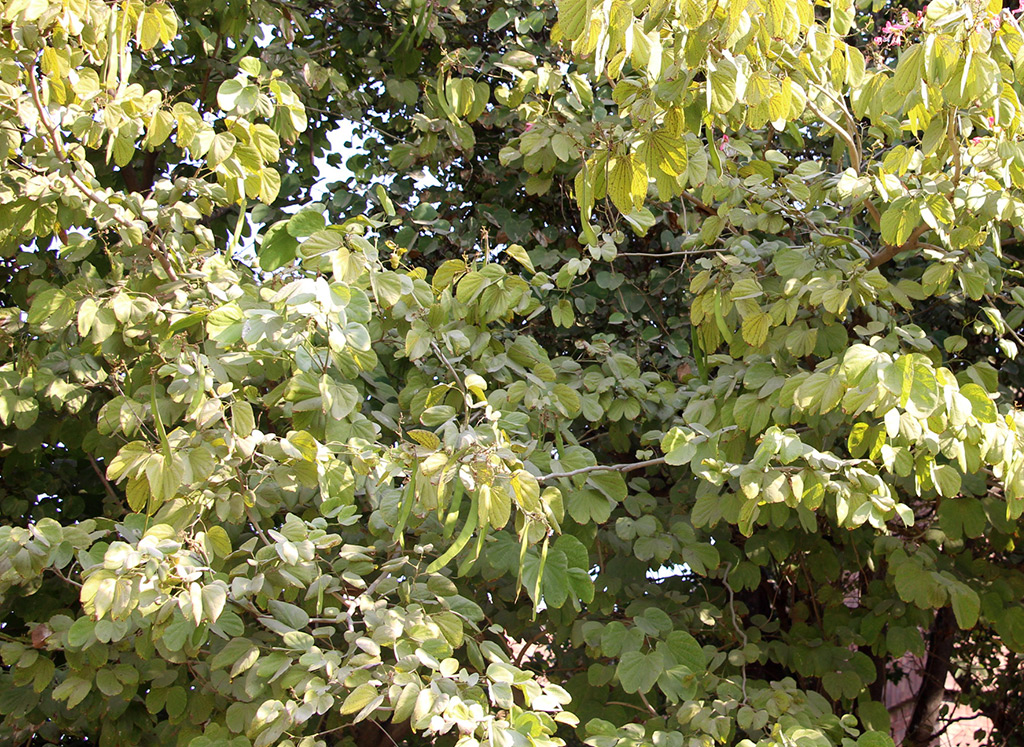
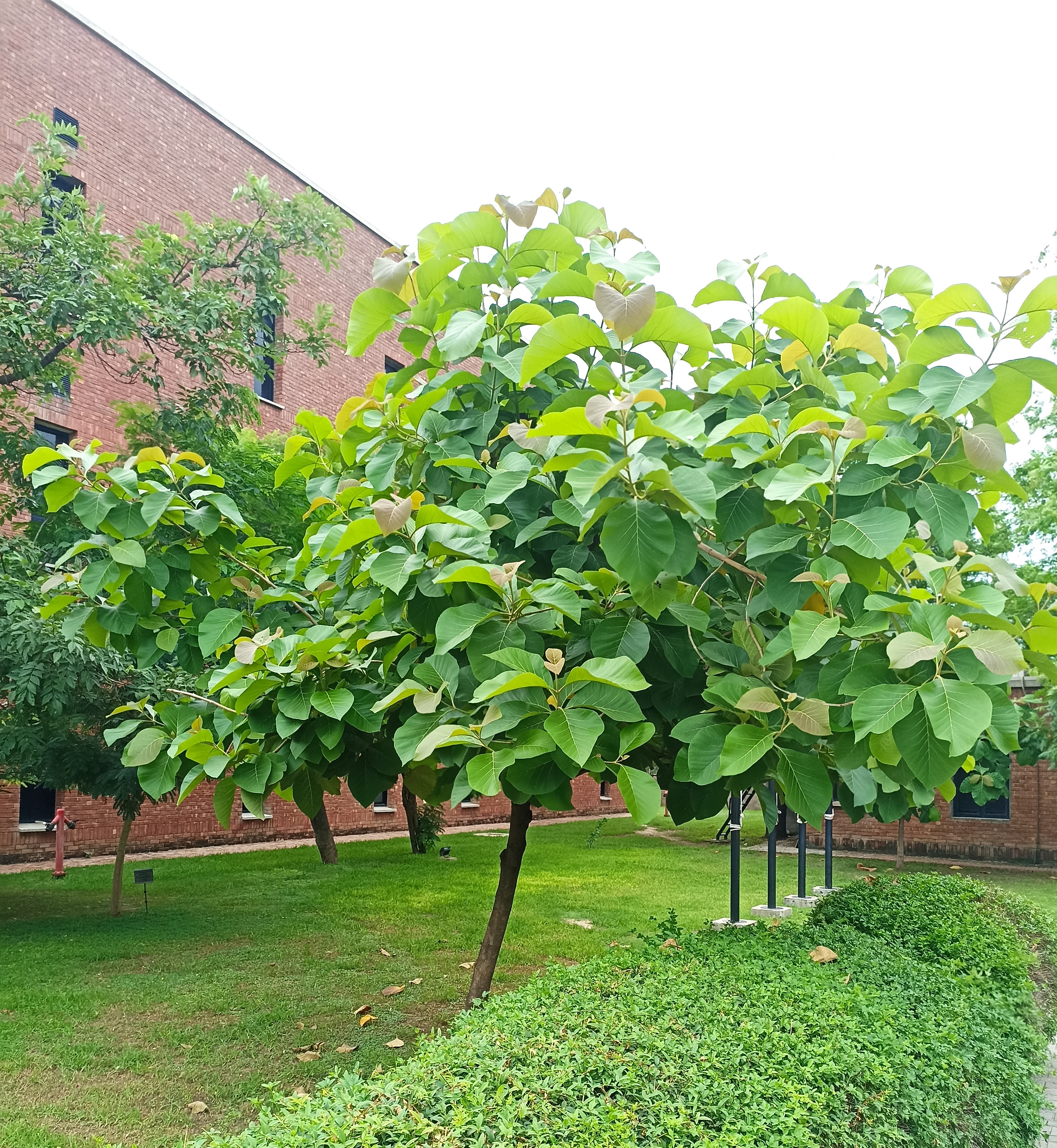
Salmalia malabarica
Species
Families
Local Names
Genus
Native/Introduced
DNA Barcode
Description
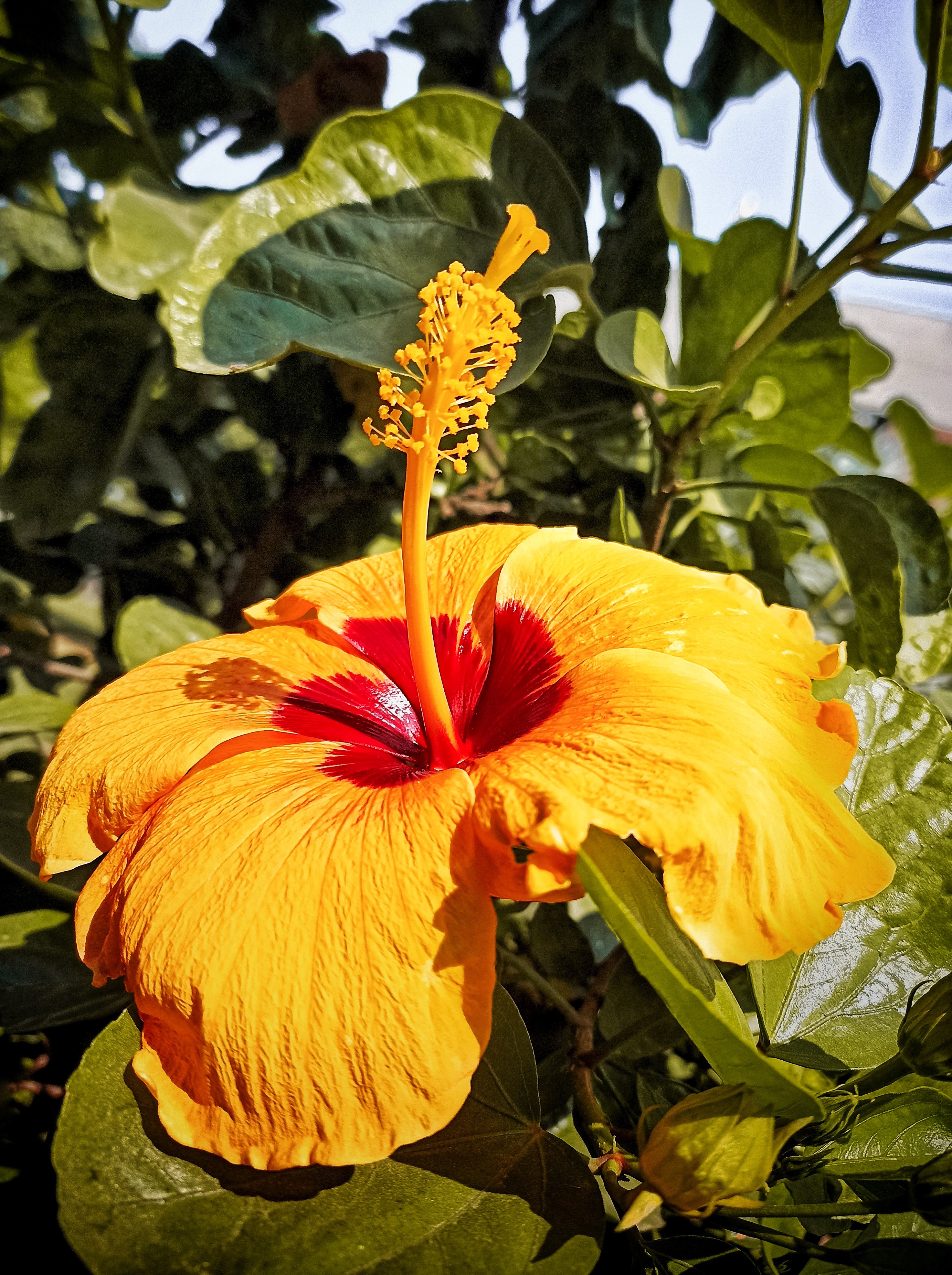
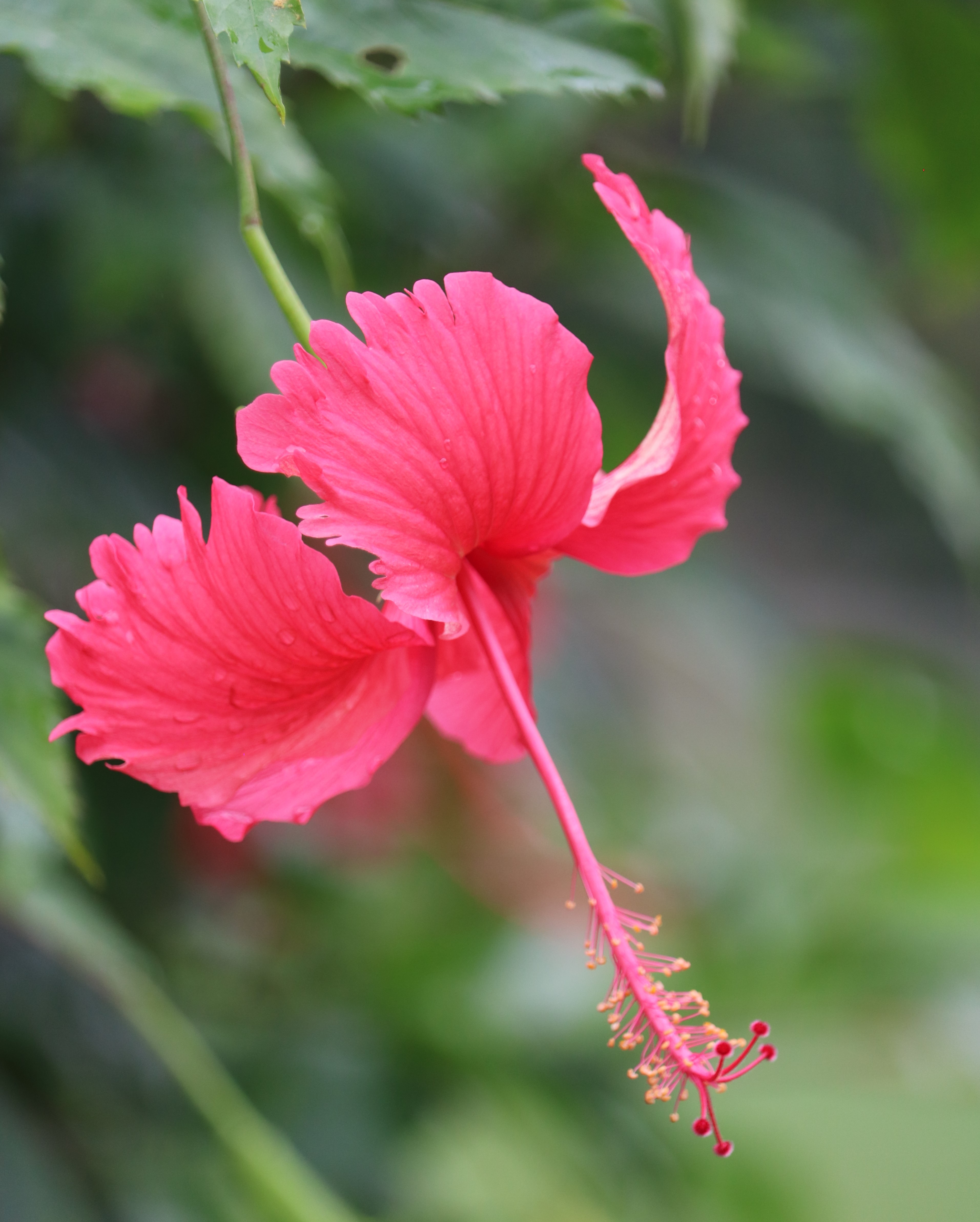
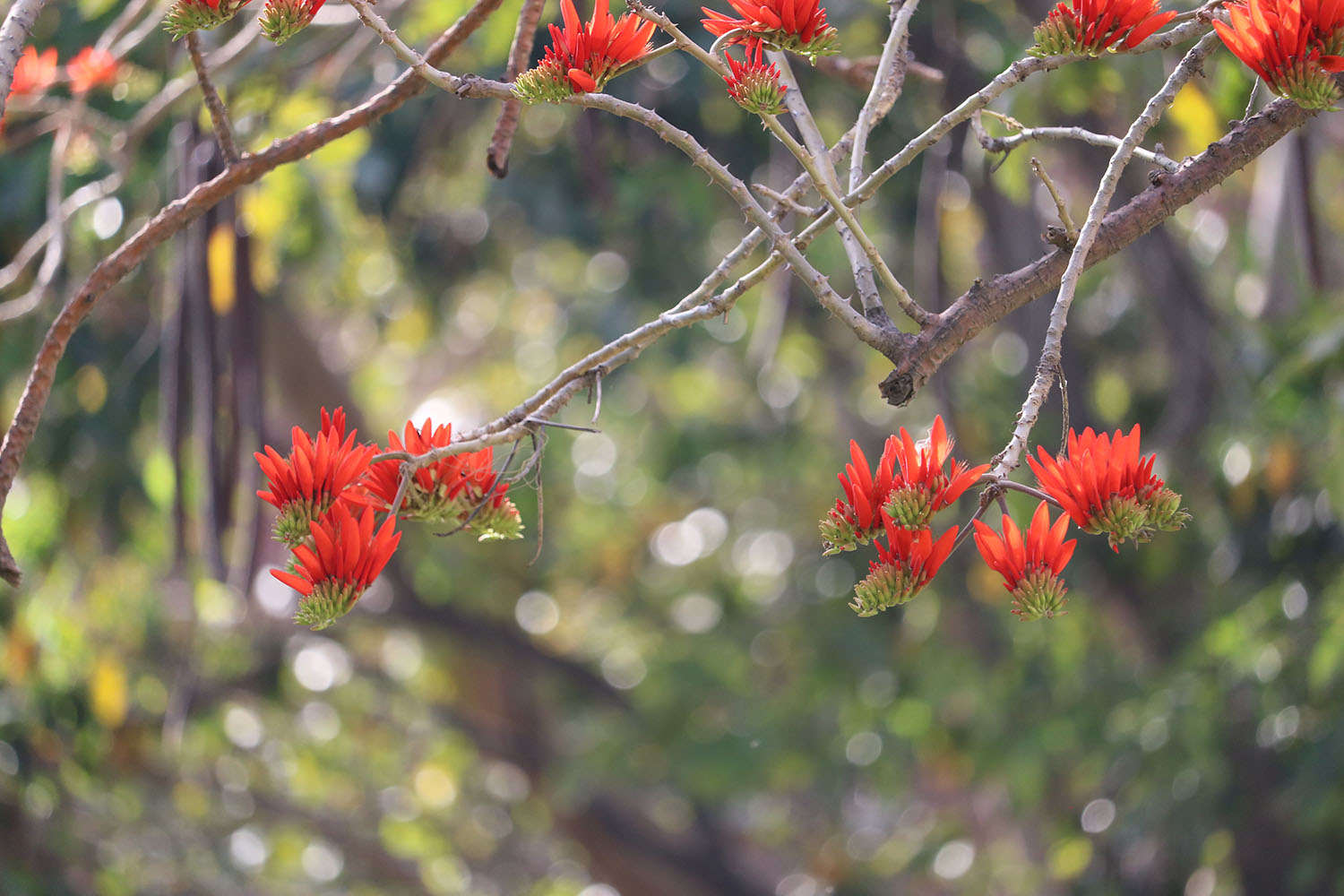
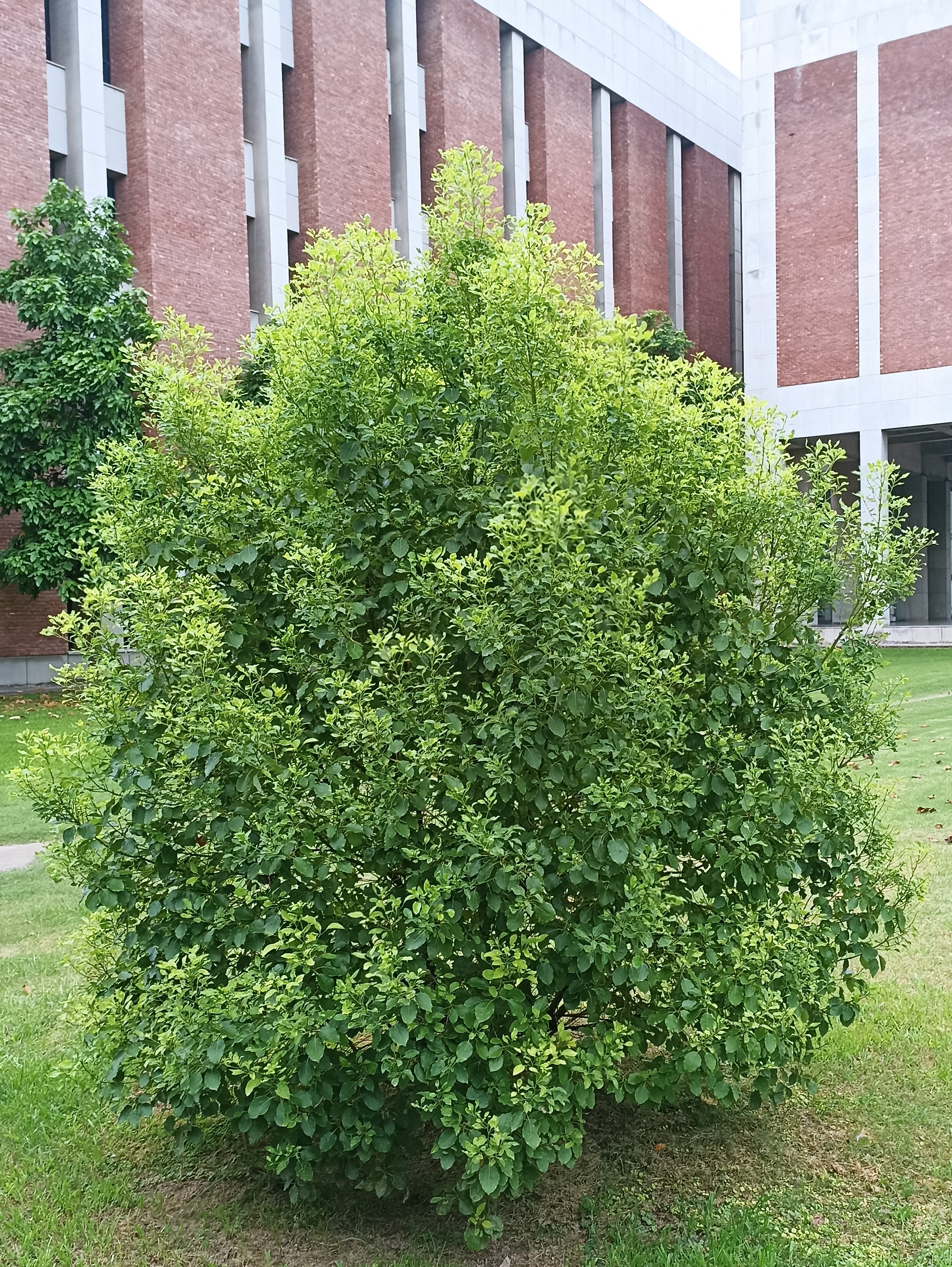
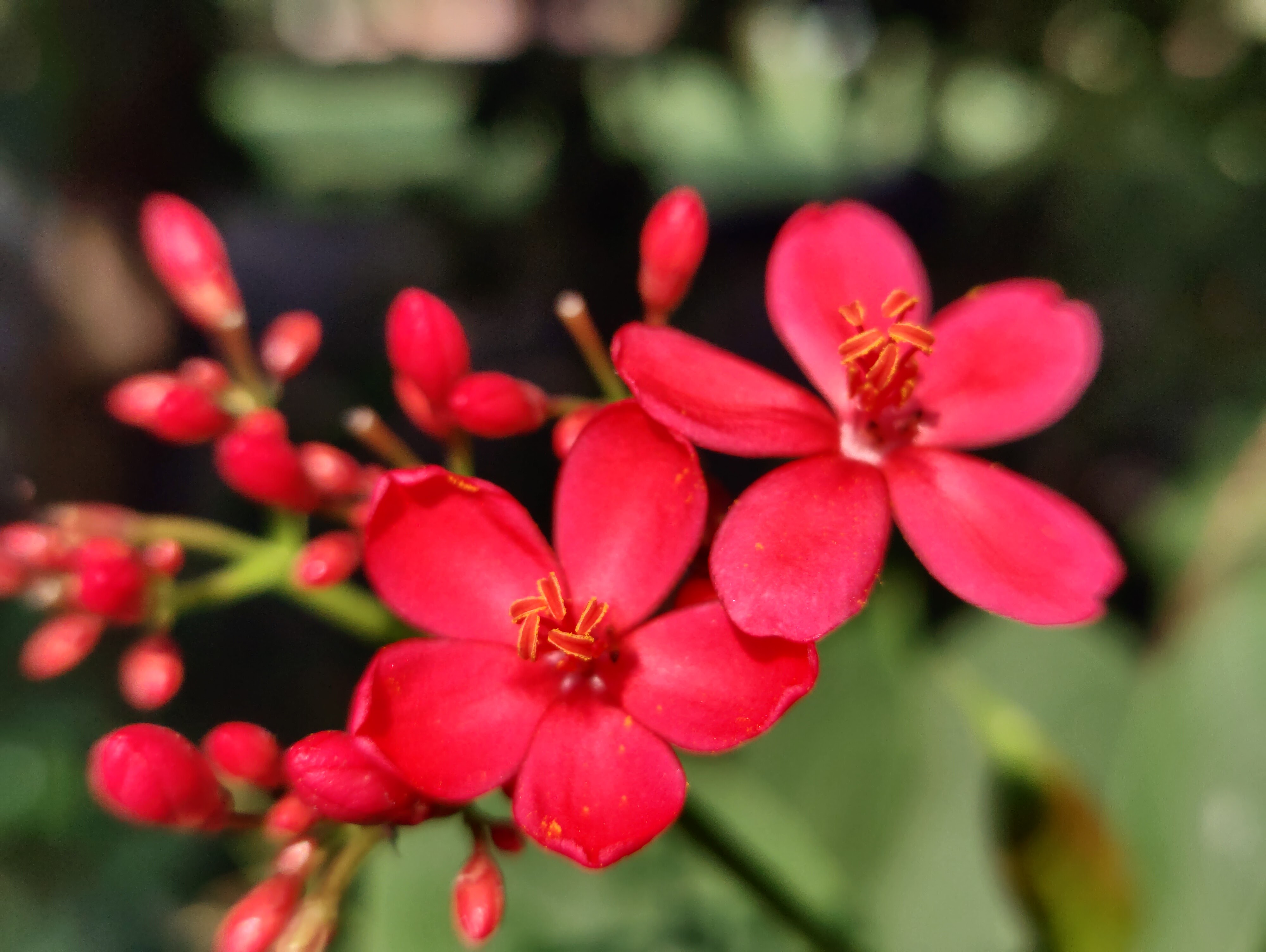
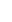
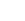
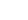
Salmali, commonly known as silk cotton tree is one of the most readily available herbs in India. Salmali bears beautiful red flowers which stops diarrhoea and hence given the name. The species name malabarica indicates that the plant is native to Kerala.
