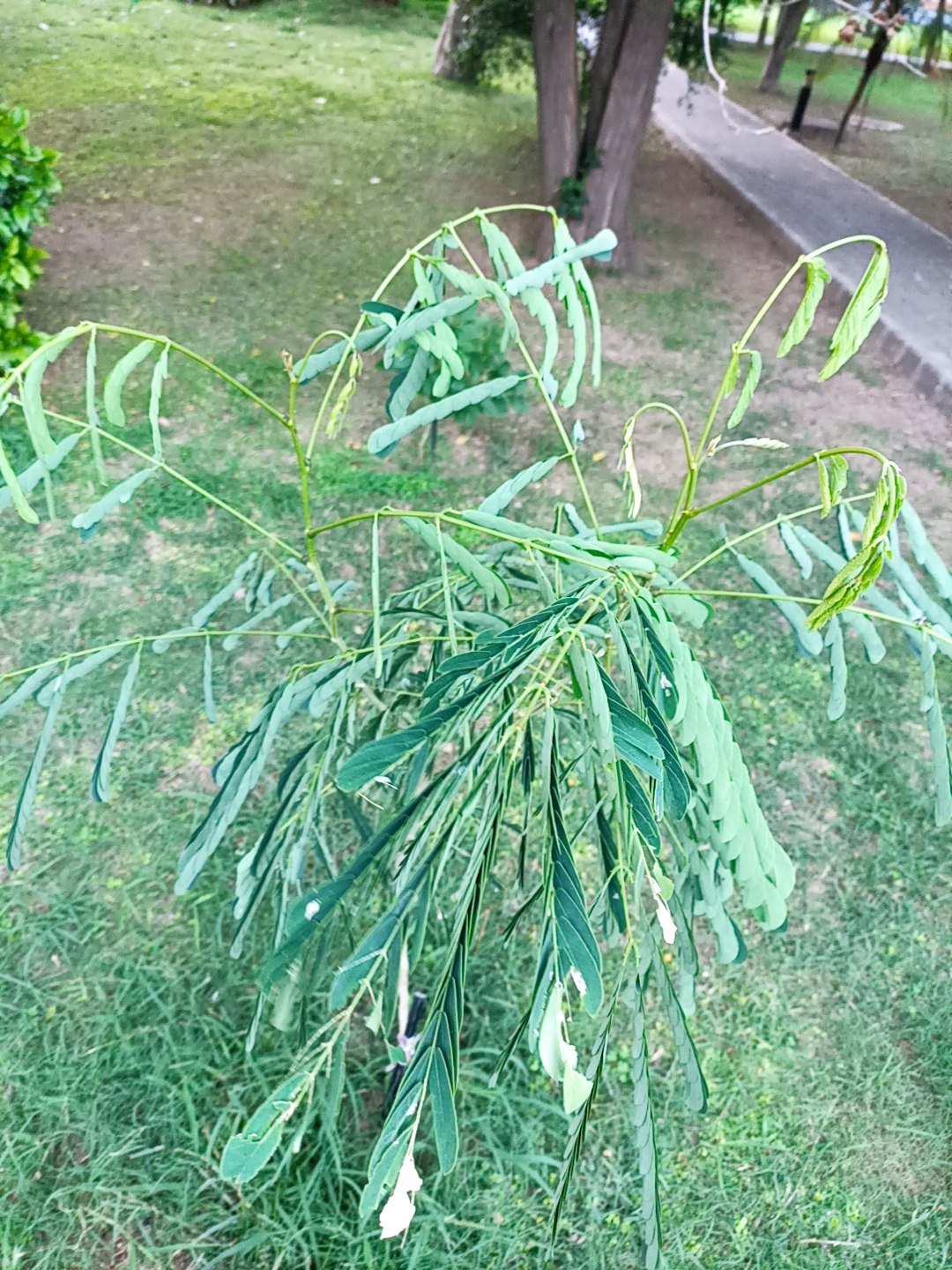
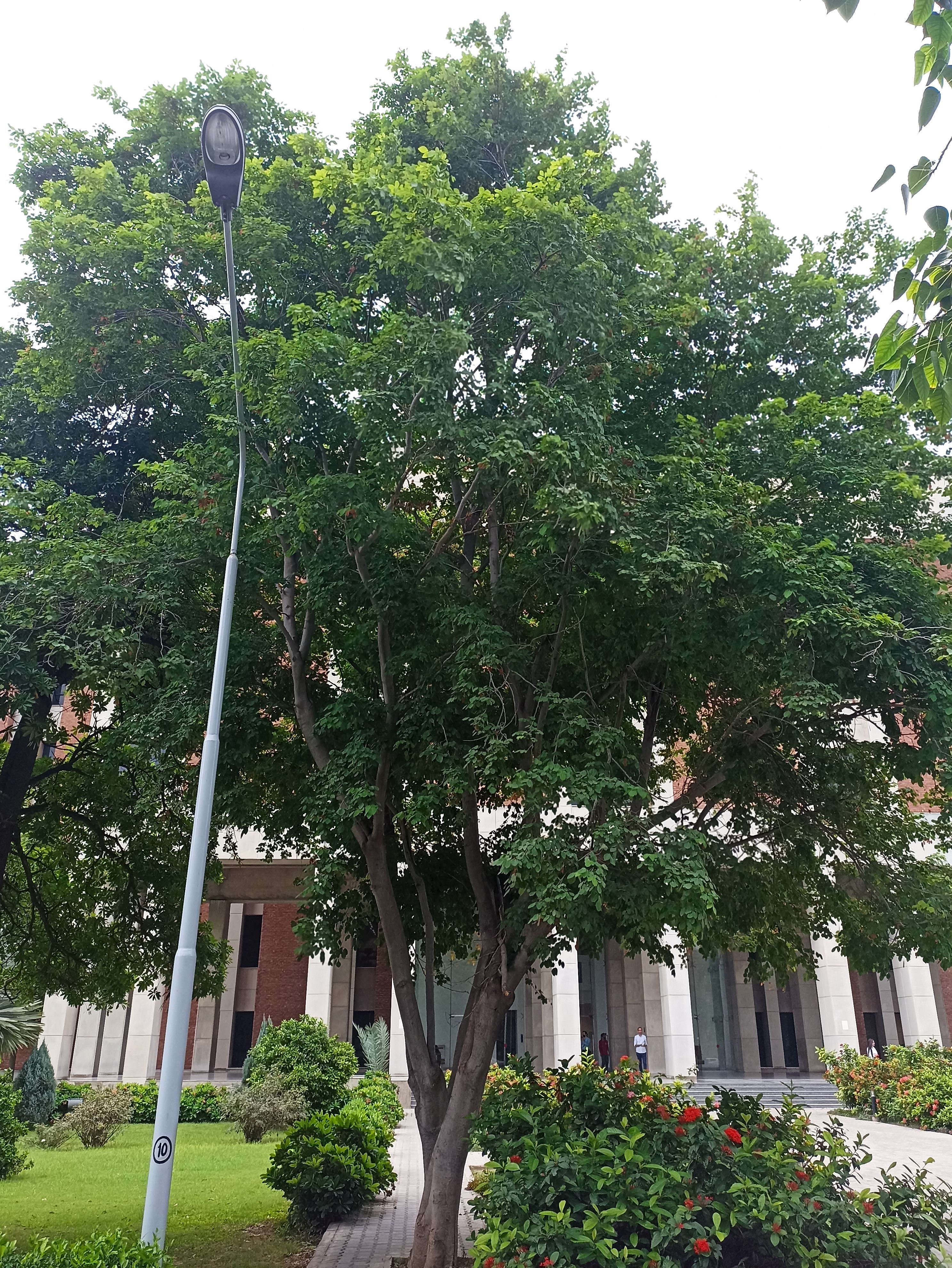
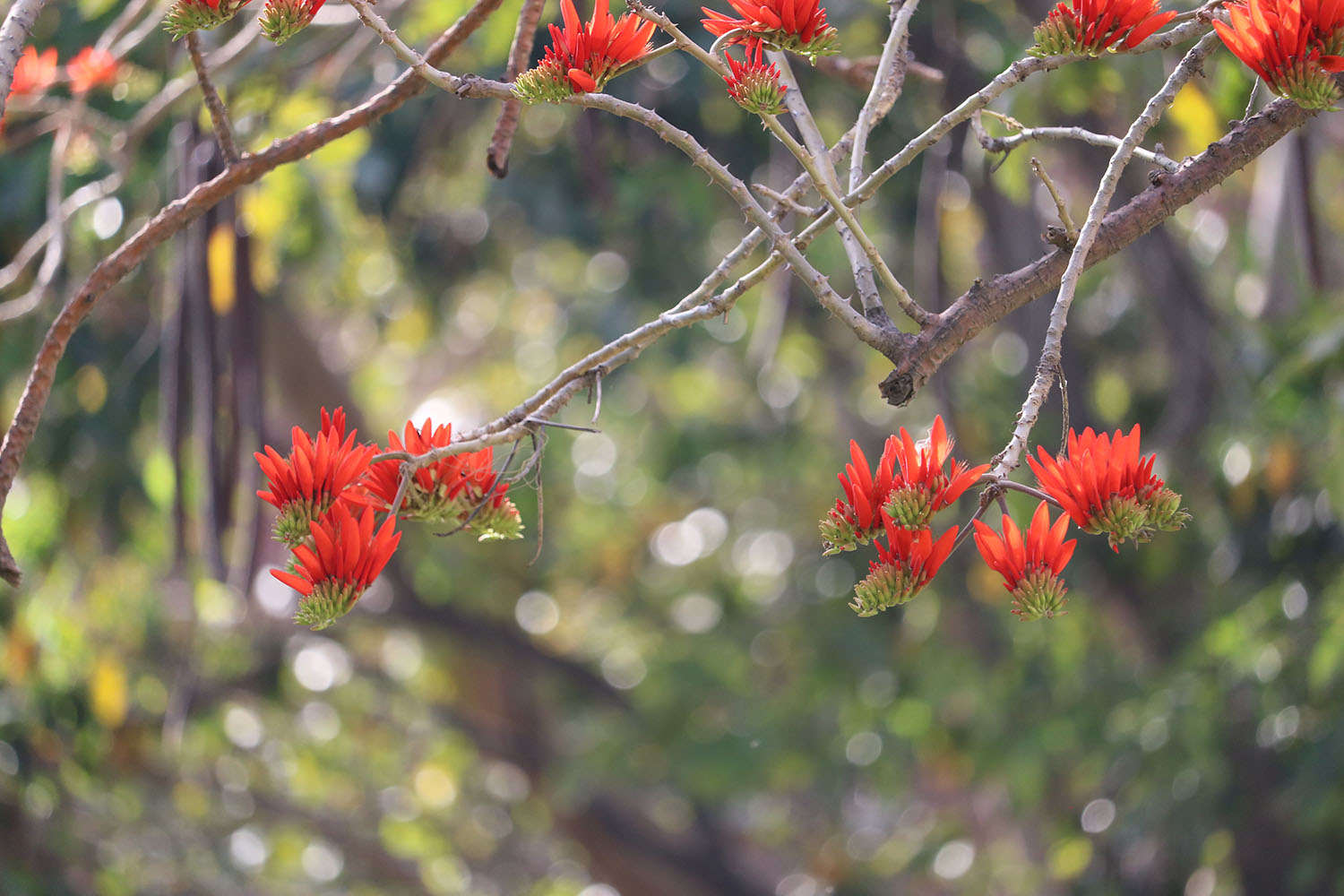
Albizia julibrissin
Species
Families
Local Names
Genus
Native/Introduced
DNA Barcode
Description
Albizia julibrissin, the Persian silk tree or pink silk tree, is a species of tree in the family Fabaceae, native to southwestern and eastern Asia.
