaining. Since its last assessment as an endangered species in 2011, it was estimated that another 13–19% of the population (or 9,761–13,637 mature trees) was destroyed during the Castle Fire of 2020 and the KNP Complex & Windy Fire in 2021, events attributed to fire suppression, drought and global warming. Despite their large size and adaptations to fire, giant sequoias have become severely threatened by a combination of fuel load from fire suppression, which fuels extremely destructive fires that are also exacerbated by drought and climate change. These conditions have led to the death of many populations in large fires in recent decades. Prescribed burns to reduce available fuel load may be crucial for saving the species.
The etymology of the genus name has been presumed—initially in The Yosemite Book by Josiah Whitney in 1868—to be in honor of Sequoyah (1767–1843), who was the inventor of the Cherokee syllabary. An etymological study published in 2012 concluded that Austrian Stephen L. Endlicher is actually responsible for the name. A linguist and botanist, Endlicher corresponded with experts in the Cherokee language including Sequoyah, whom he admired. He also realized that coincidentally the genus could be described in Latin as sequi (meaning to follow) because the number of seeds per cone in the newly classified genus aligned in mathematical sequence with the other four genera in the suborder. Endlicher thus coined the name "Sequoia" as both a description of the tree's genus and an honor to the indigenous man he admired.
Uses
Albert Bierstadt's "Giant Redwood Trees of California", 1874 – a large oil on canvas painting in the Berkshire Museum, Massachusetts, United States.
Wood from mature giant sequoias is highly resistant to decay, but due to being fibrous and brittle, it is generally unsuitable for construction. From the 1880s through the 1920s, logging took place in many groves in spite of marginal commercial returns. The Hume-Bennett Lumber Company was the last to harvest giant sequoia, going out of business in 1924. Due to their weight and brittleness, trees would often shatter when they hit the ground, wasting much of the wood. Loggers attempted to cushion the impact by digging trenches and filling them with branches. Still, as little as 50% of the timber is estimated to have made it from groves to the mill. The wood was used mainly for shingles and fence posts, or even for matchsticks.
Pictures of the once majestic trees broken and abandoned in formerly pristine groves, and the thought of the giants put to such modest use, spurred the public outcry that caused most of the groves to be preserved as protected land. The public can visit an example of 1880s clear-cutting at Big Stump Grove near General Grant Grove. As late as the 1980s, some immature trees were logged in Sequoia National Forest, publicity of which helped lead to the creation of Giant Sequoia National Monument.
The wood from immature trees is less brittle, with recent tests on young plantation-grown trees showing it similar to coast redwood wood in quality. This is resulting in some interest in cultivating giant sequoia as a very high-yielding timber crop tree, both in California and also in parts of western Europe, where it may grow more efficiently than coast redwoods. In the northwest United States, some entrepreneurs have also begun growing giant sequoias for Christmas trees. Besides these attempts at tree farming, the principal economic uses for giant sequoia today are tourism and horticulture.