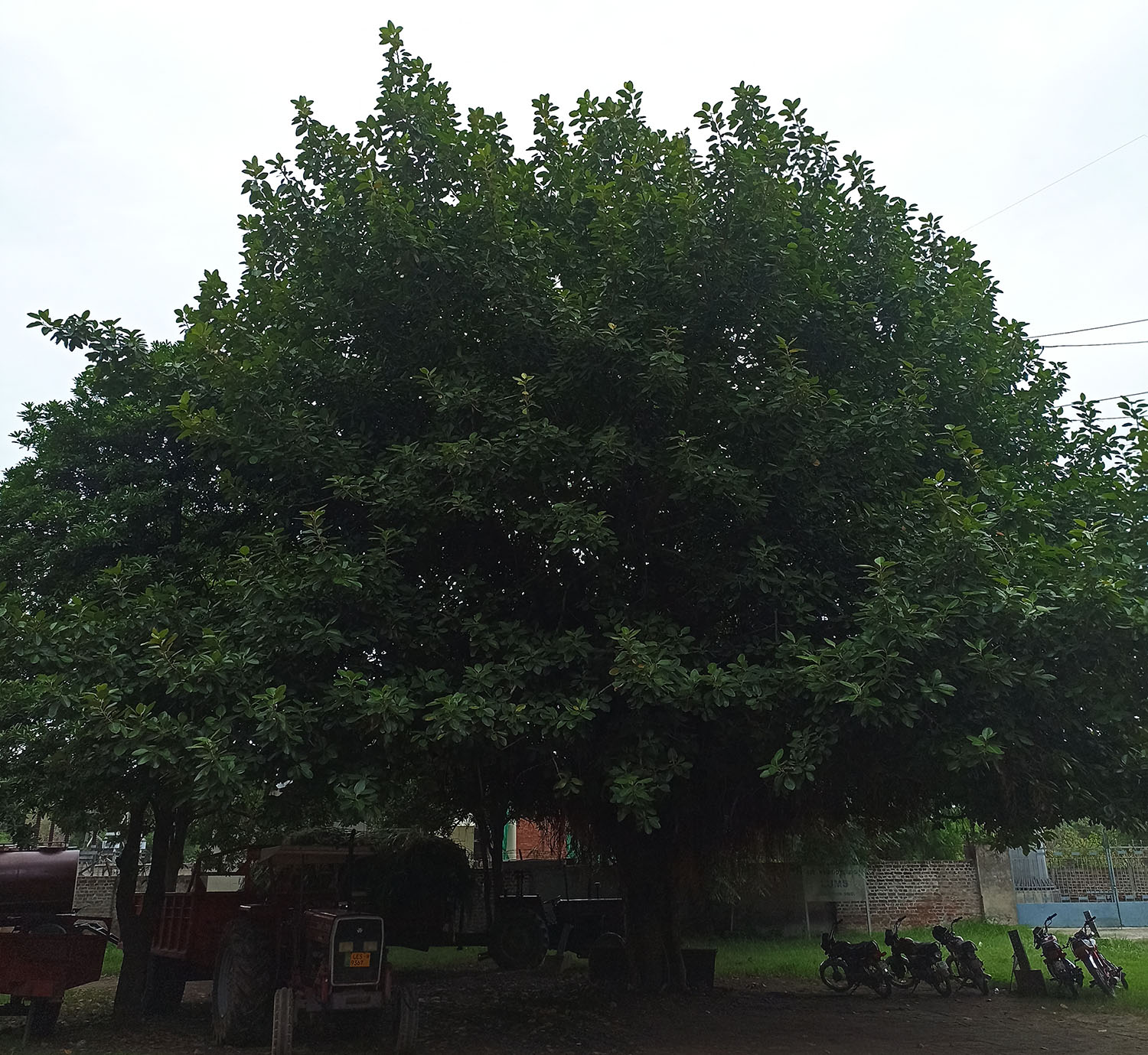
Shalmali (Salmalia malabarica), also called Silk cotton tree, Indian Kapok tree, Semal, Buruga, Sittan, Unnamurika or Sanmali is an Ayurvedic herb that is loaded with health benefits. It is known as the king of the forest because of its massive size and beautiful flowers. Shalmali is native to India and Burma. It is considered a sacred tree in India. In India, it is found in hotter regions up to altitudes of 1500mts. It is also found in tropical Southern Asia, Australia, and Africa. The fascinating health benefits of Shalmali have made it one of the prominent herbs in the Ayurvedic system.