The genus is named after the Italian nobleman Filippo degli Albizzi, who introduced it to Europe in the mid-18th century. It is sometimes incorrectly spelled Albizzia. The specific epithet julibrissin is a corruption of the Persian word gul-i abrisham, which means "silk flower" (from"flower" + abrisham"silk").
Albizia julibrissin was described by Antonio Durazzini. John Gilbert Baker used the same scientific name to refer to Prain's Albizia kalkora, the Mimosa kalkora of William Roxburgh.
Albizia julibrissin is known by a wide variety of common names, such as Persian silk tree and pink siris. It is also called Lankaran acacia or bastard tamarind, though it is not too closely related to either genus. The species is called Chinese silk tree, silk tree or mimosa in the United States, which is misleading—the former can refer to any species of Albizia which is most common in any one locale; and, although once included in Mimosa, neither is it very close to the Mimoseae. To add to the confusion, several species of Acacia, notably Acacia baileyana and Acacia dealbata, are also known as "mimosa" (especially in floristry), and many Fabaceae trees with highly divided leaves are called thus in horticulture.
Sleeping tree by day and night
Its leaves slowly close during the night and during periods of rain, the leaflets bowing downward; thus its modern Persian name shabkhosb means "night sleeper". This tendency also explains the Chinese common name hehuan, which means "shut happy" and symbolizes a happy couple in bed. In Japan its common names are nemunoki, nemurinoki and nenenoki which all mean "sleeping tree". Nemu tree is a partial translation of nemunoki.
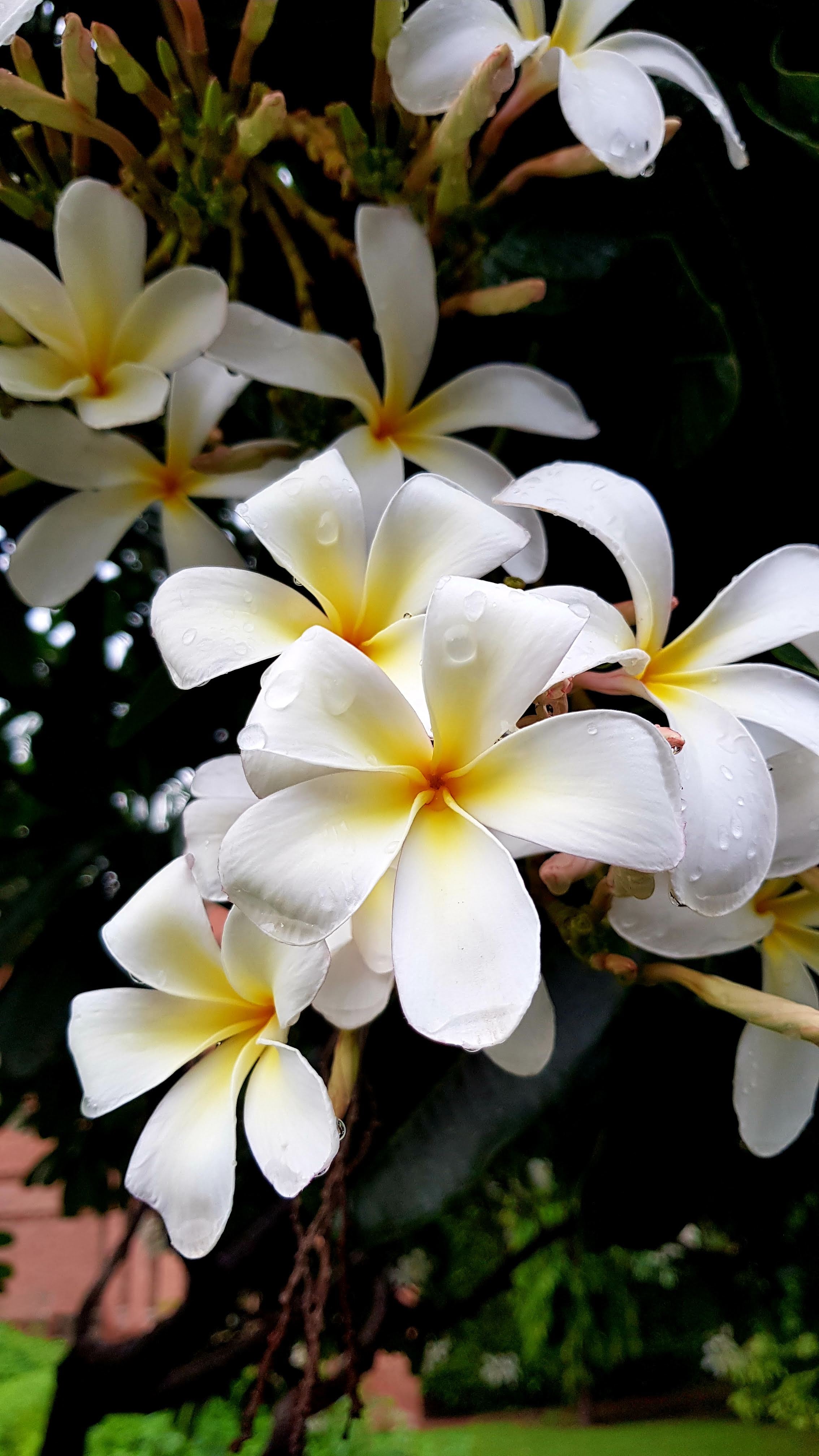
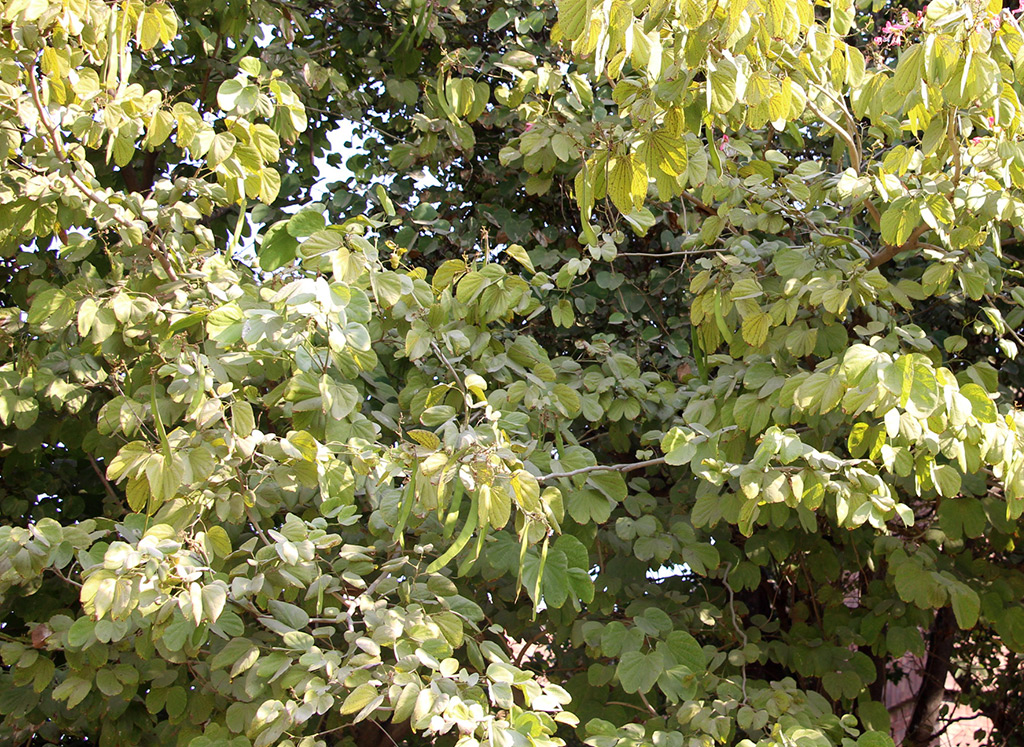
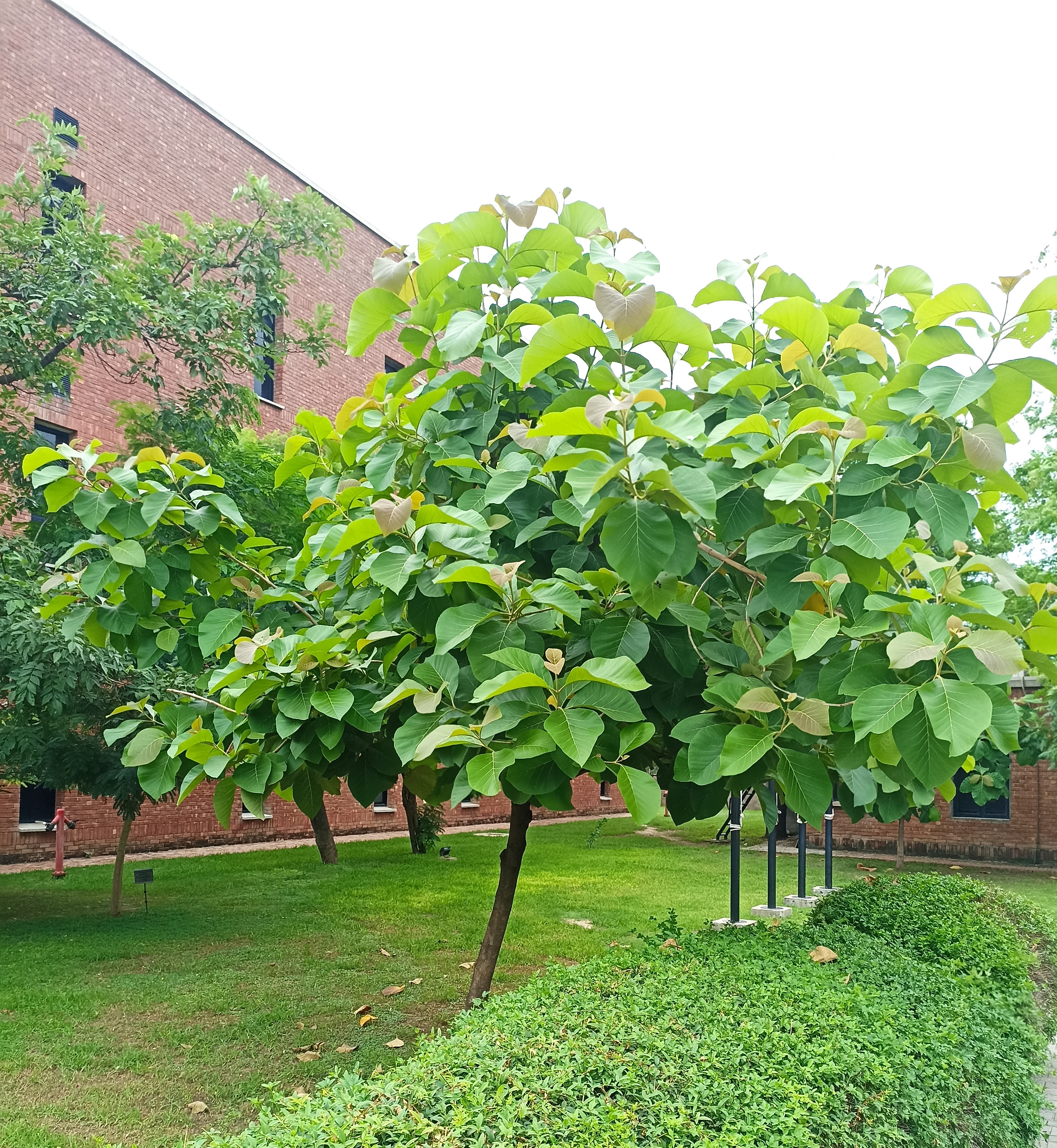
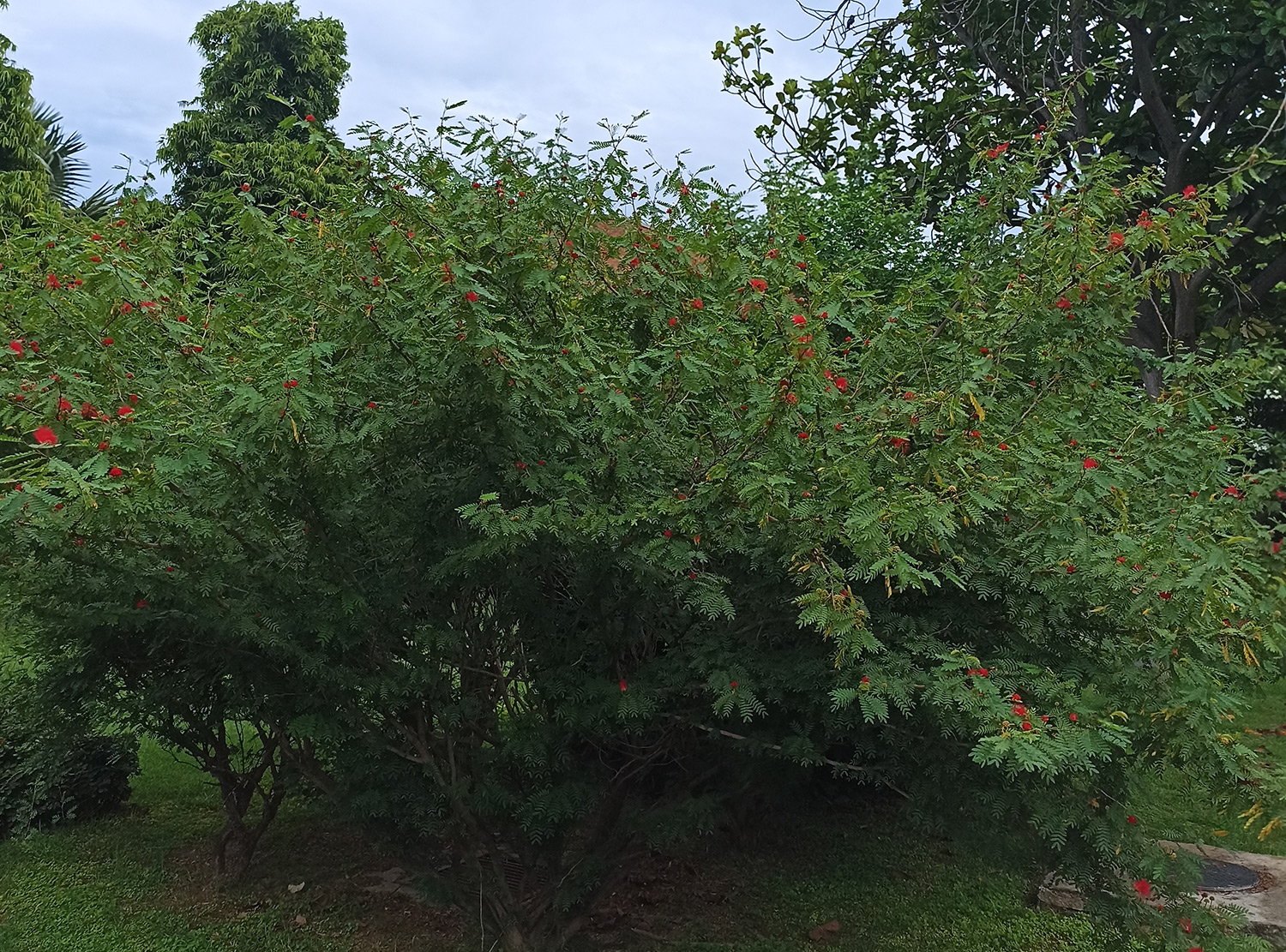
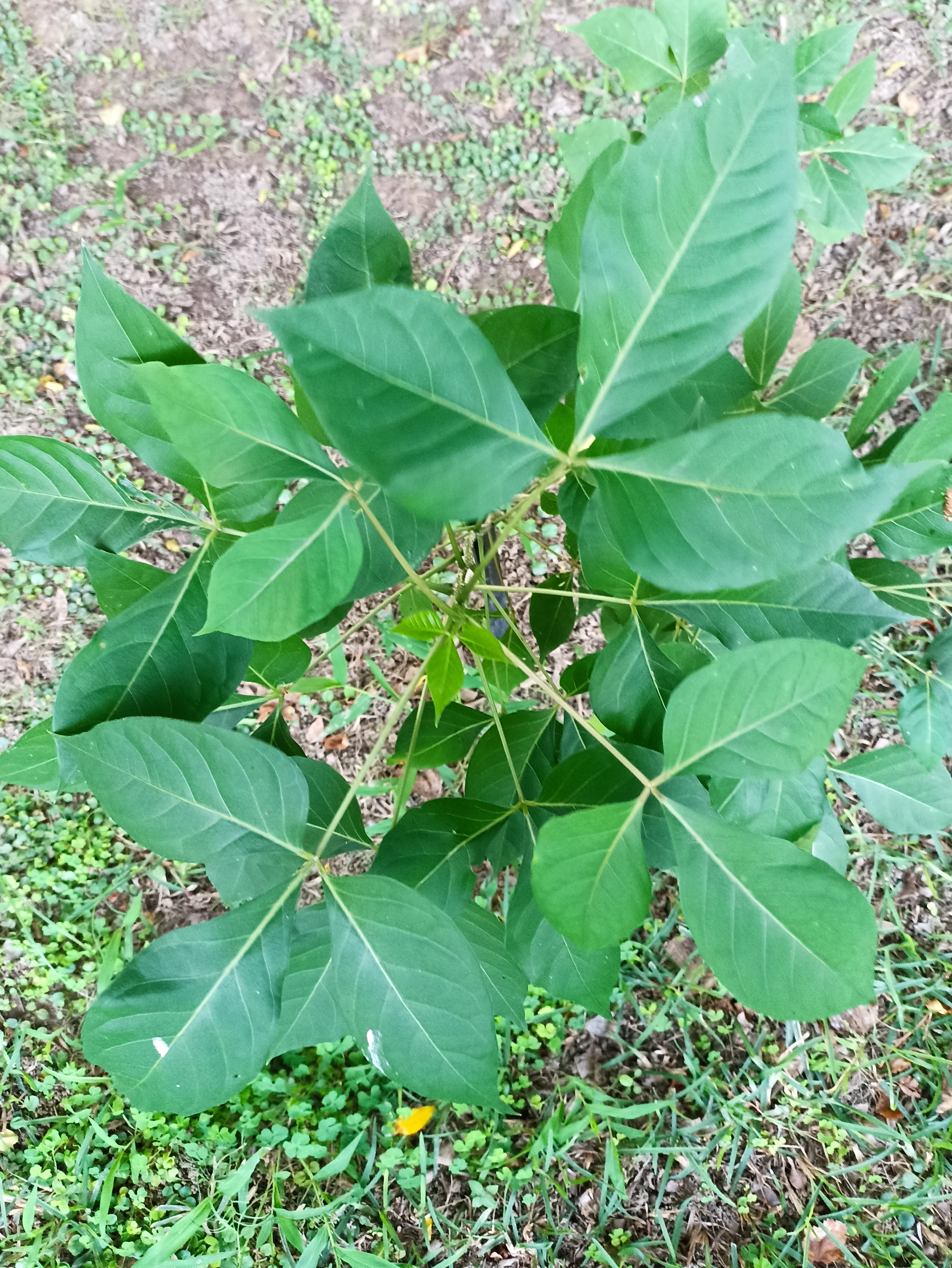
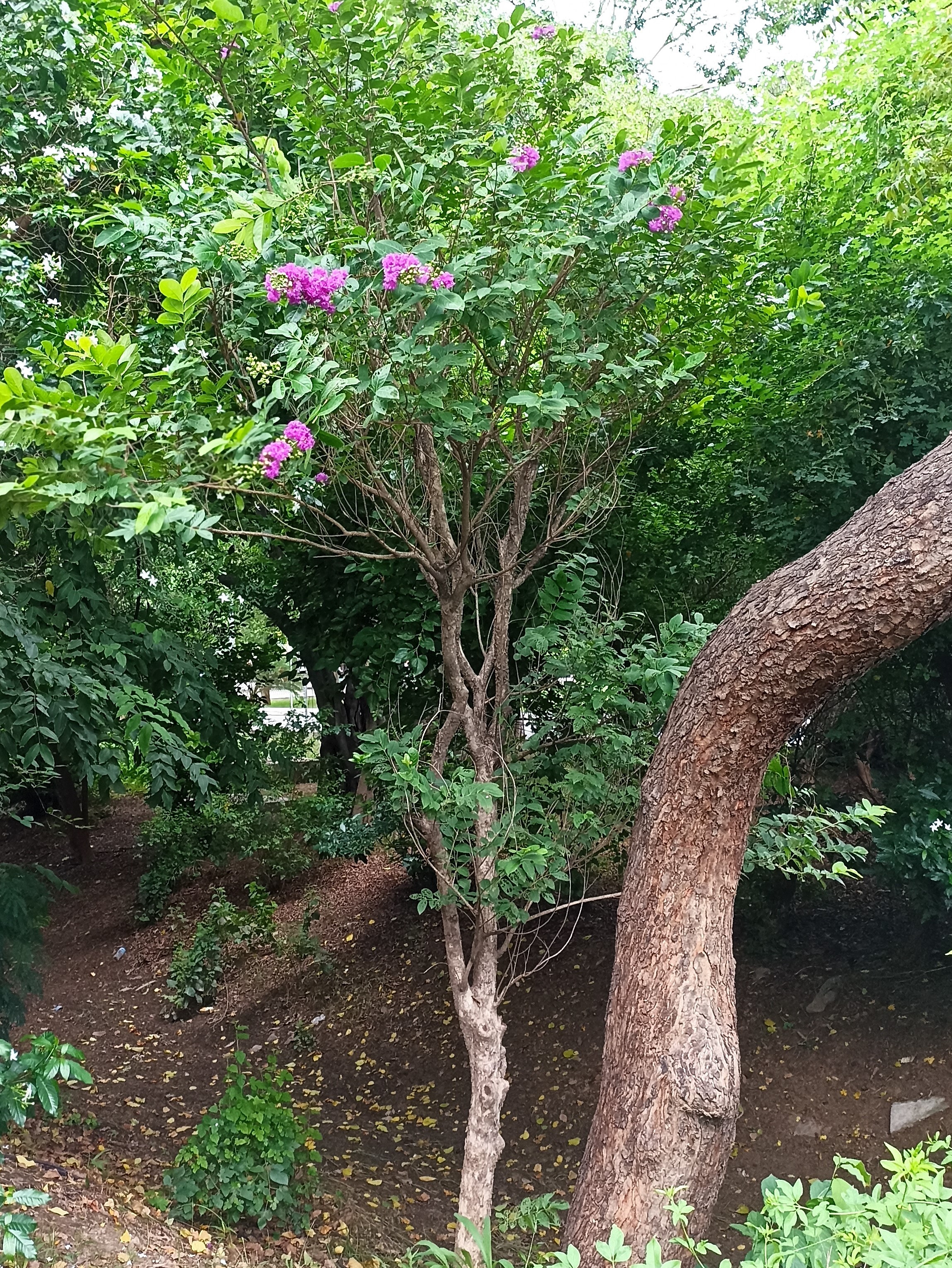
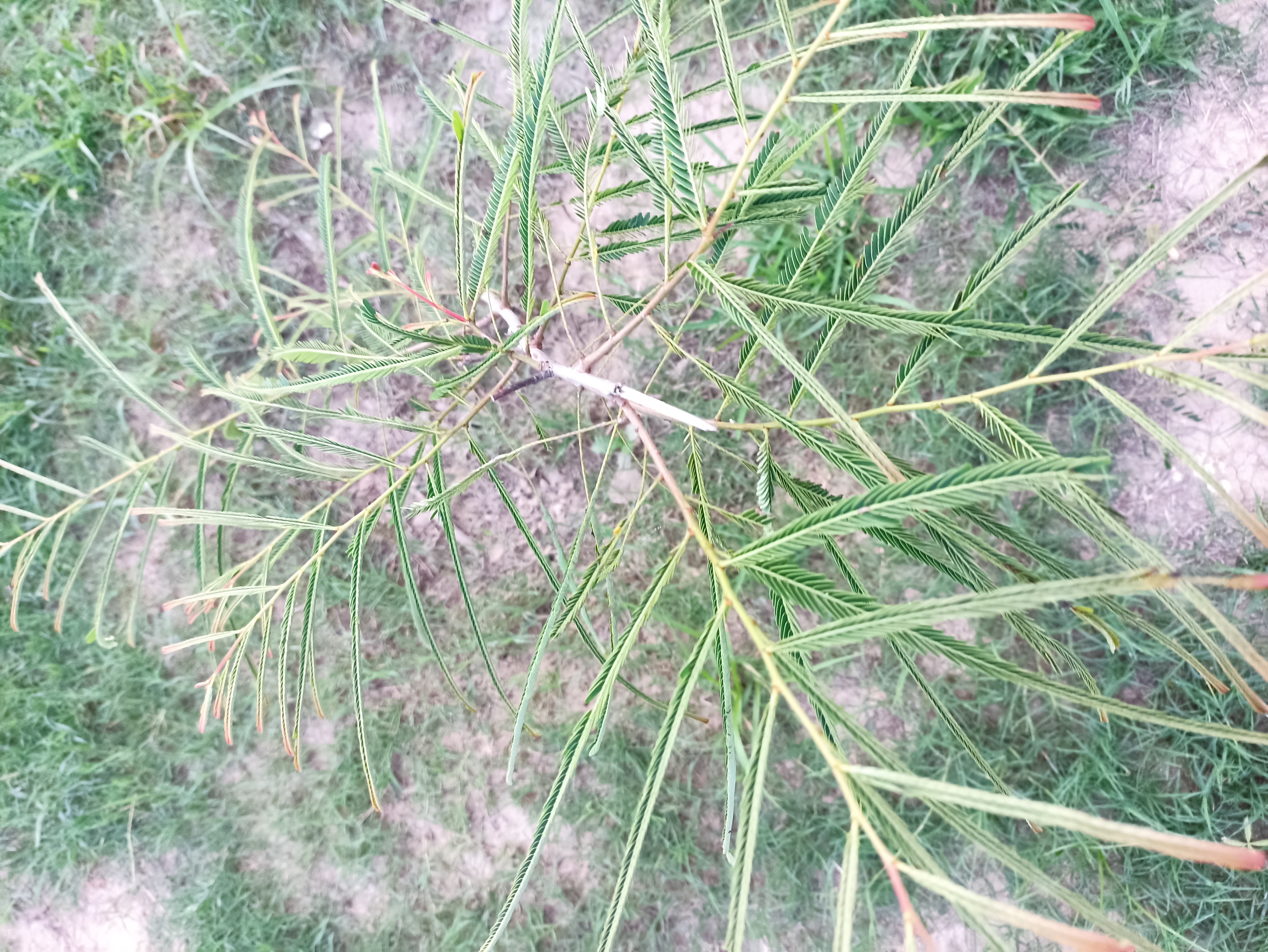
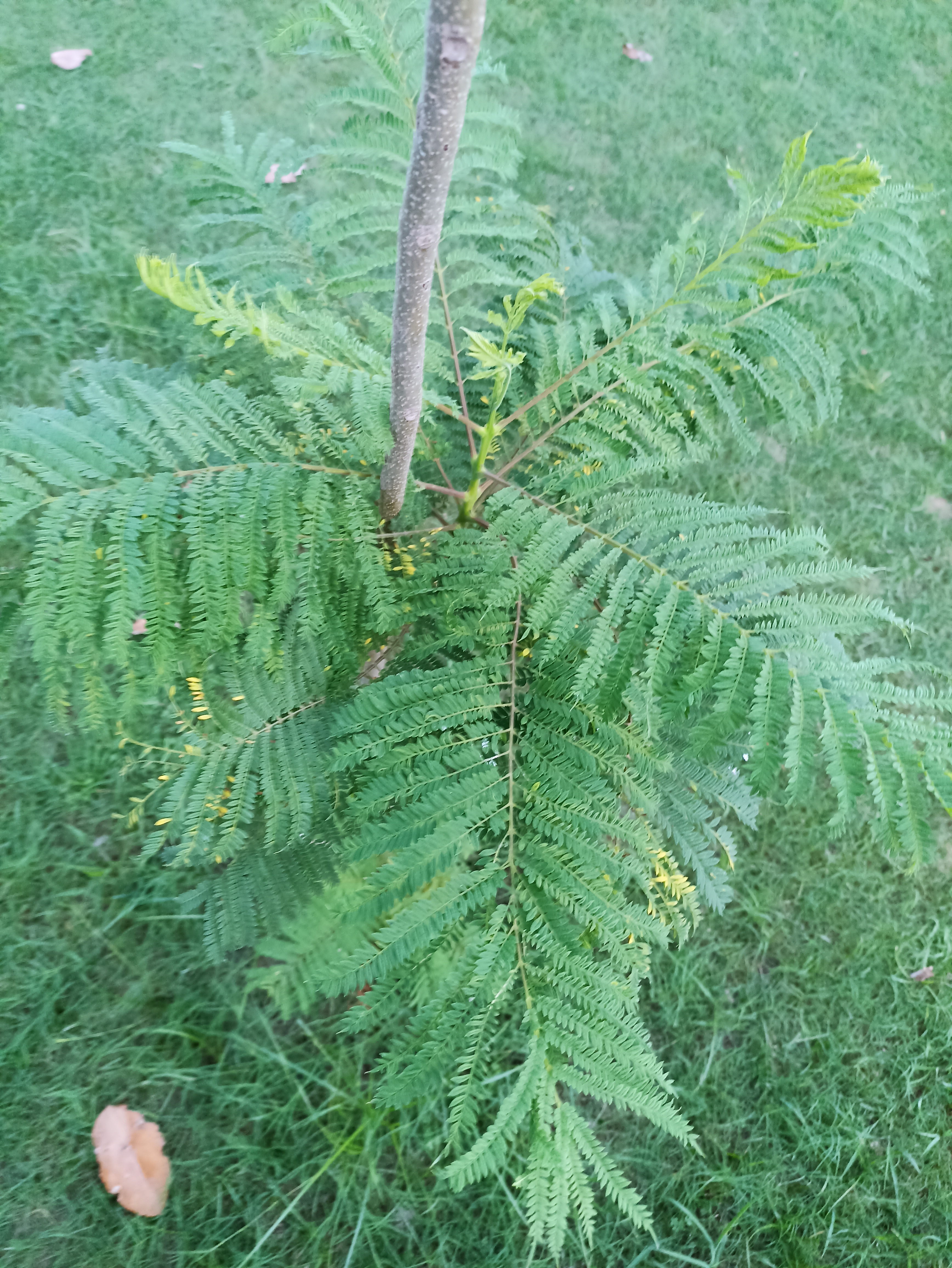
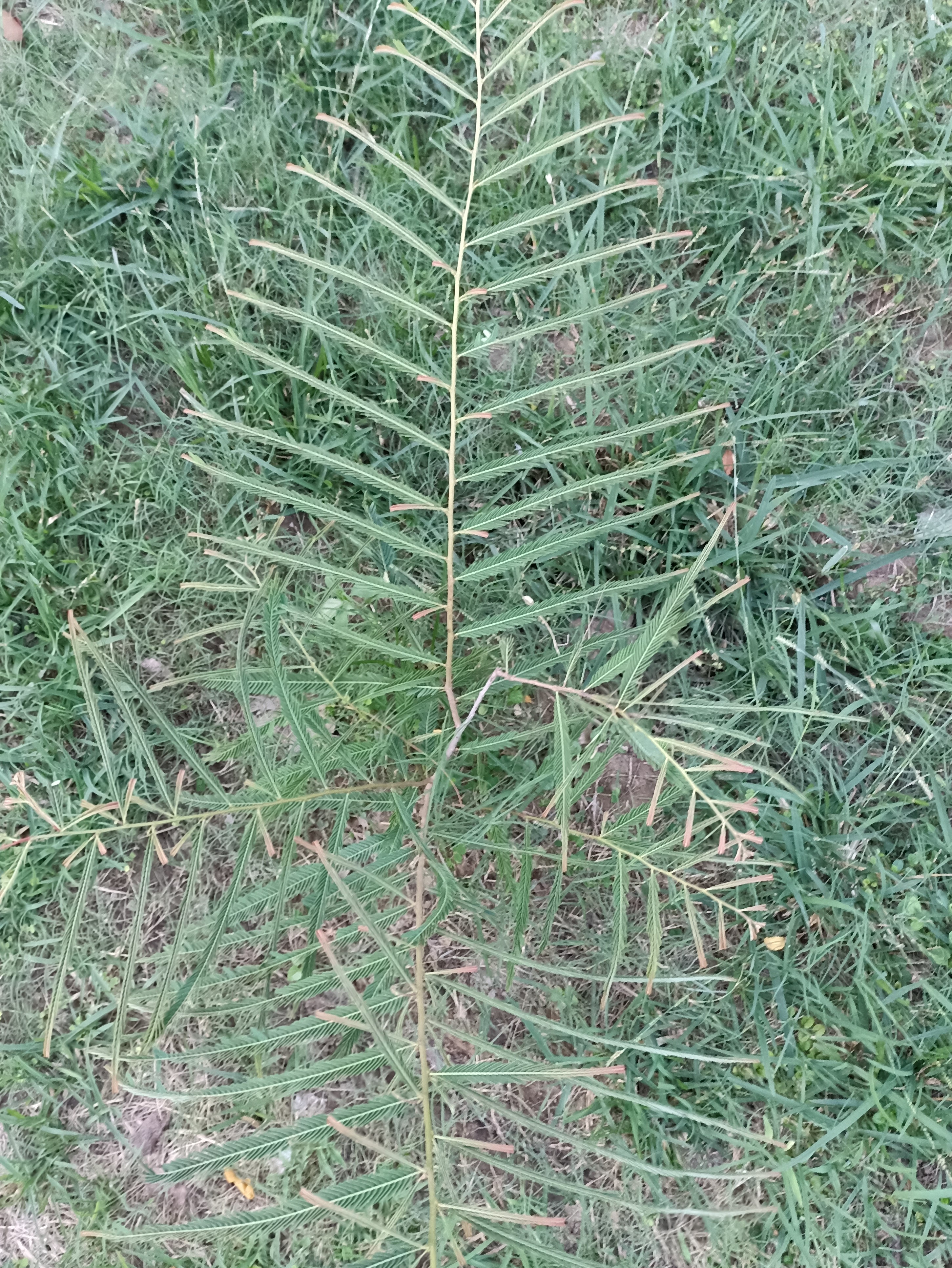
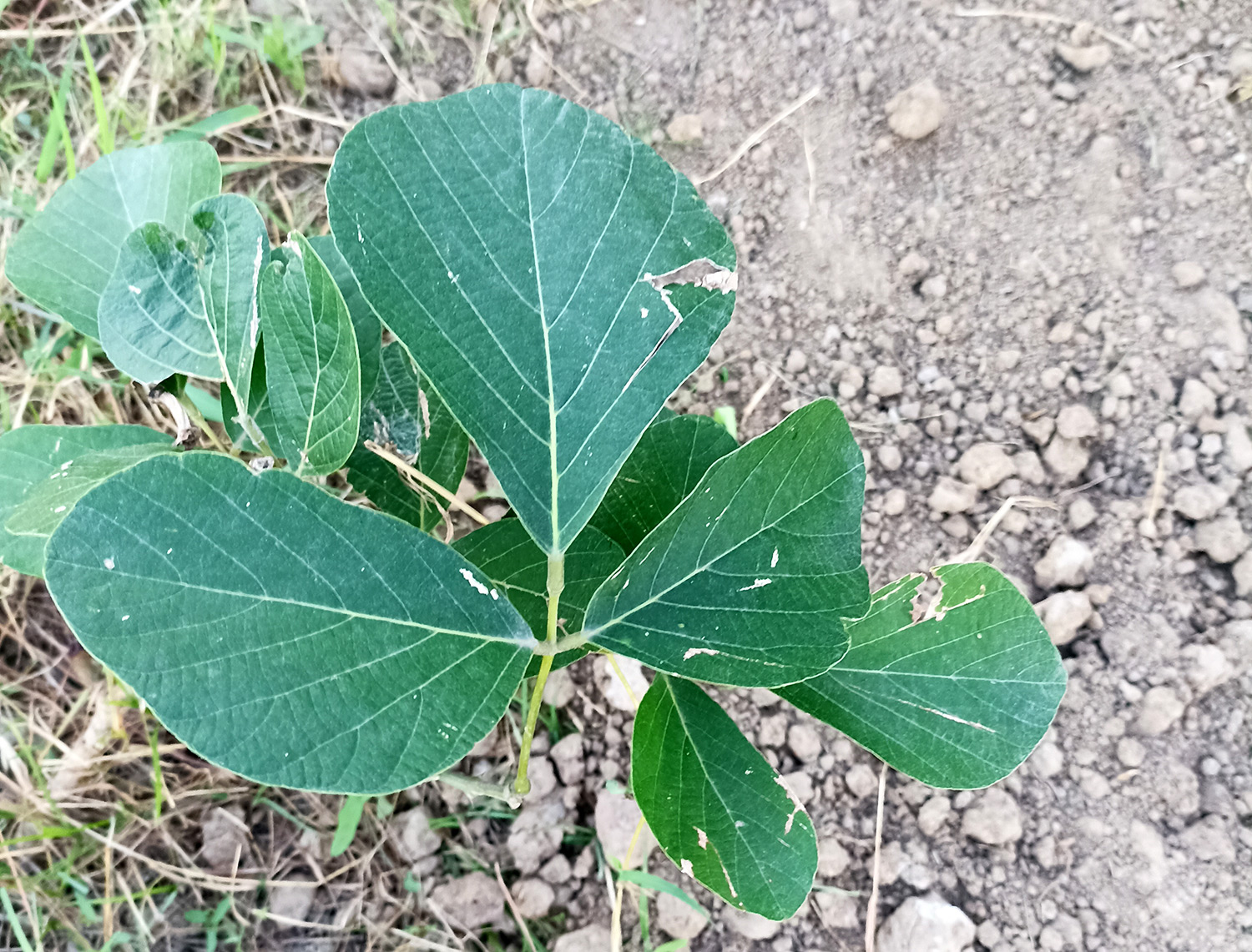