Shalmali in Ayurveda:
Almost all parts of the tree including flower, gum, stem bark, petiole, peduncle, and thorns are used in Ayurveda due to its therapeutic properties. According to Ayurveda, Shalmali balances Pitta and Vata doshas. It has an astringent taste and cold potency. The main chemical constituents of Shalmali include beta-sitosterol, glucosides, lupeol, hydroxycadalene, hentriacontane, and various acids. It also has aphrodisiac, astringent, stimulant, tonic, anti-diarrhoeal, anti-dysentery, anti-microbial, and antipyretic properties. Here are some of the fascinating health benefits of Shalmali.
Health benefits of Shalmali or Silk Cotton:
Treatment of dysentery
The chemical compounds present in the root of Shalmali are used for treating dysentery, diarrhoea, piles, and hemorrhoids. It is also effective for treating pulmonary tuberculosis and other chronic diseases.
Beneficial for curing wounds
The gum and bark of salmali are loaded with antibacterial, antipyretic, and wound-healing properties. It can be applied to the affected area for quick healing of wounds. It also arrests bleeding.
Shalmali as an aphrodisiac
salmali is a potent aphrodisiac. It is very beneficial for the male reproductive system. Consuming this herb improves both the quantity and quality of semen. It also helps cure nocturnal emission.
Excellent for treating skin disorders
salmali is loaded with purifying and healing properties. The paste obtained from the flowers of this plant is beneficial for treating various skin disorders like acne and pimples. The paste of seeds is also used to restore the colour of the skin.
Shalmali as a diuretic
Shalmali is an excellent diuretic. The flowers of this plant are given to patients suffering from low urine output. It is also used to cure splenomegaly and conjunctivitis.
Shalmali is a well-recognized and highly effective Ayurvedic herb that is used in the treatment of numerous diseases. From curing skin problems to providing relief from dysentery, Shalmali is a miraculous Ayurvedic herb that does it all. Thus, these are some of the fascinating health benefits of Shalmali or silk cotton. The long silky seed hairs ('cotton') have been used as a source of kapok.
Habitat
It is found all over India and other parts of tropical Asia up to an altitude of 1500 m.
Botanical Description
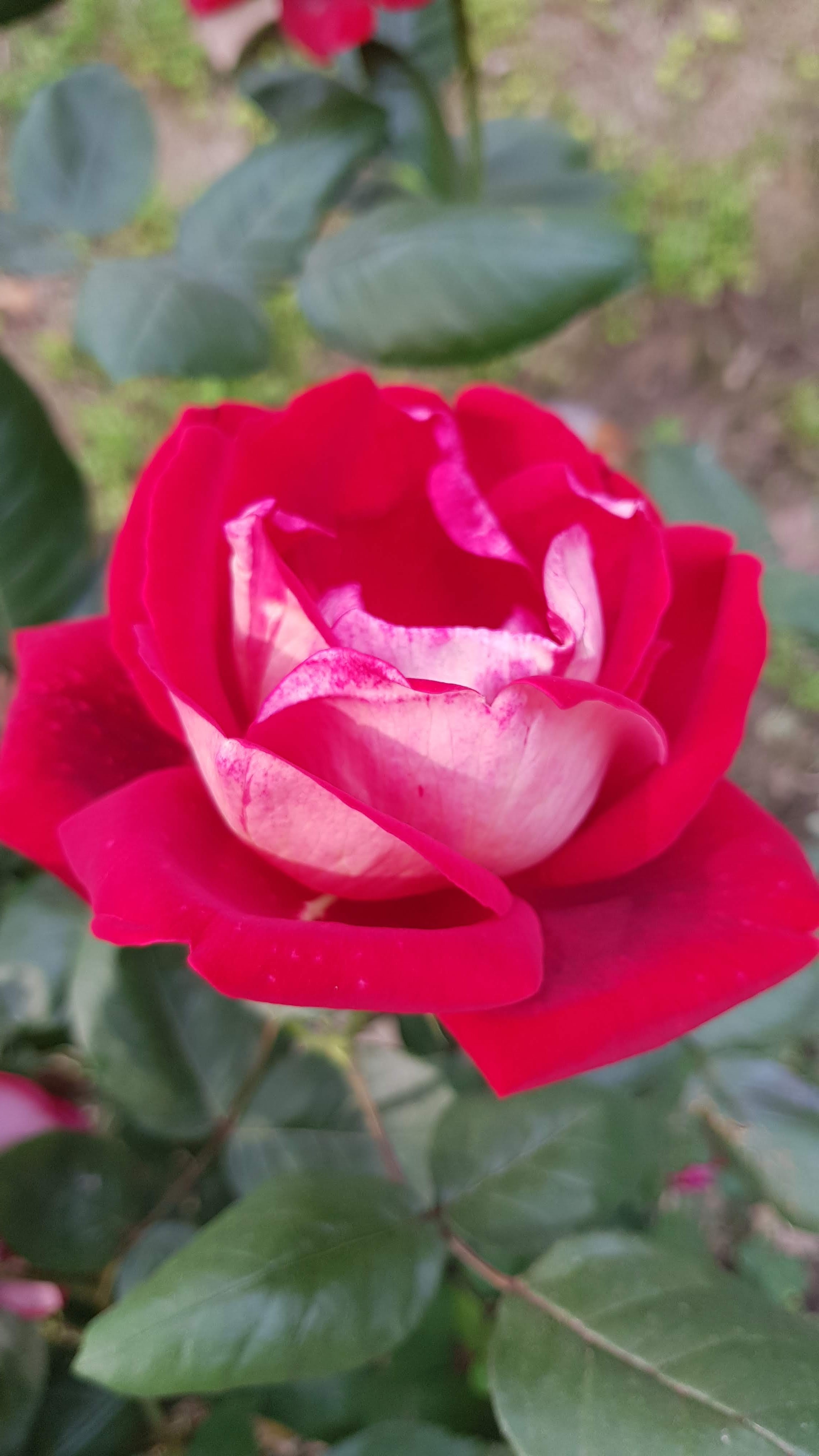
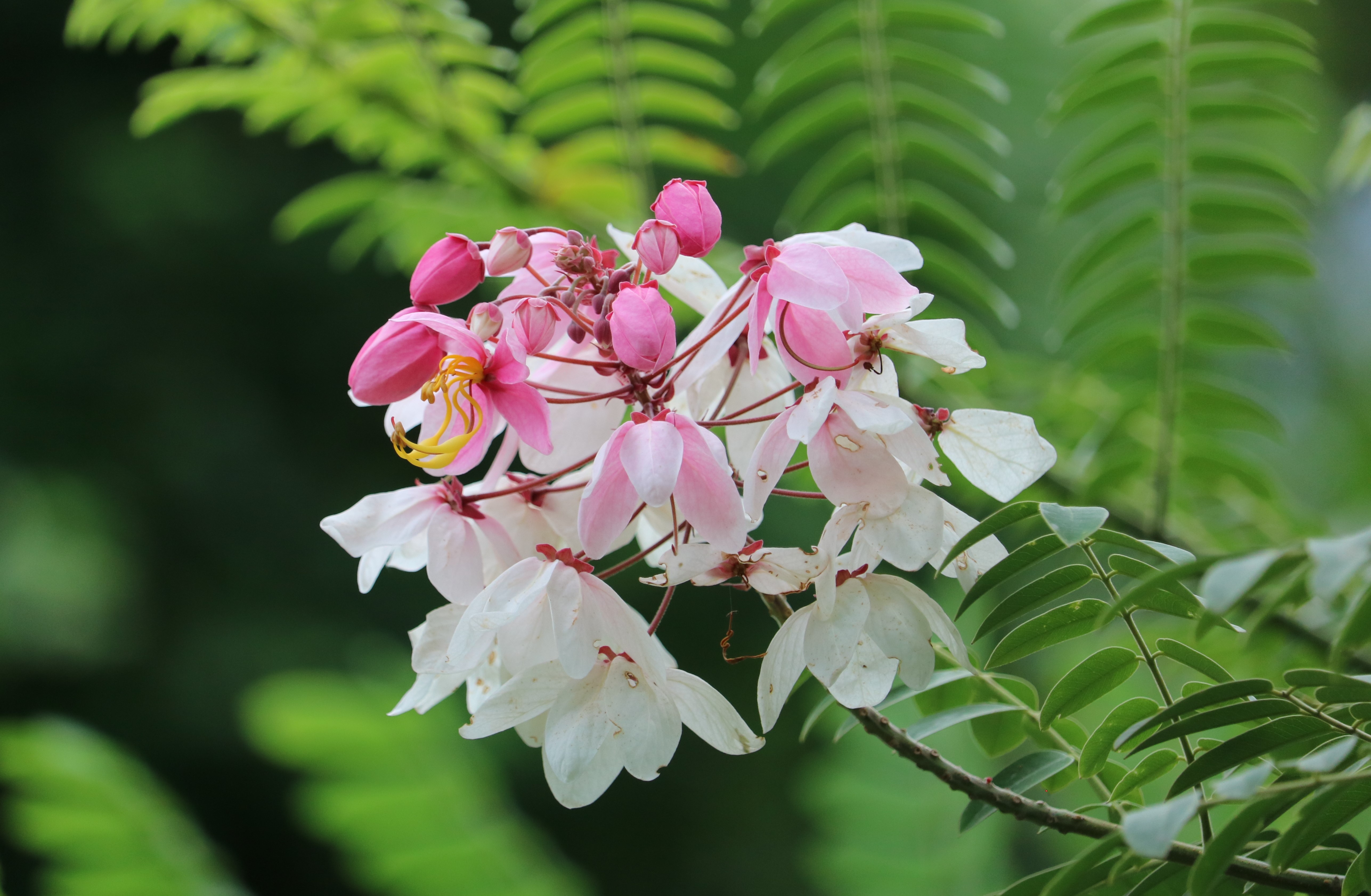
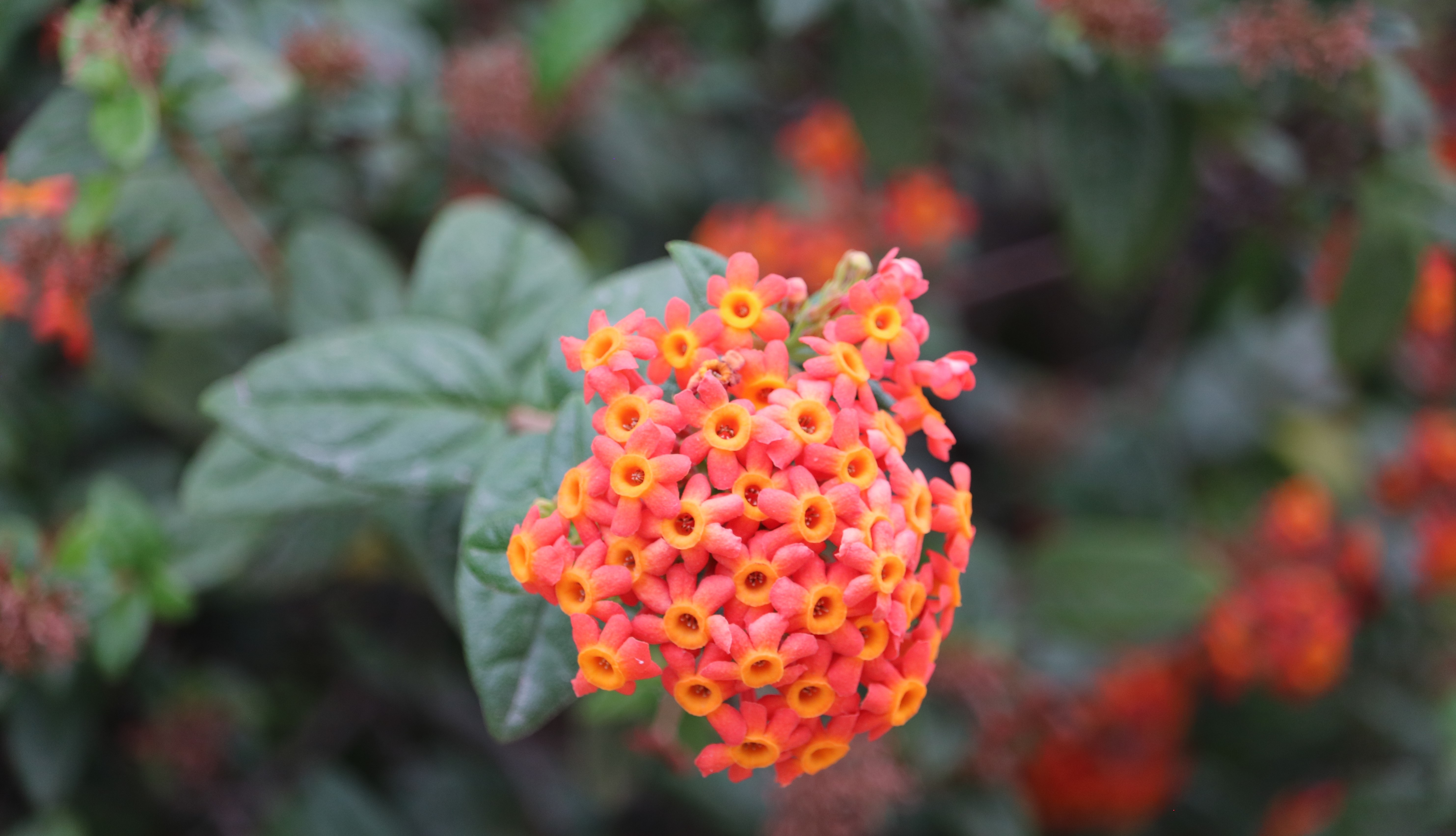
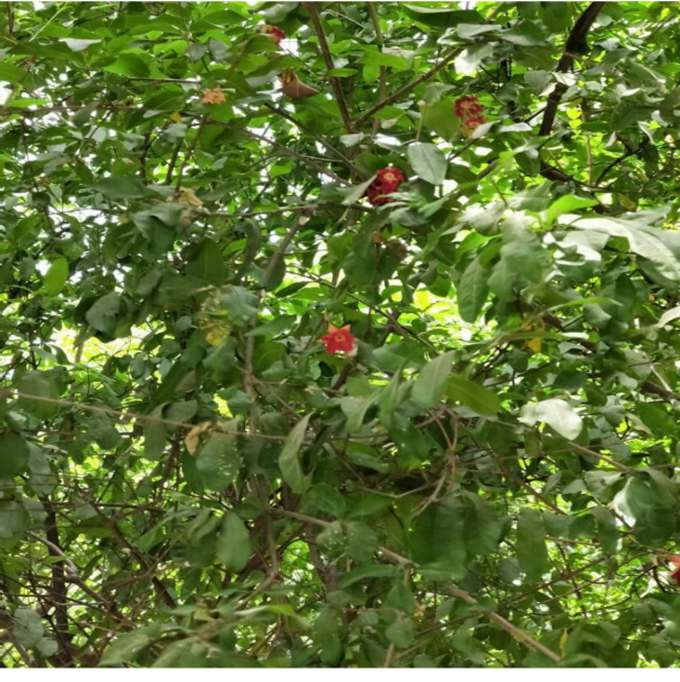
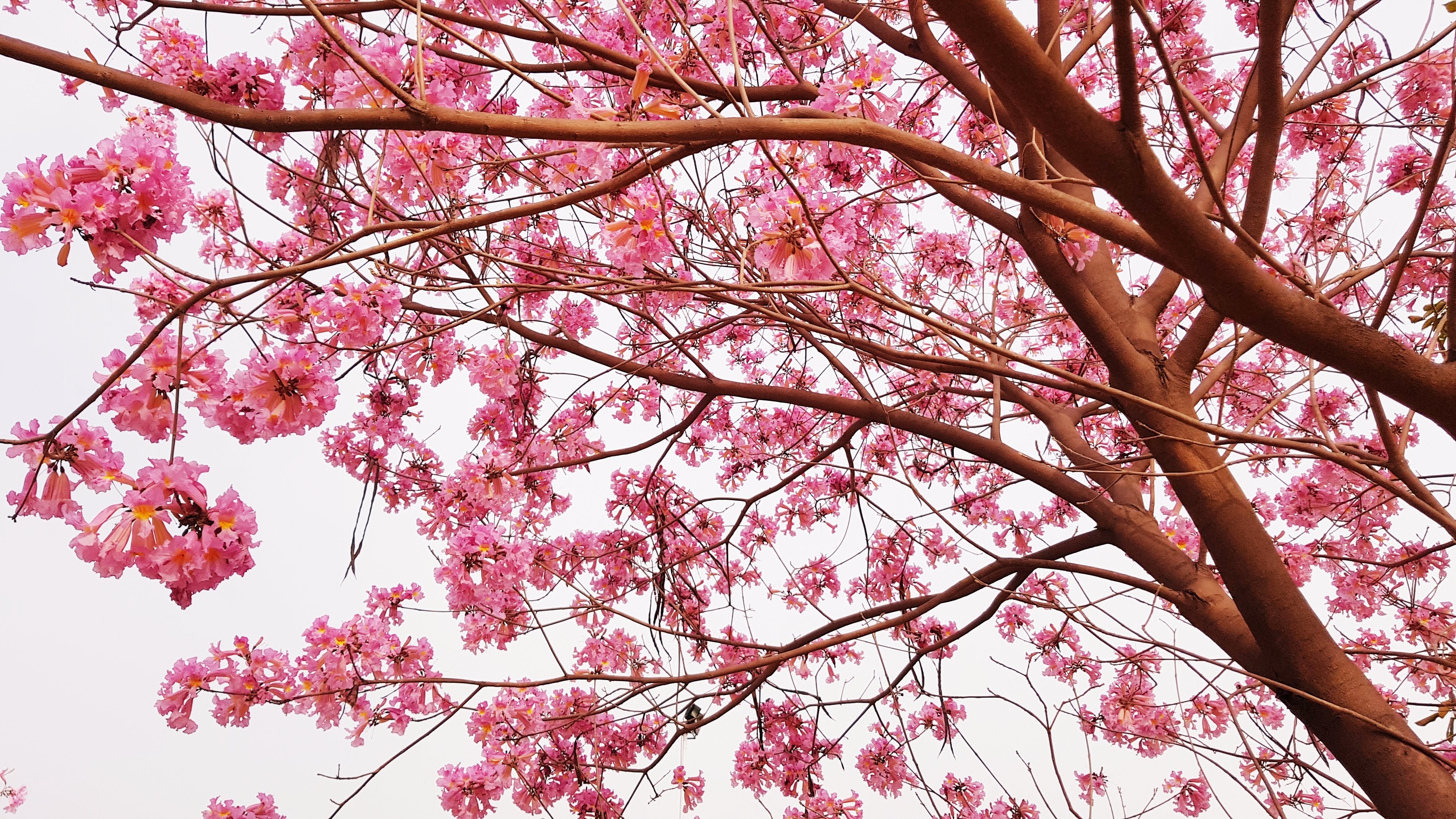
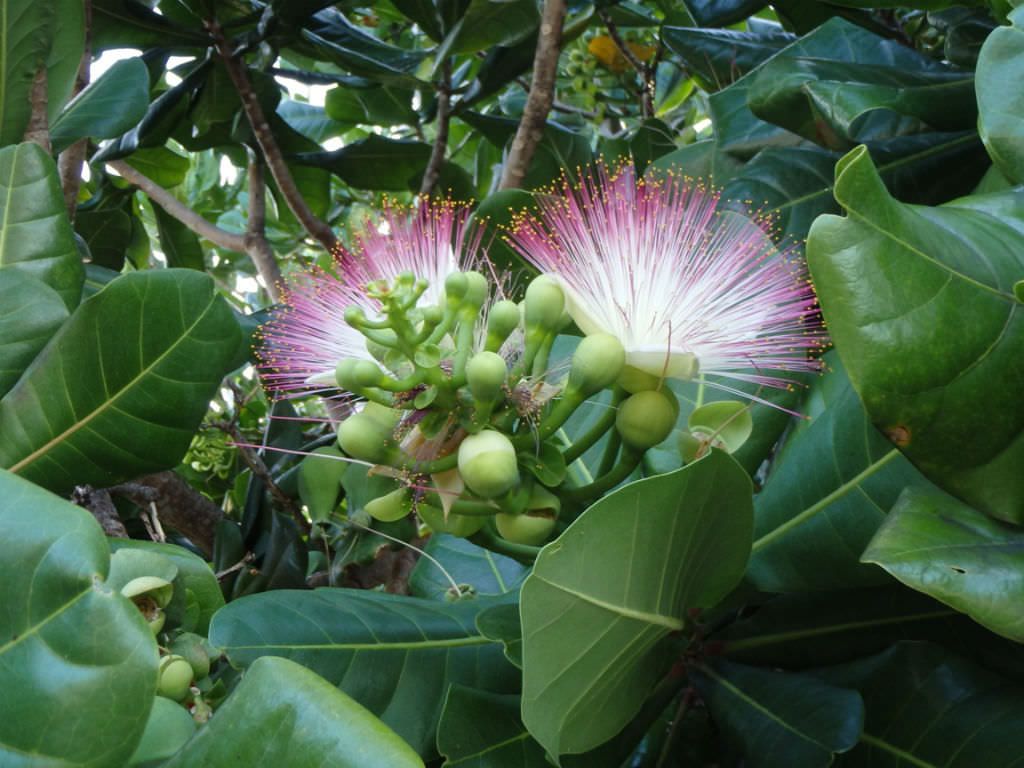
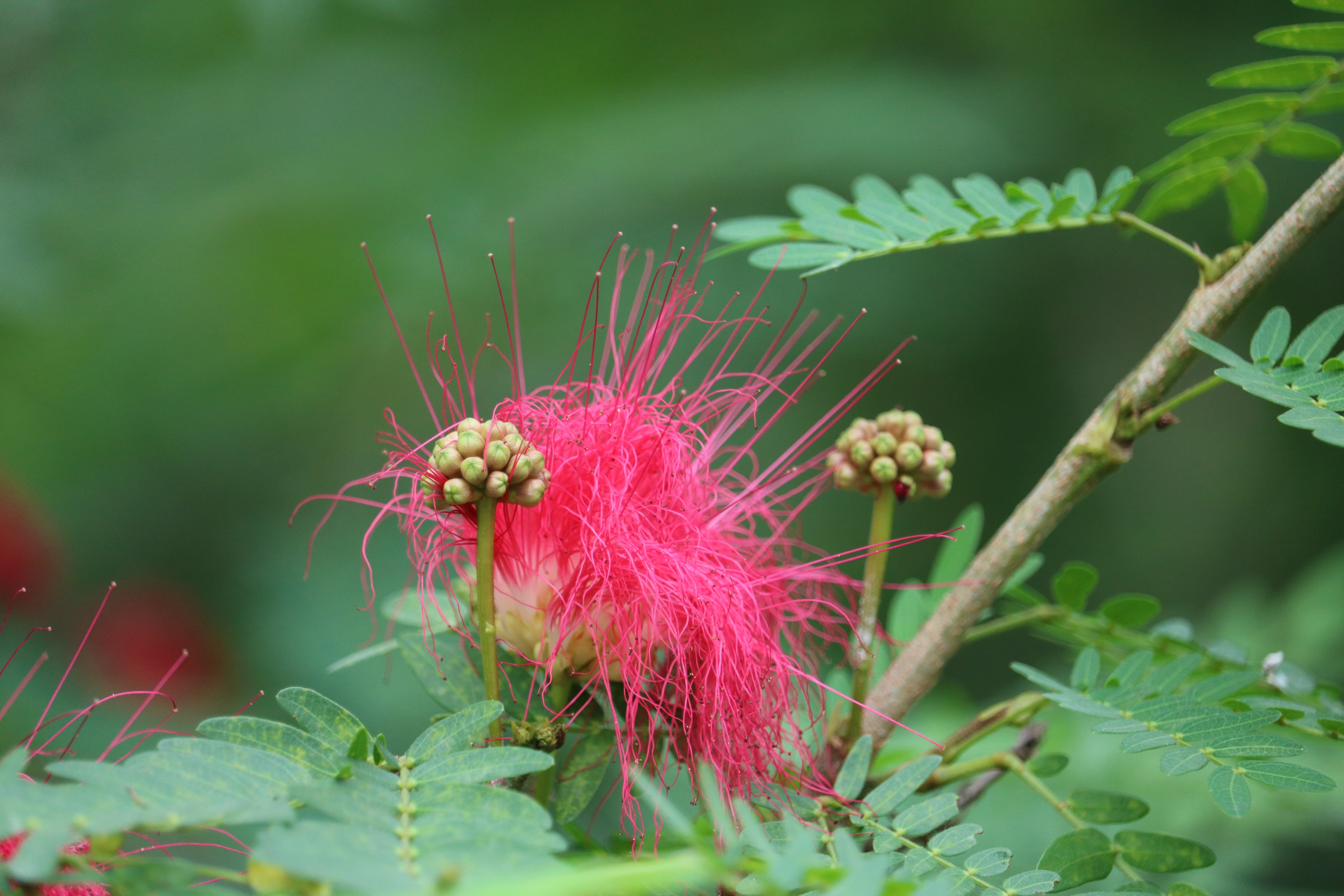
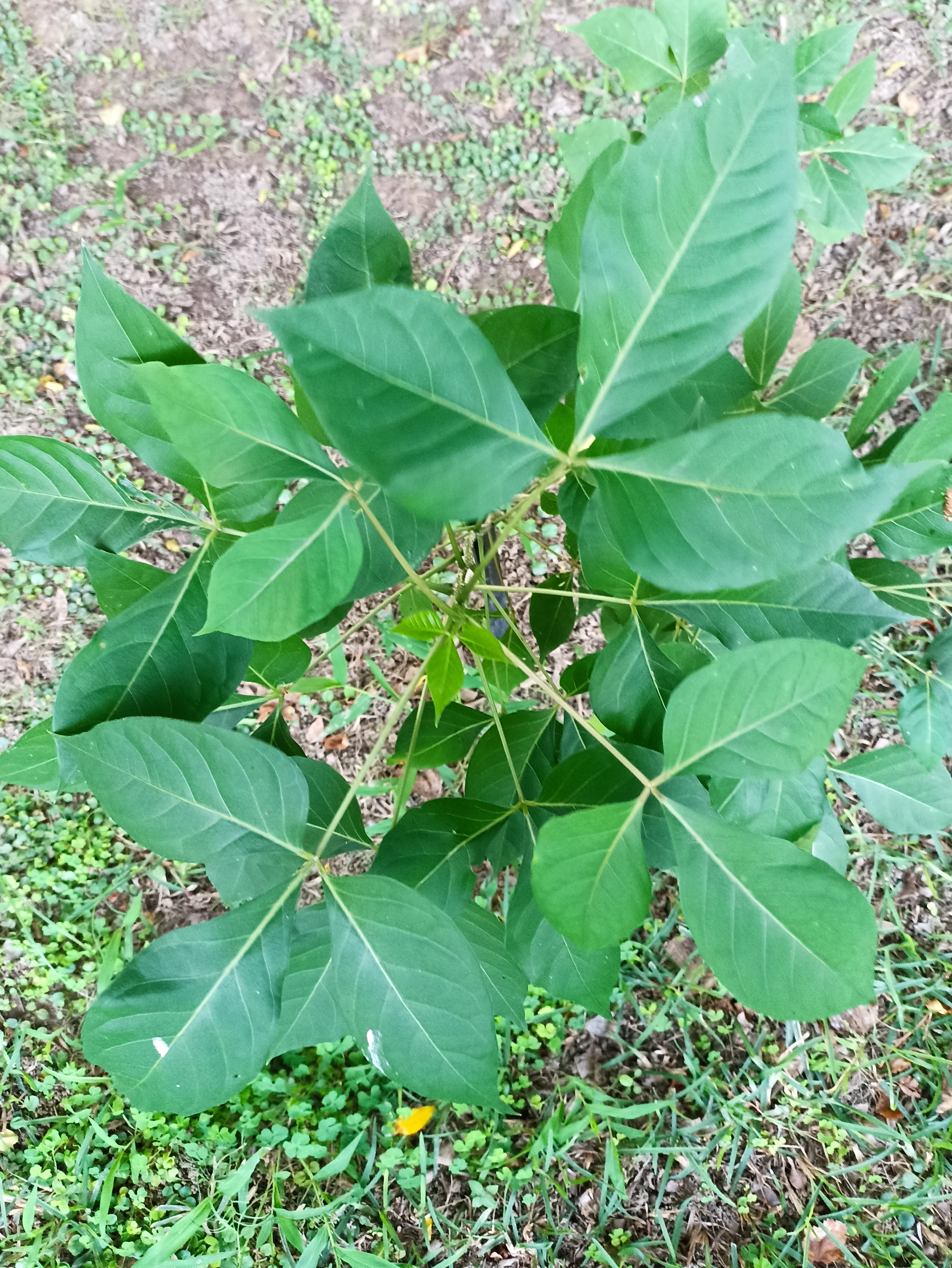
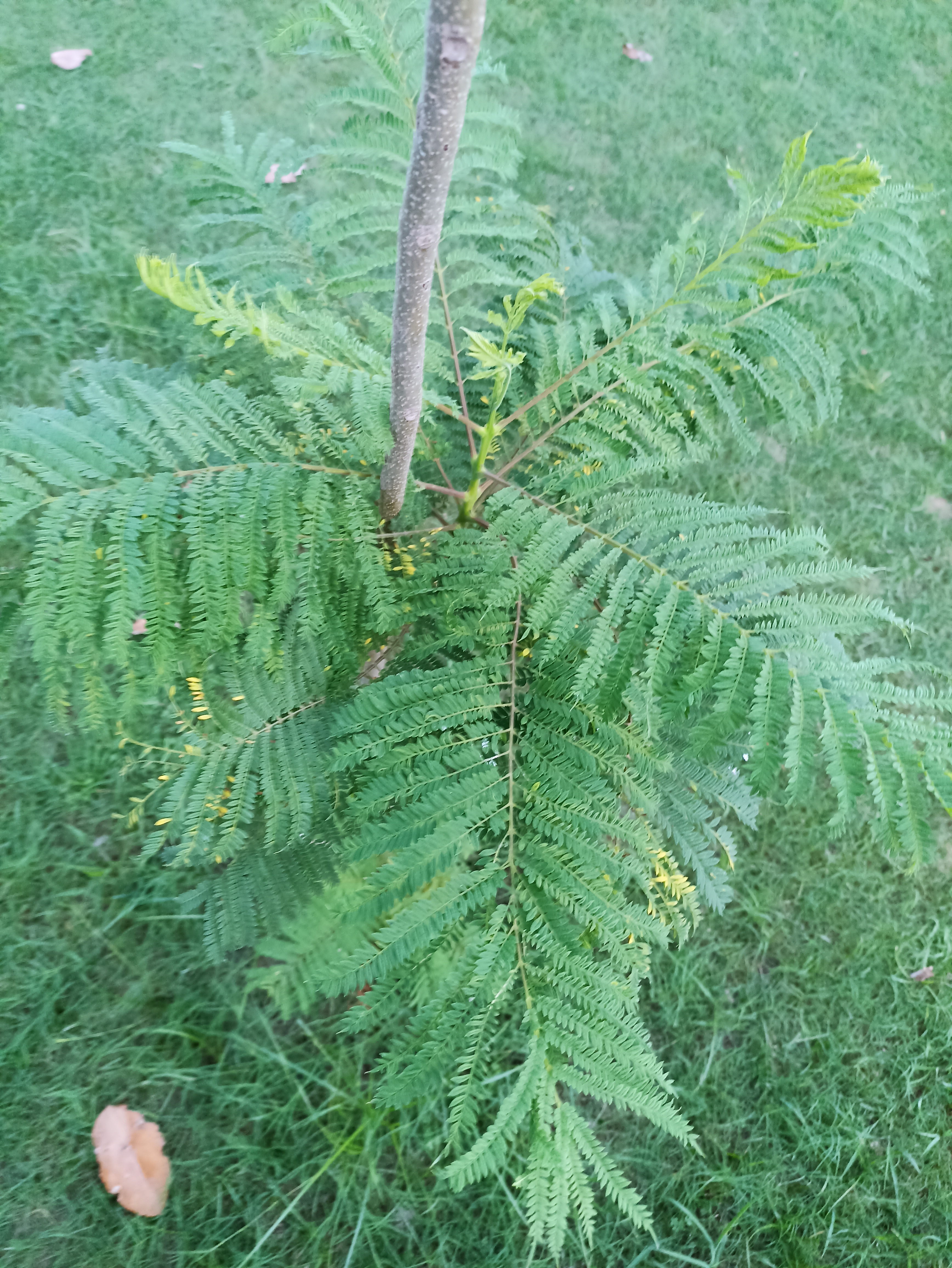
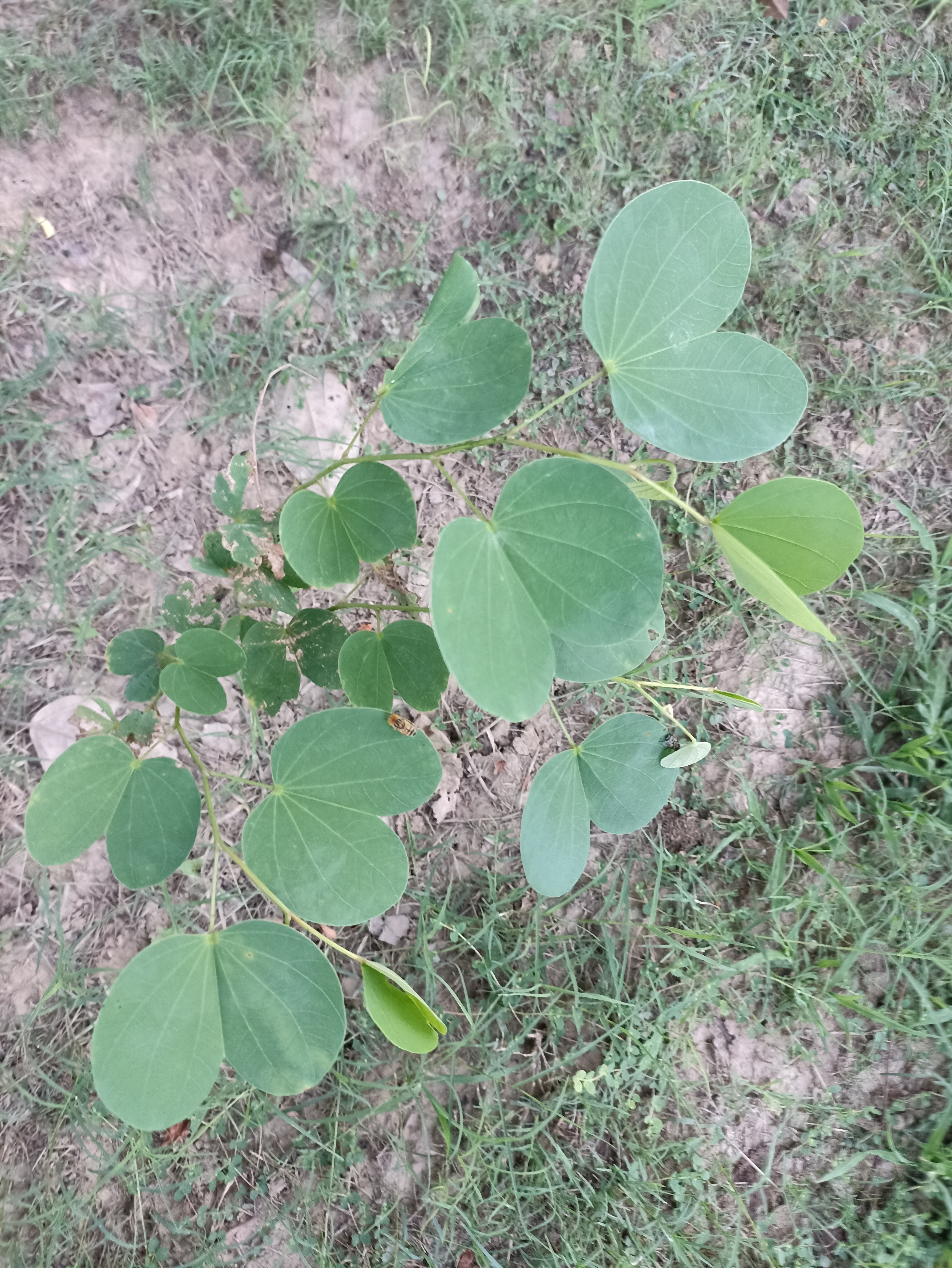
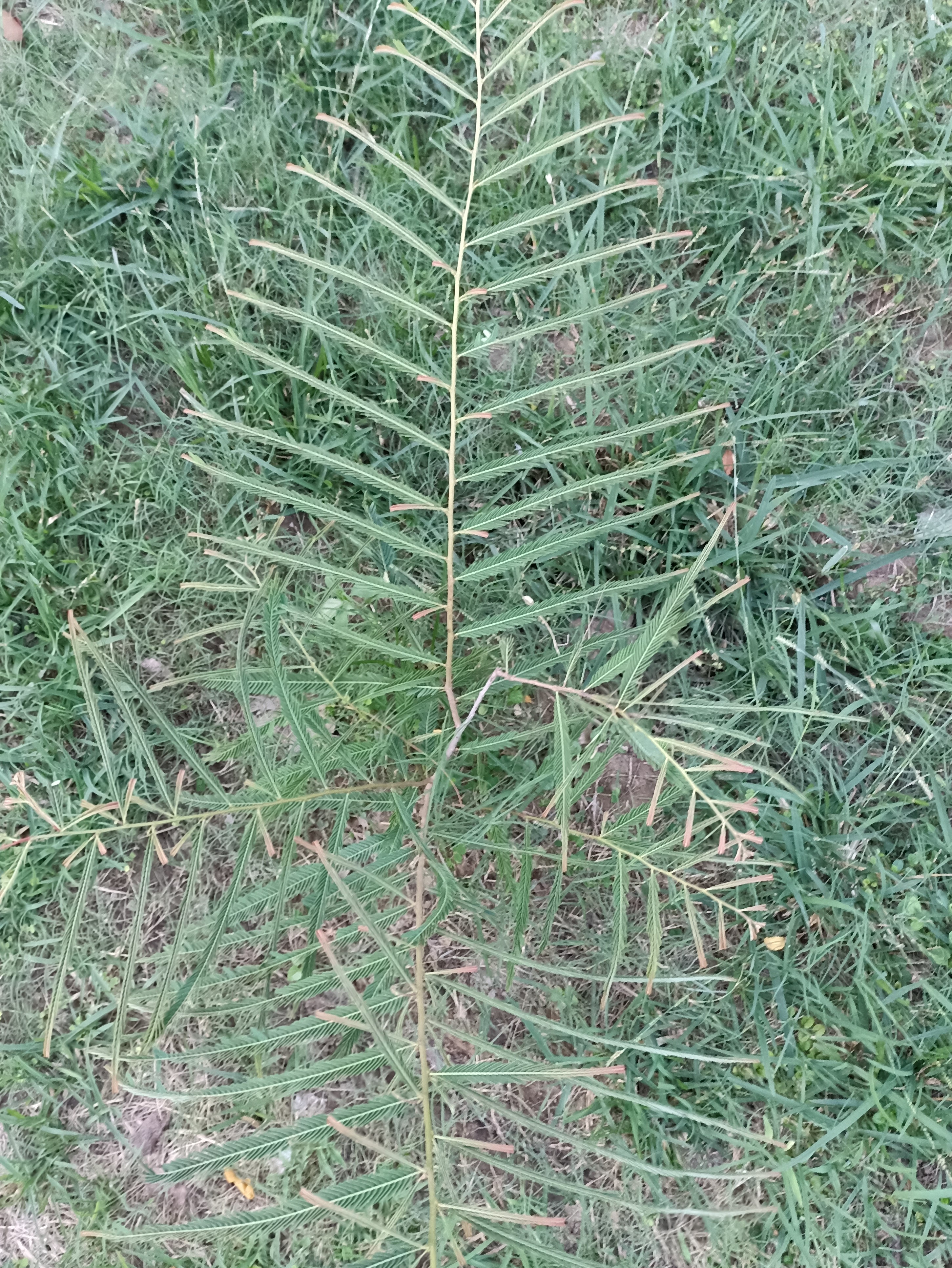
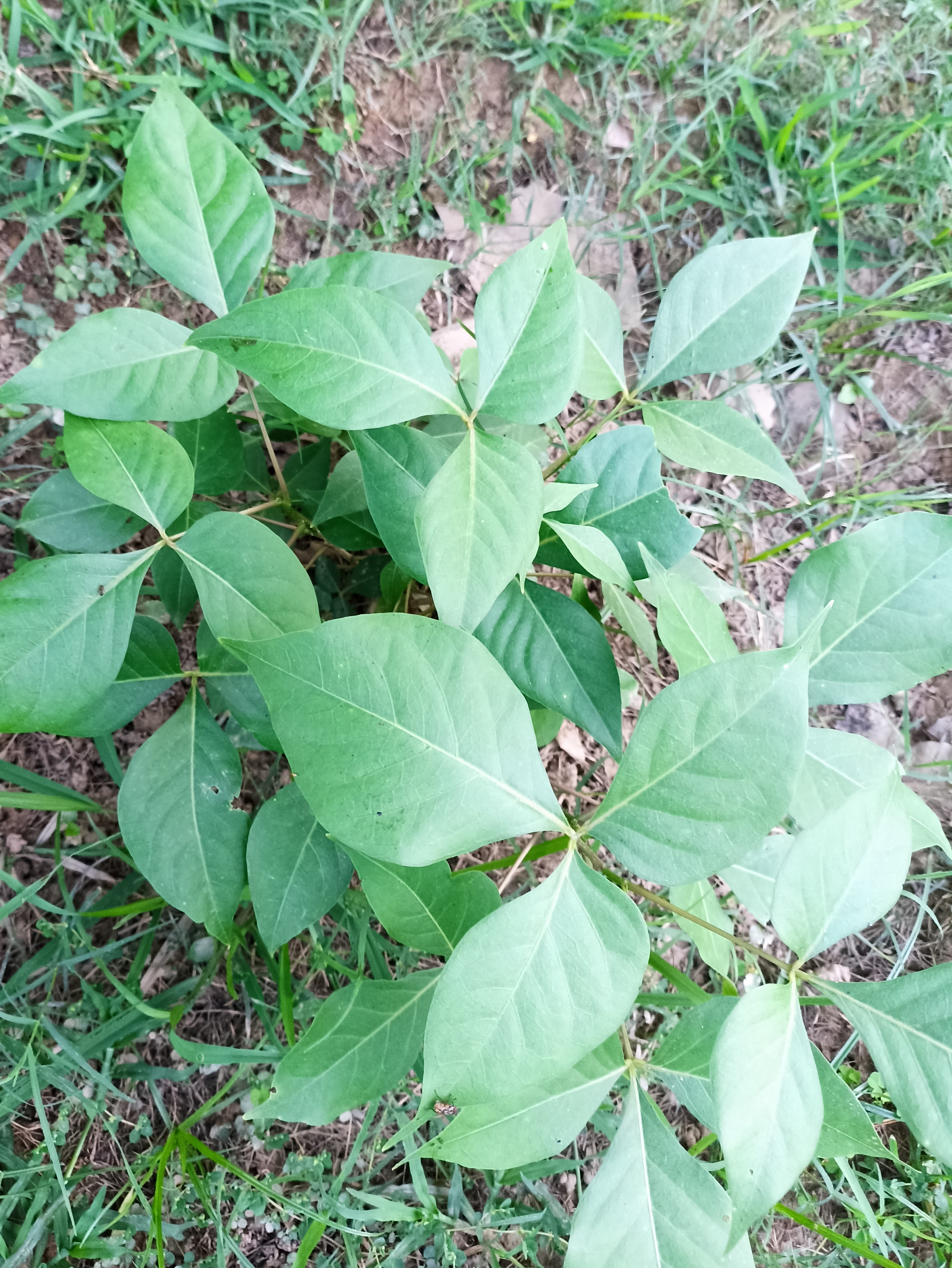
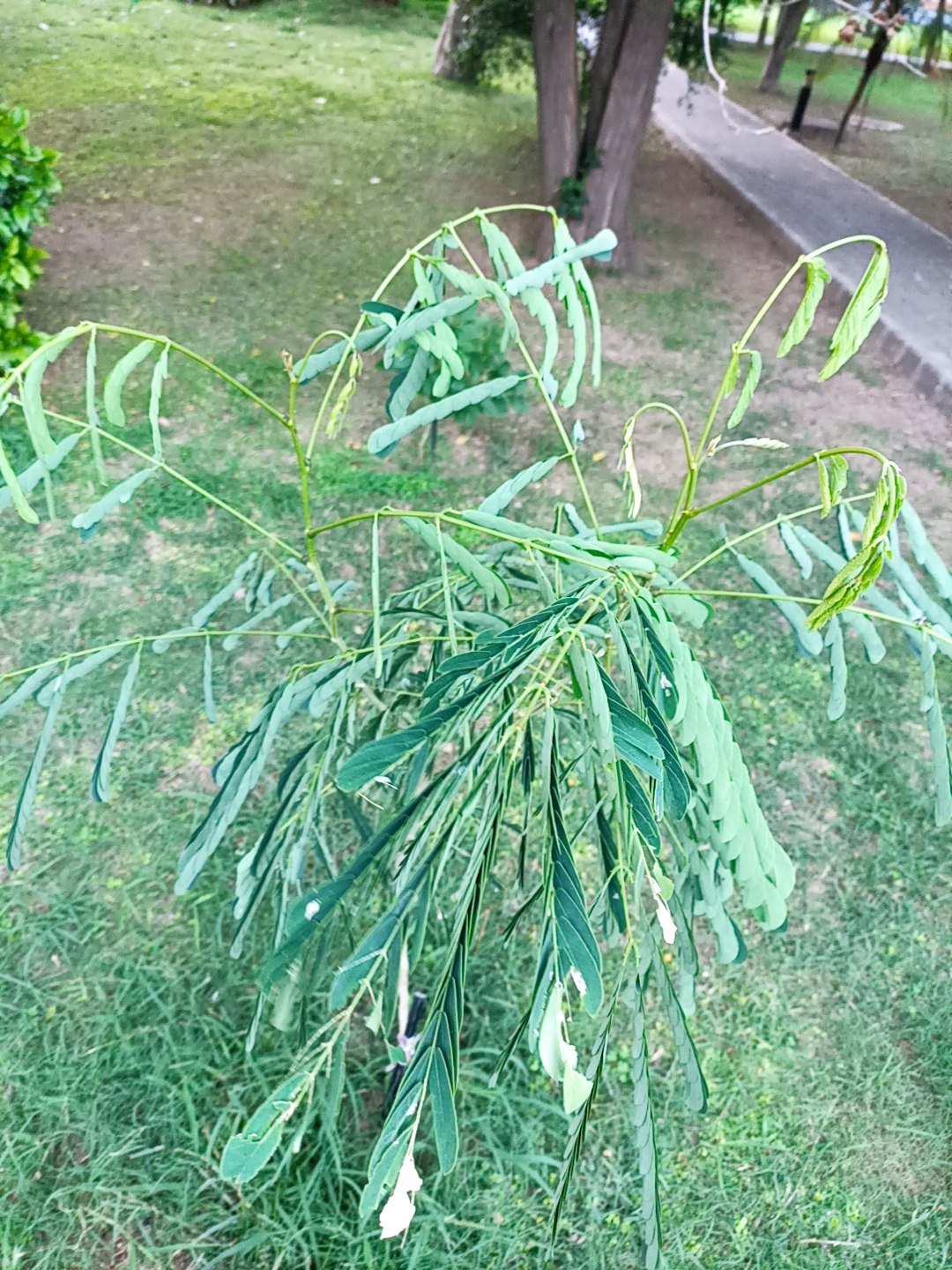
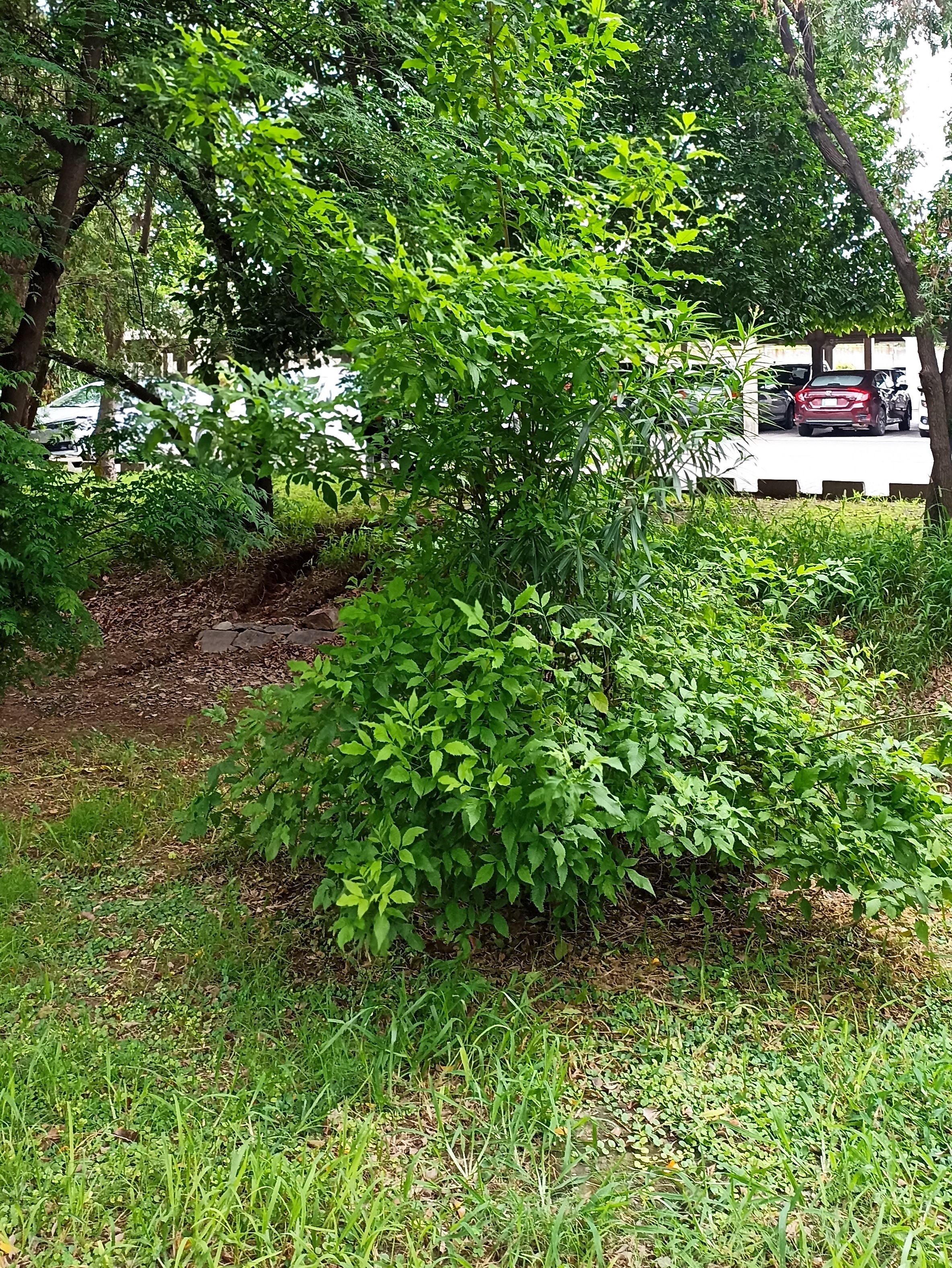
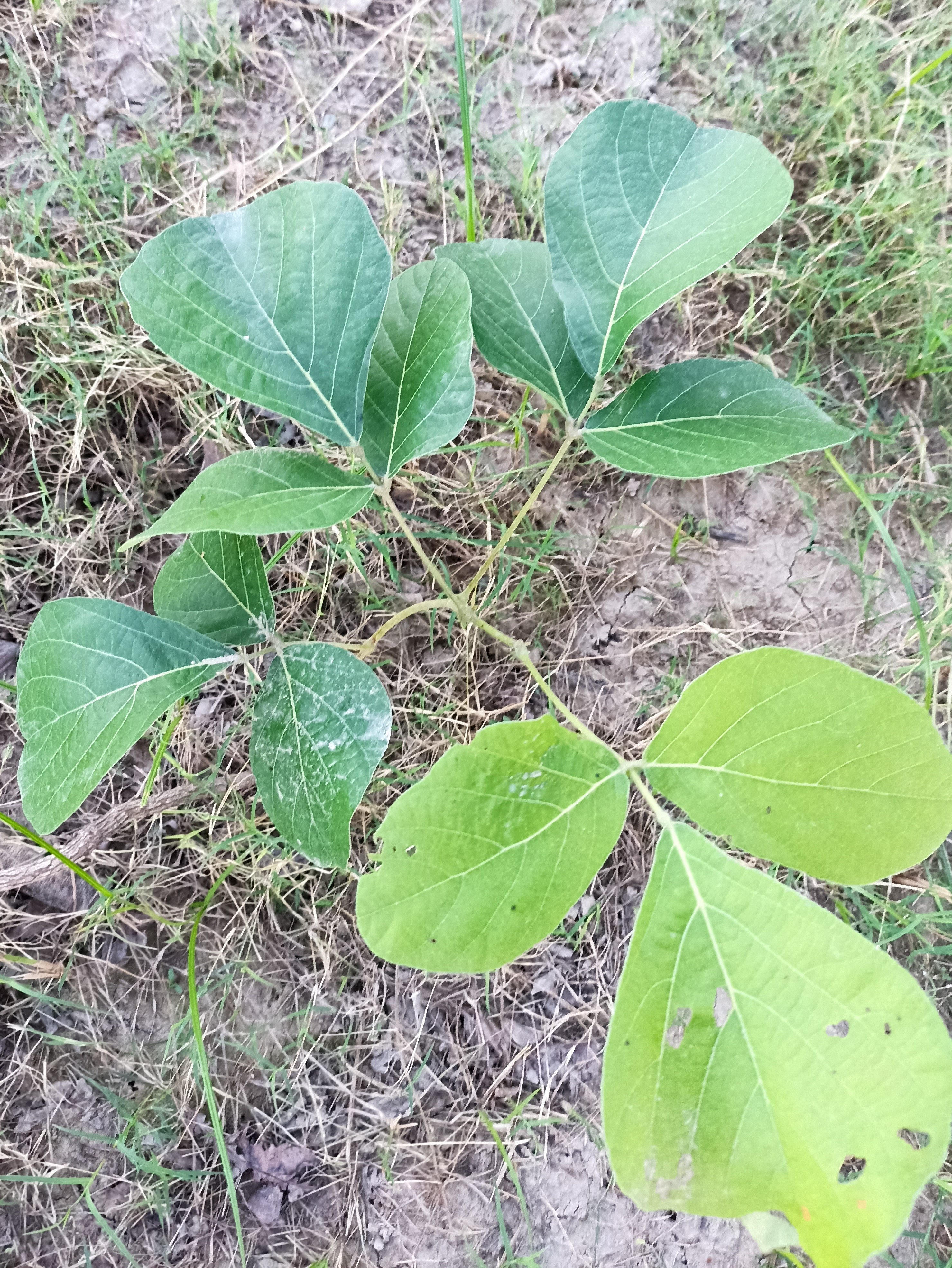
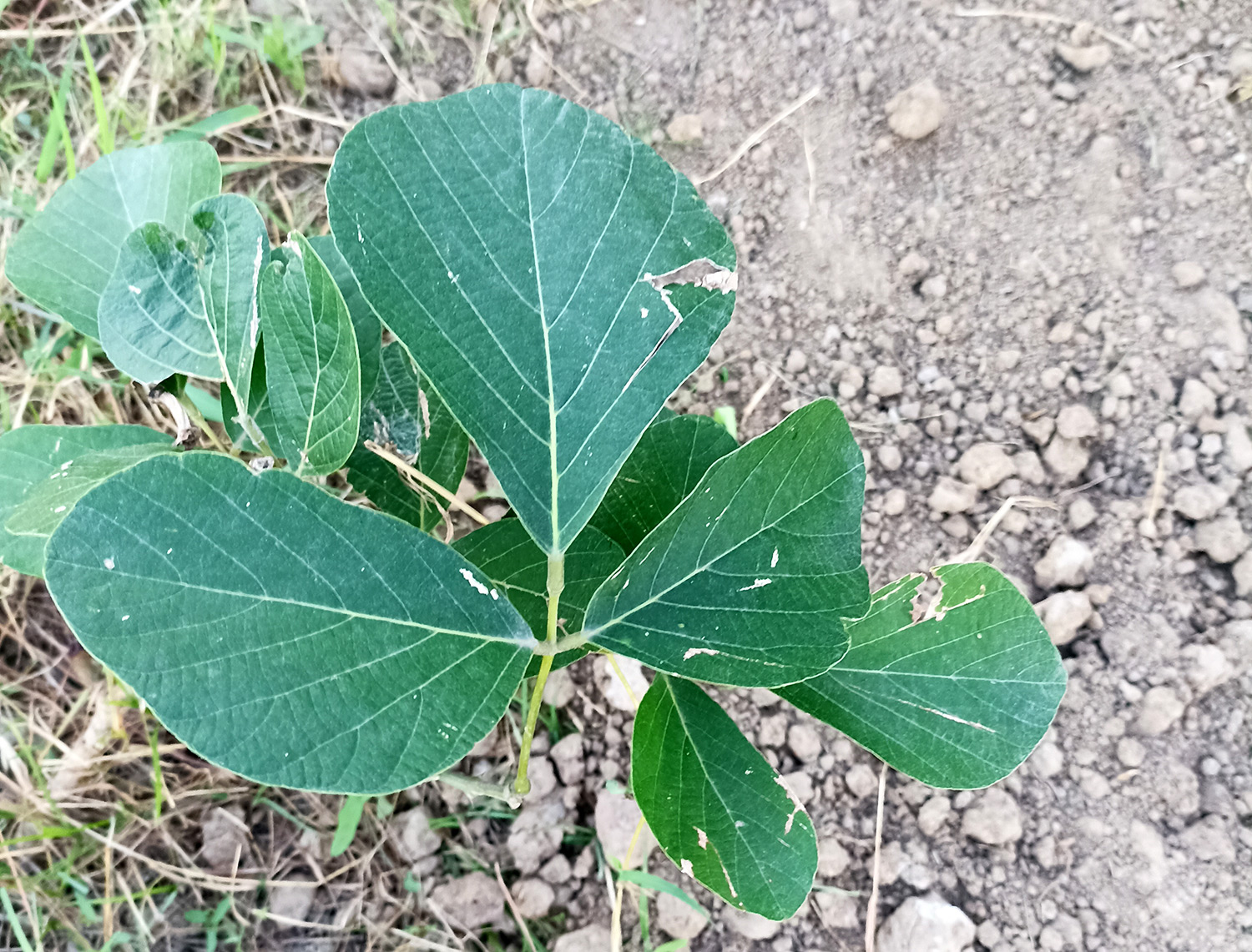
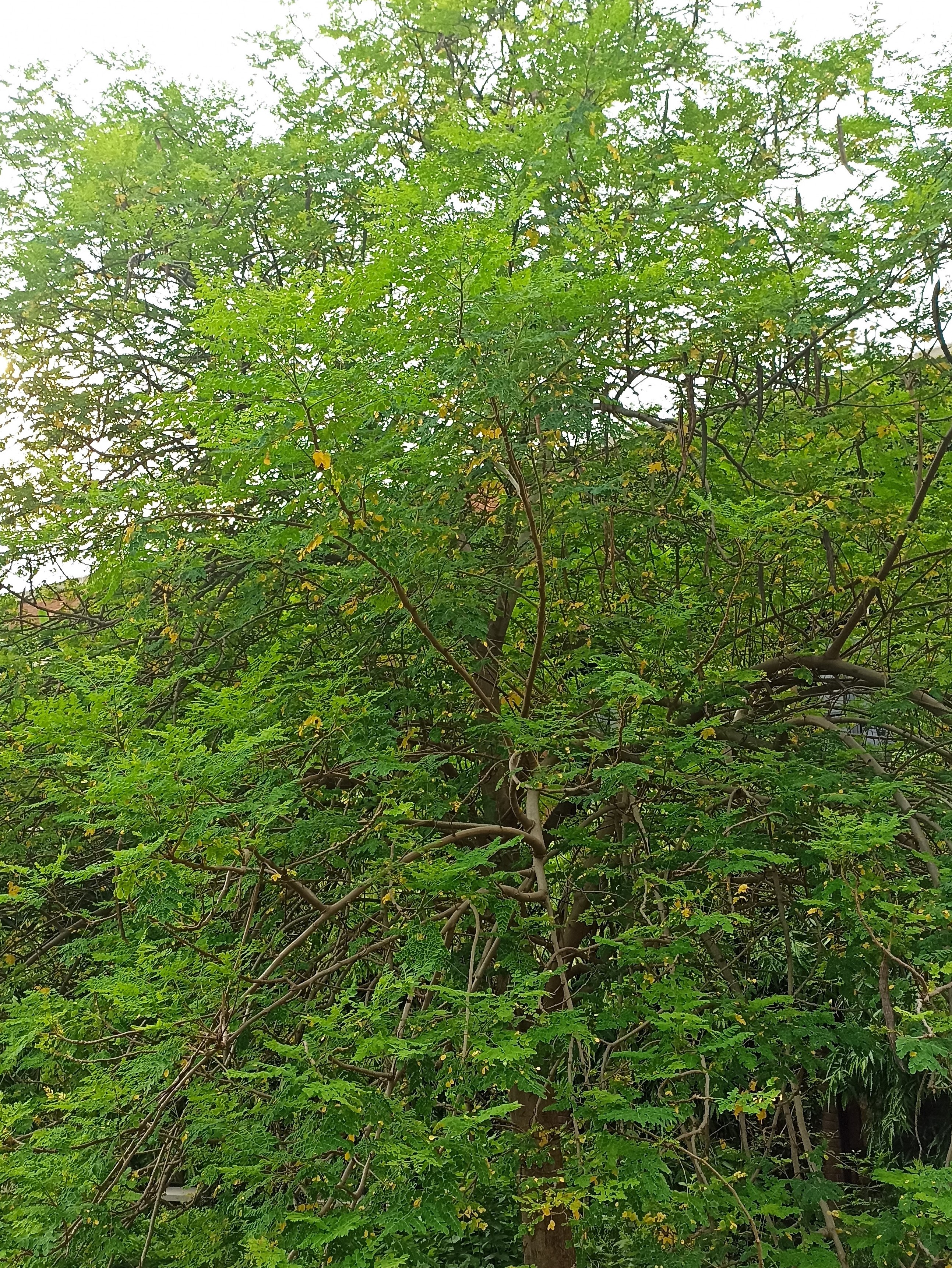
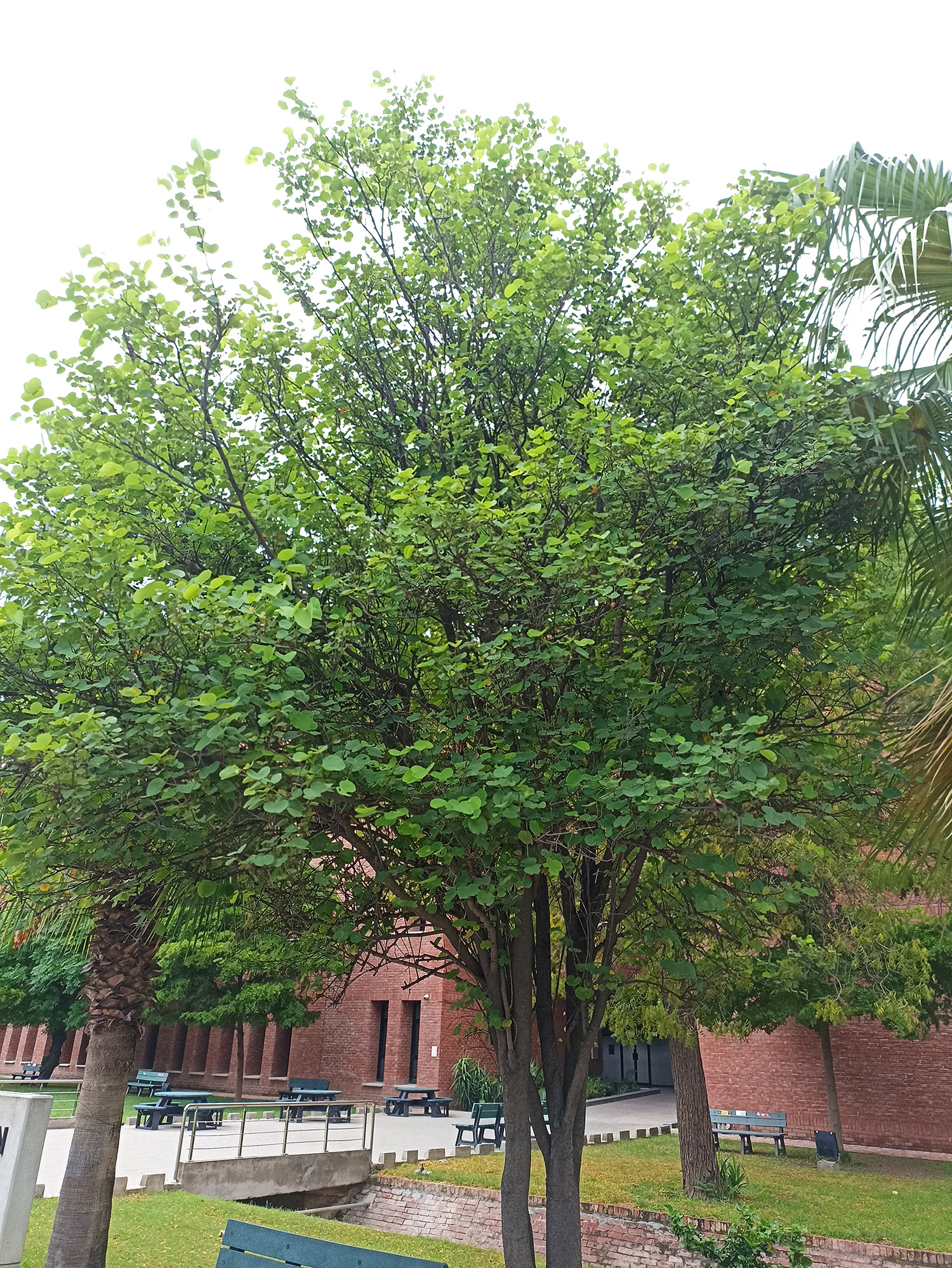
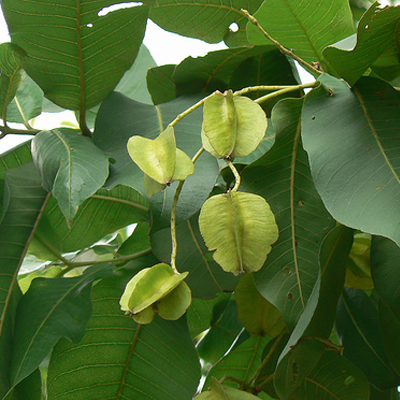
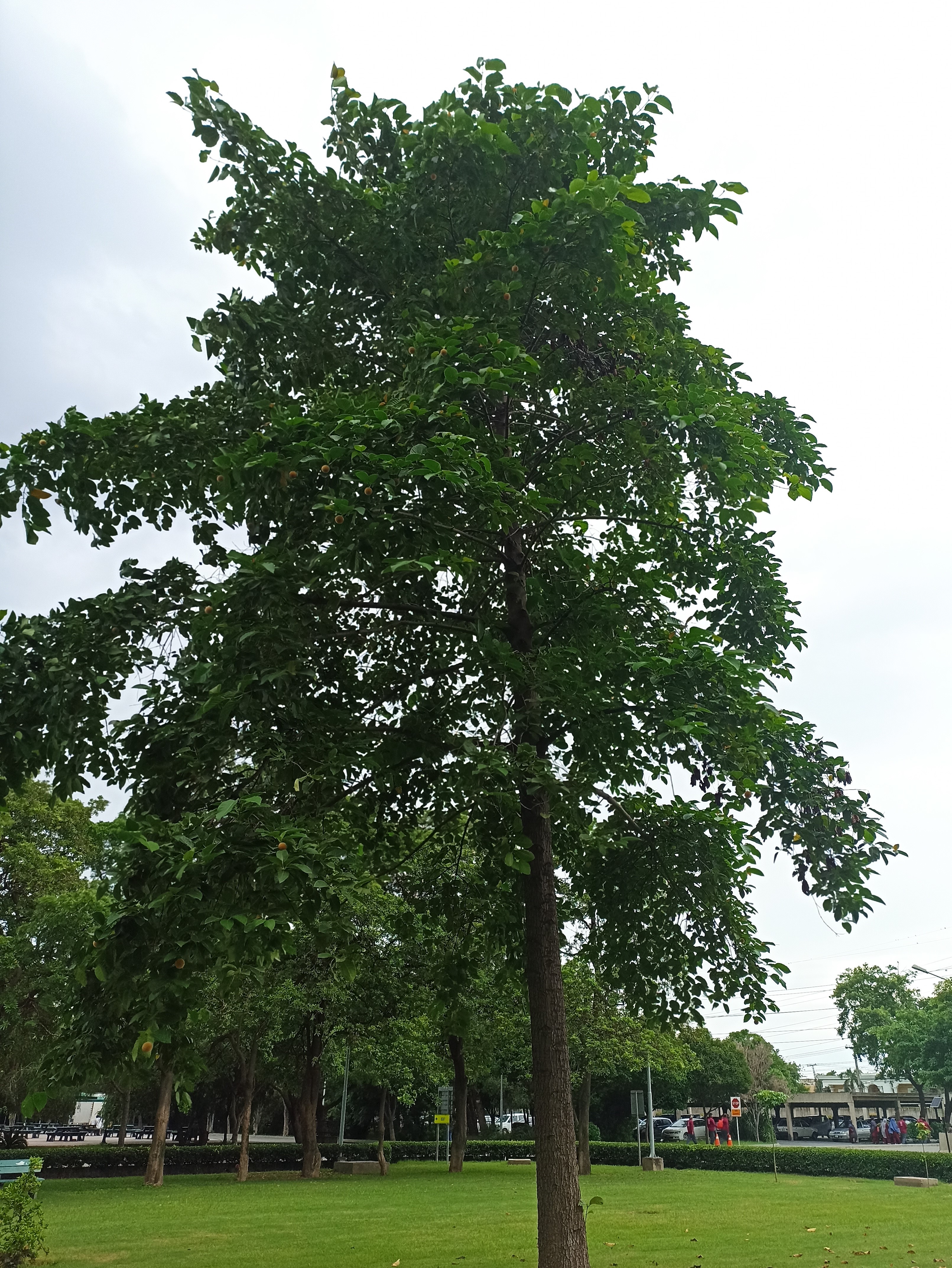
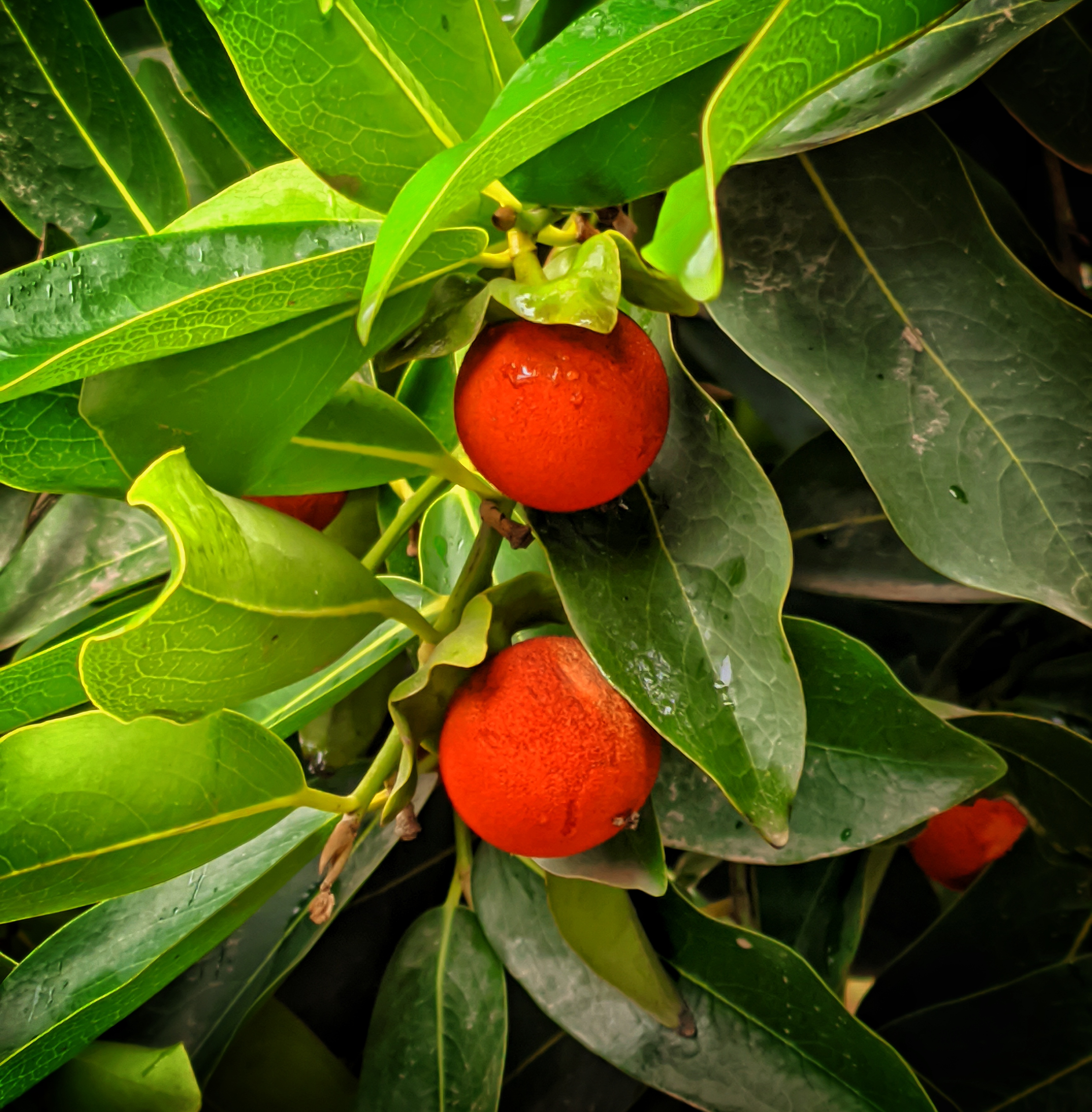
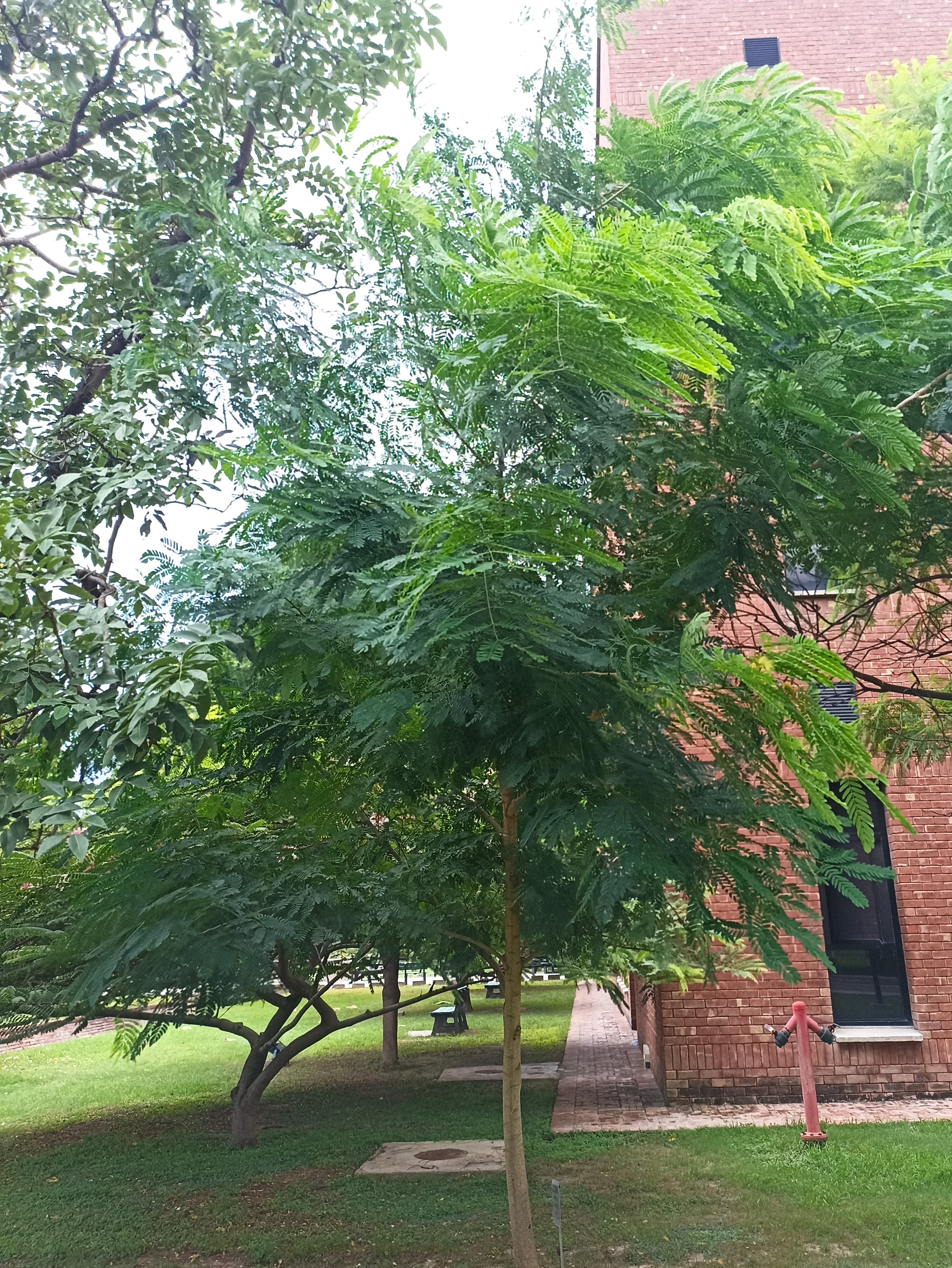
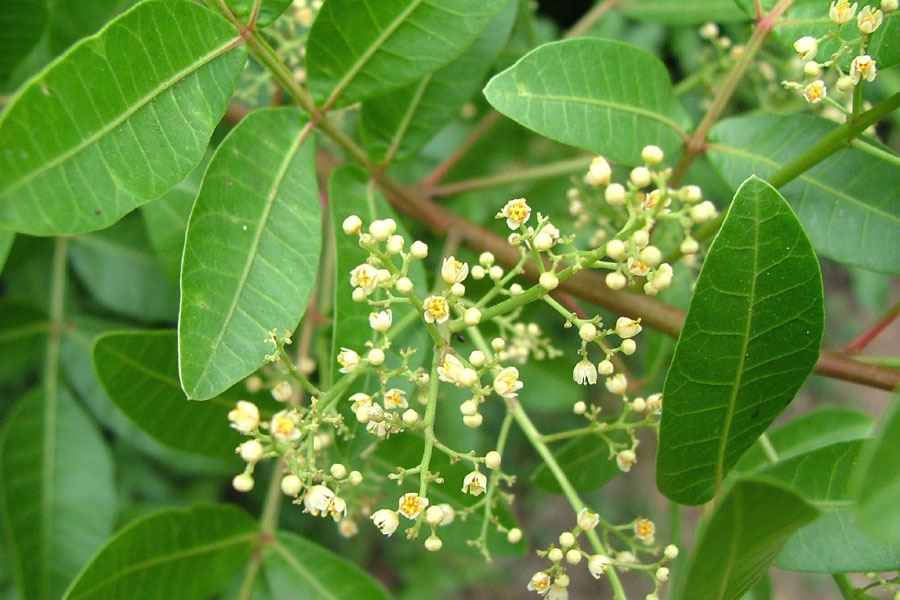
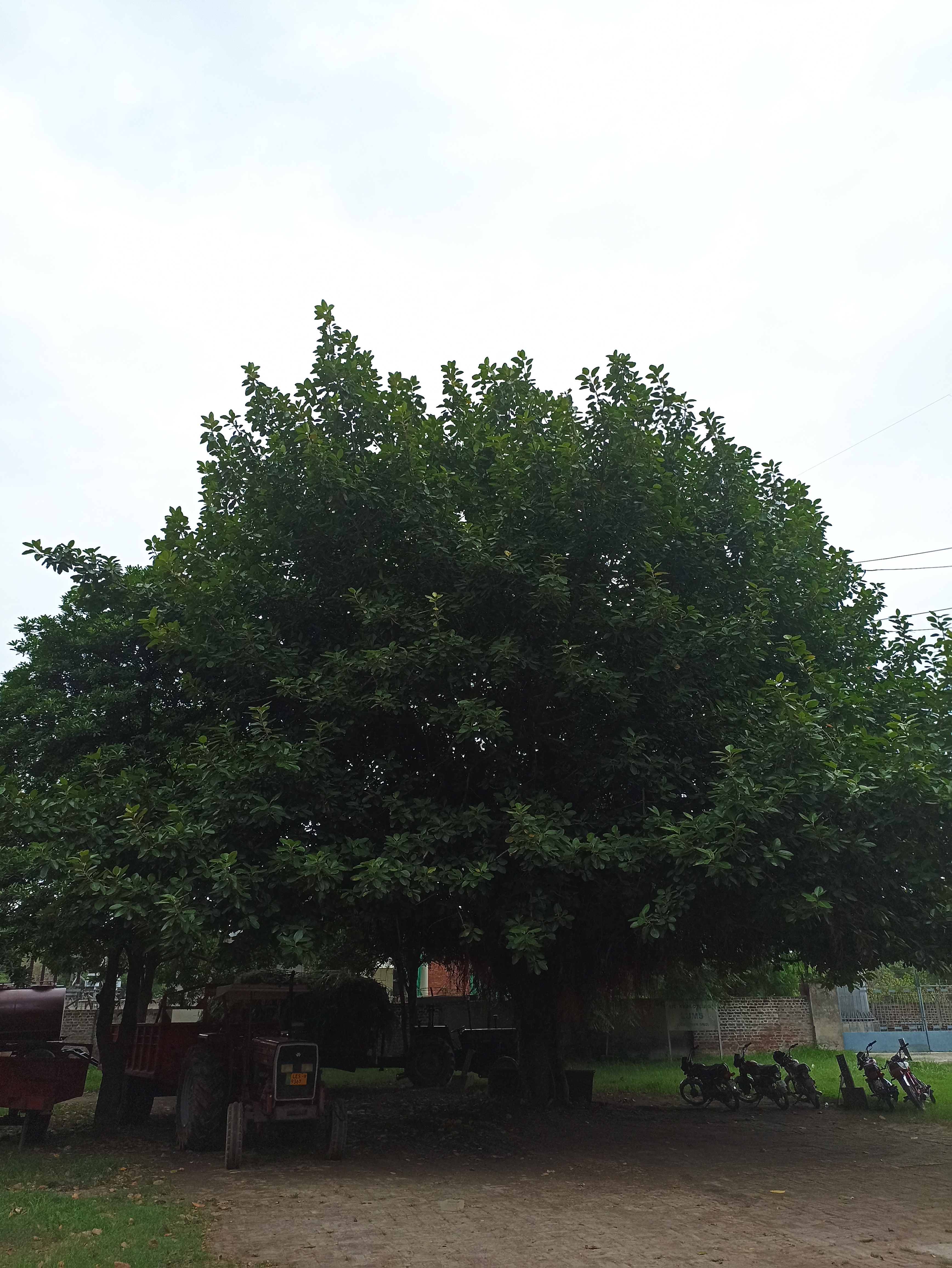
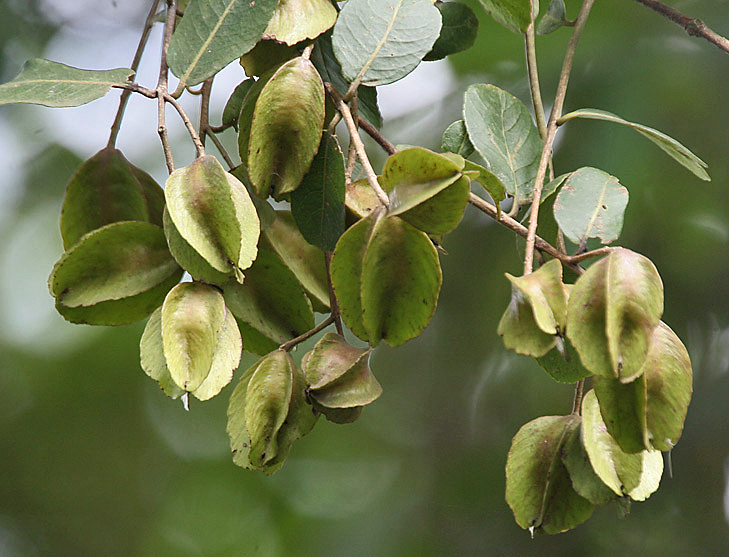
A tall deciduous tree up to 40 m in height, with horizontally spread branches. The bark is ash coloured or silvery grey, leaves large and digitate with lanceolate leaflets. The flowers are bright crimson or yellow to orange, bunched at the tip of branches, the fruits oblong-ovoid capsules with many seeds.
Parts Used
Seeds, leaves, fruit, roots, flowers and gum exuded by the stem bark (known as 'mocharus').
Traditional And Modern Use
The gum is used mainly in the treatment of acute dysentery, haemoptysis of pulmonary tuberculosis, influenza and menorrhagia. It acts as an astringent, diuretic, expectorant, tonic, emetic, stimulant, alterative, antiinflammatory, styptic and demulcent. It has also been used in bladder disorders, calculus, catarrh, cystitis, gonorrhoea and skin troubles such as sores and wounds. The seeds are used in chicken pox, gonorrhoea, chronic cystitis and catarrhal affections.
Ethnoveterinary Usage
Applied to wounds and sores.
Major Chemical Constituents
Tannins
The gum contains 8.9% mineral matter and a large proportion of catechol tannin, along with tannic, gallic and catechutannic acids.
Aminoacids
The gum yielded DL-valine and indicamine.
Fatty Acids
The seeds contain linoleic acid, myristic acid, oleic acid, palmitic acid and stearic acid.
Iridoids Aucubin was isolated from the gum.
Medicinal And Pharmacological Activities
Oxytocic activity: An aqueous extract of seeds exhibits oxytocic action on rat uteri and guinea pig and rabbit uterine strips. Cardiac activity: An aqueous extract of the seeds acts as a direct and indirect stimulant to the frog heart in situ.
Safety Proftle
The maximum tolerated doses of the stem bark and flowers are 50 and 250 mg/kg body weight (IP in adult albino rats).