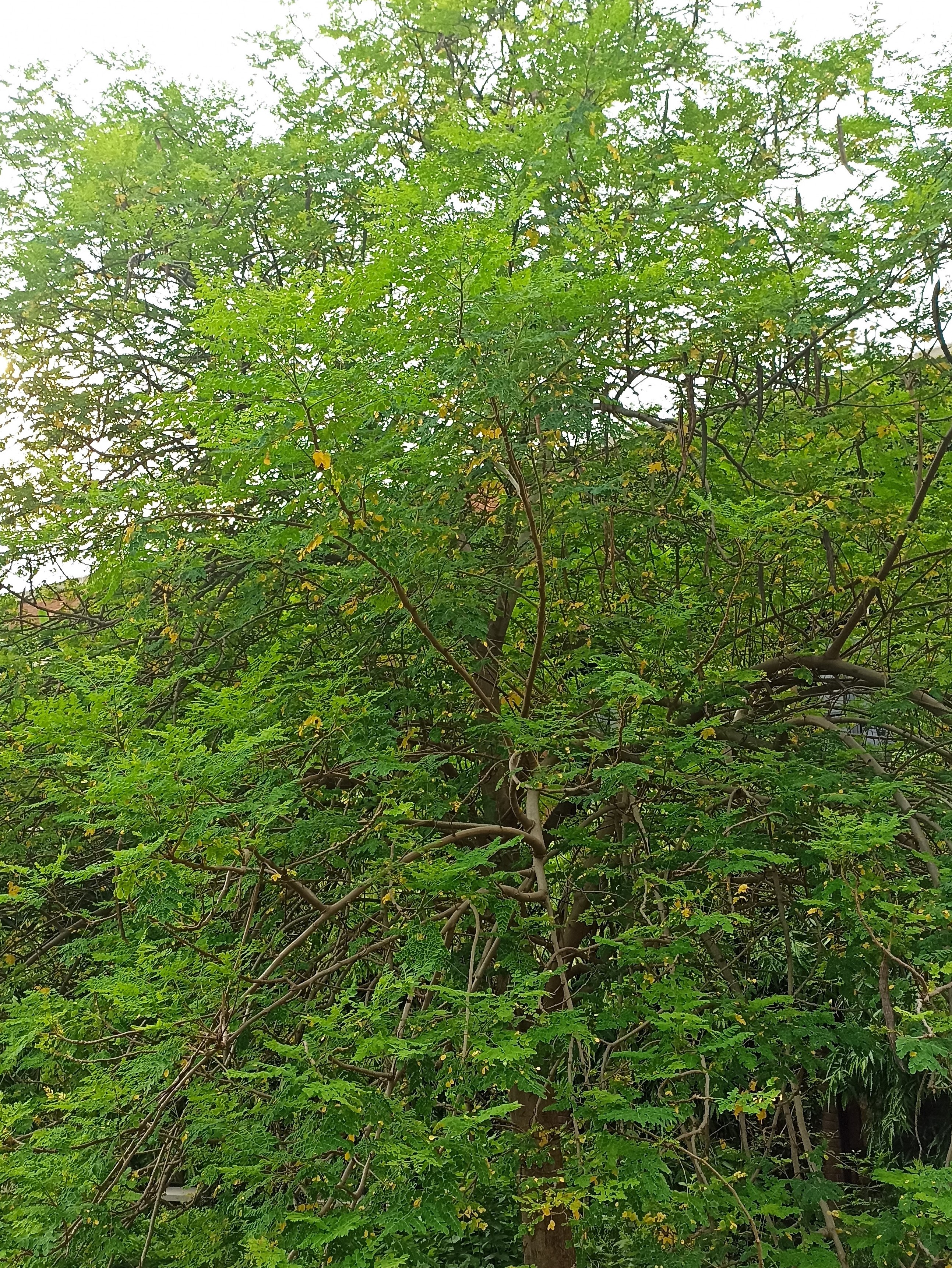
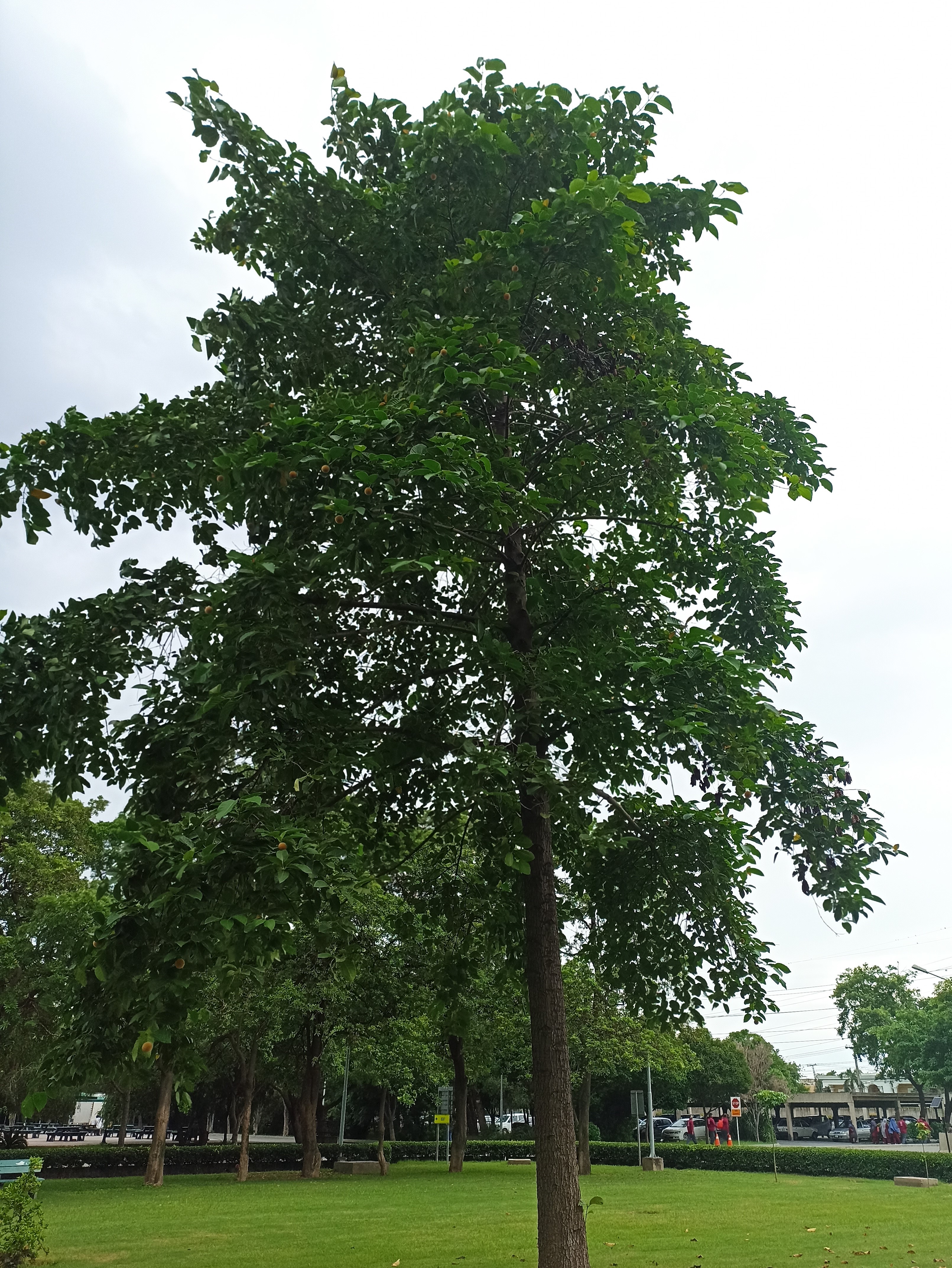
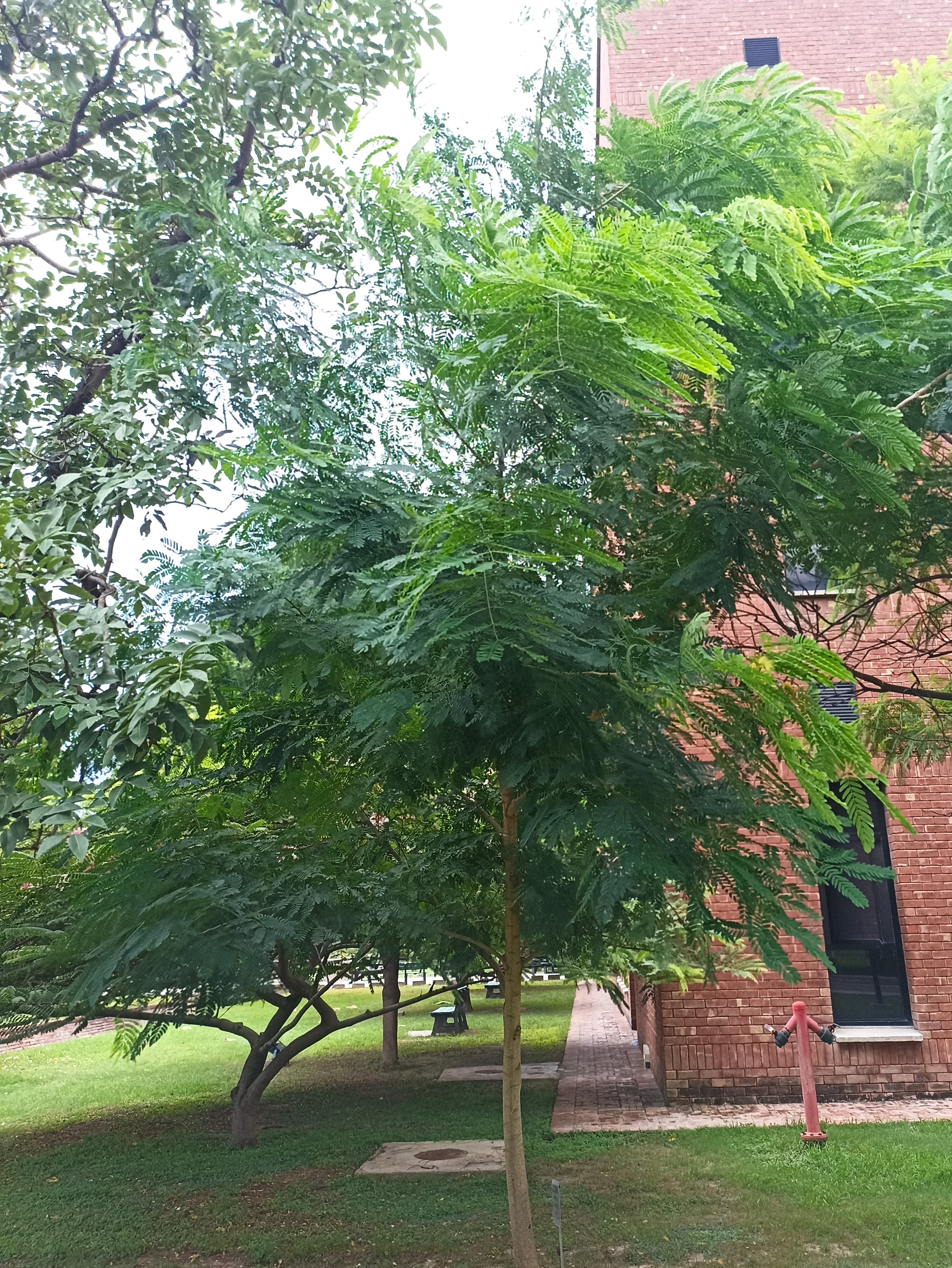
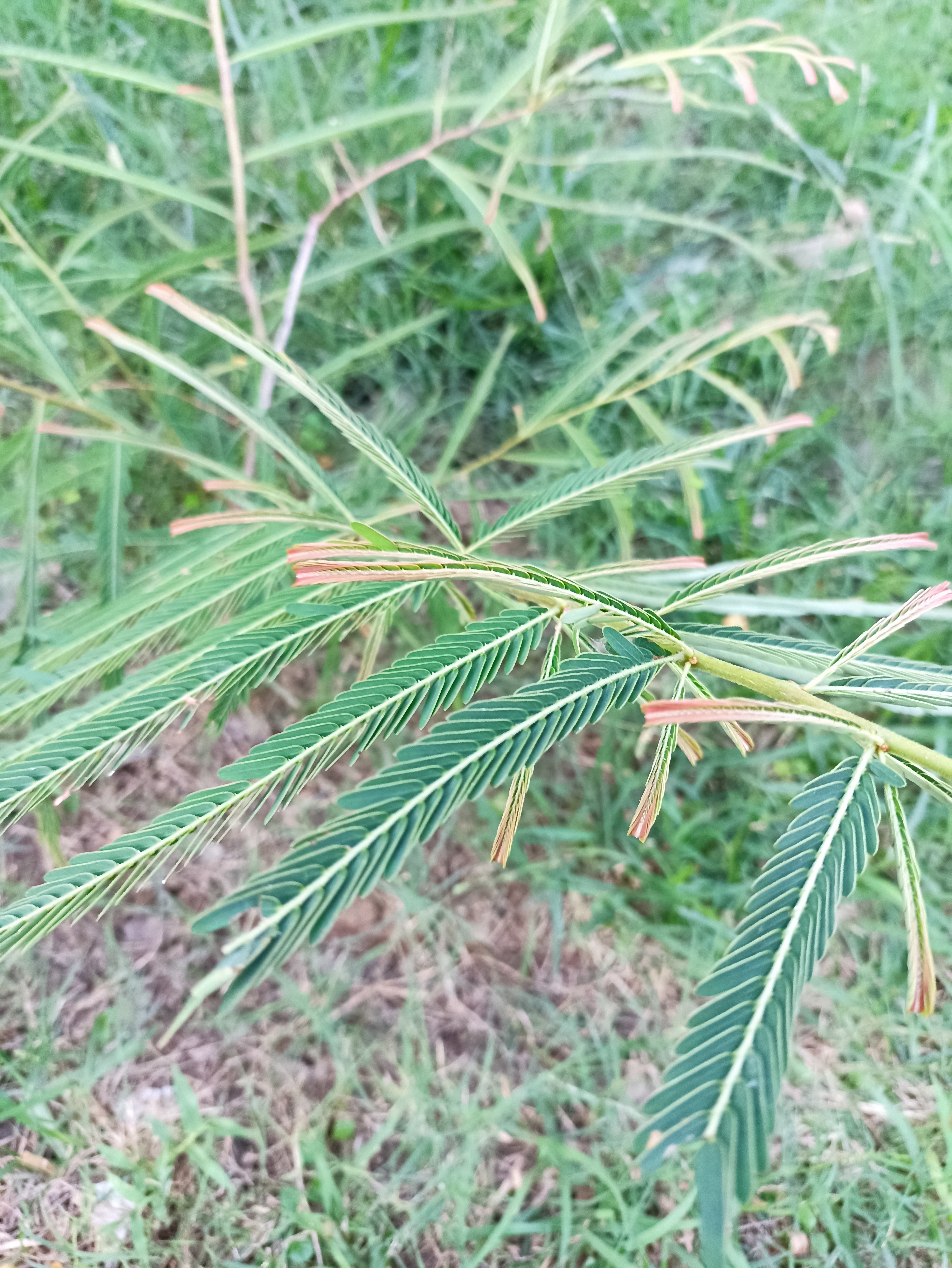
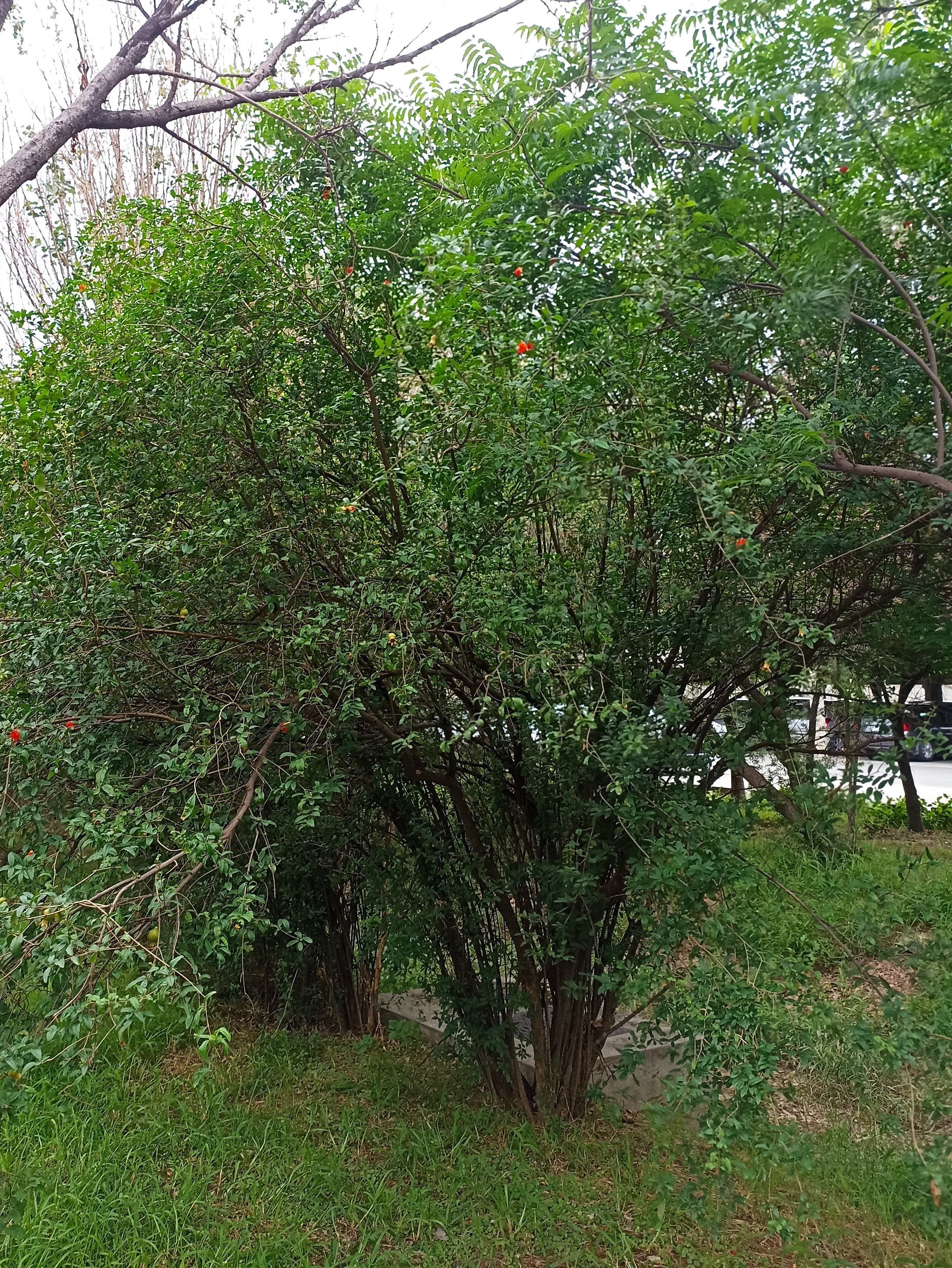
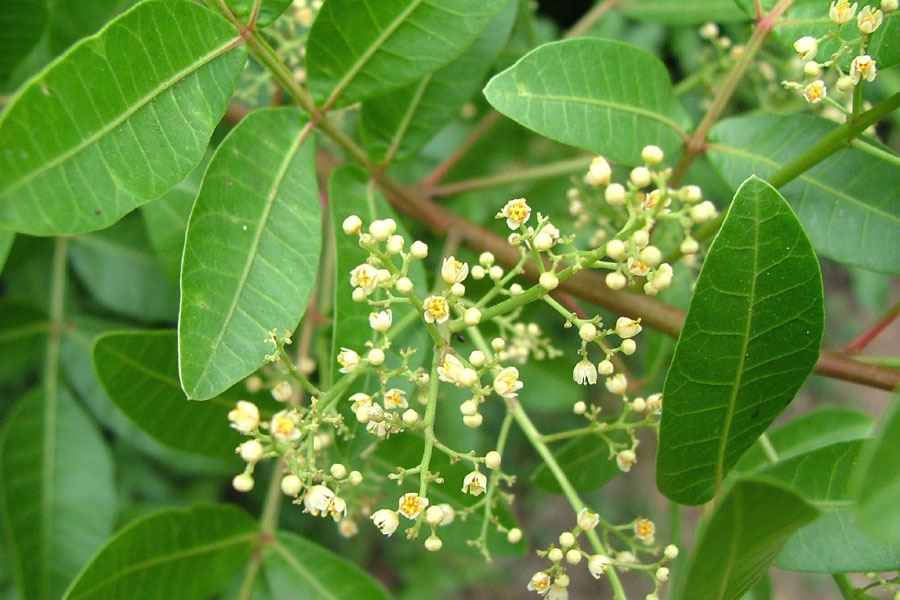
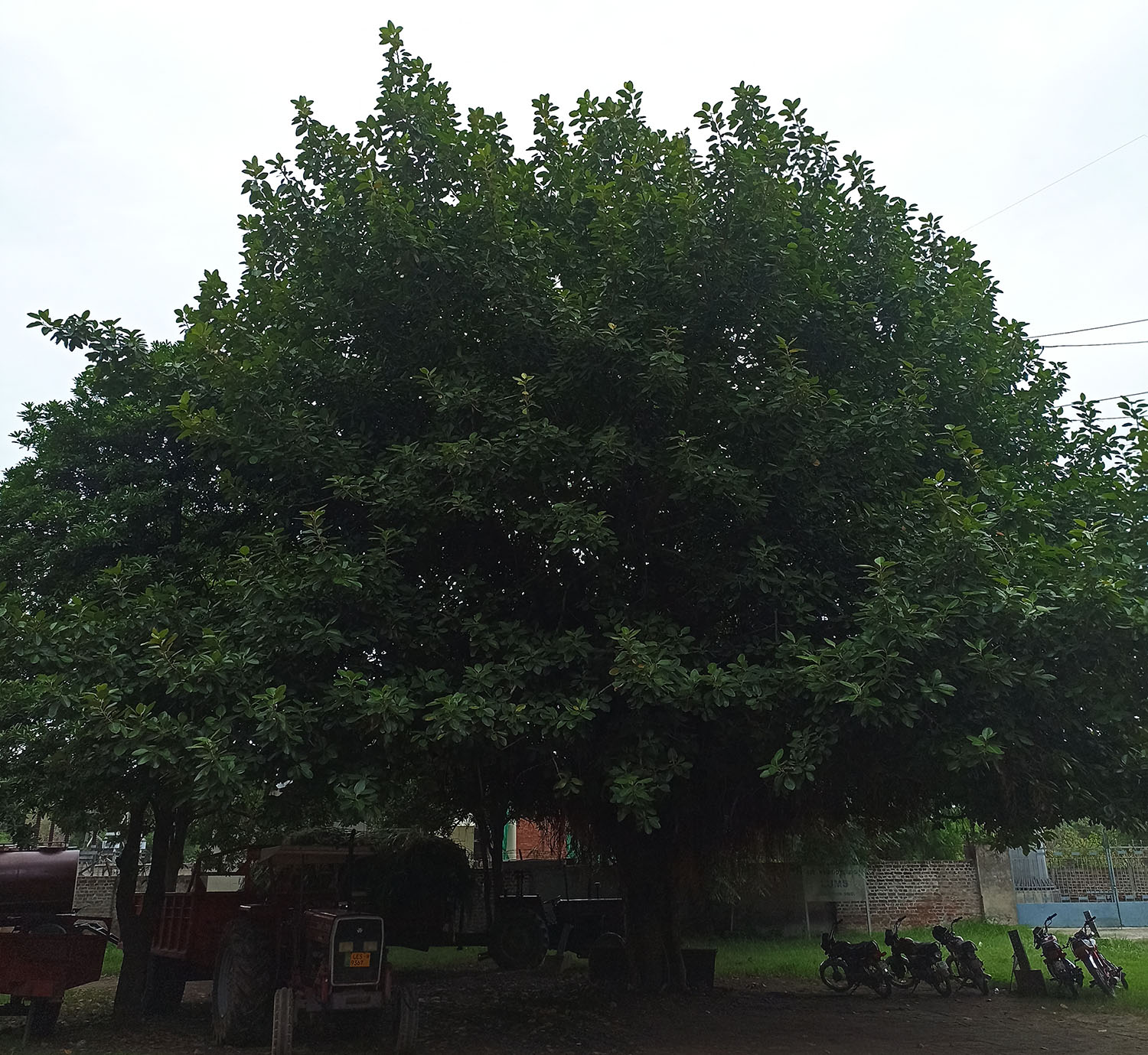
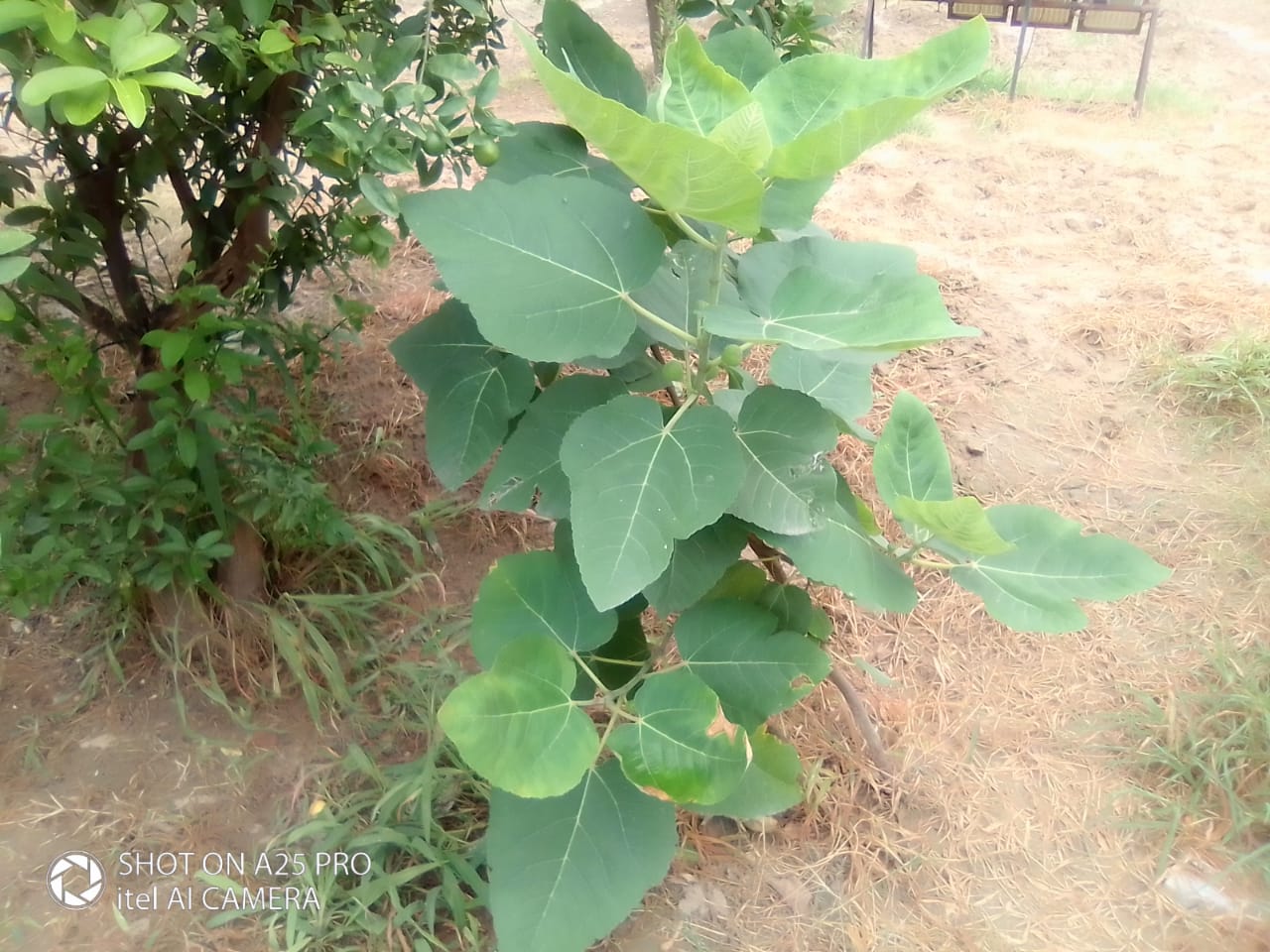
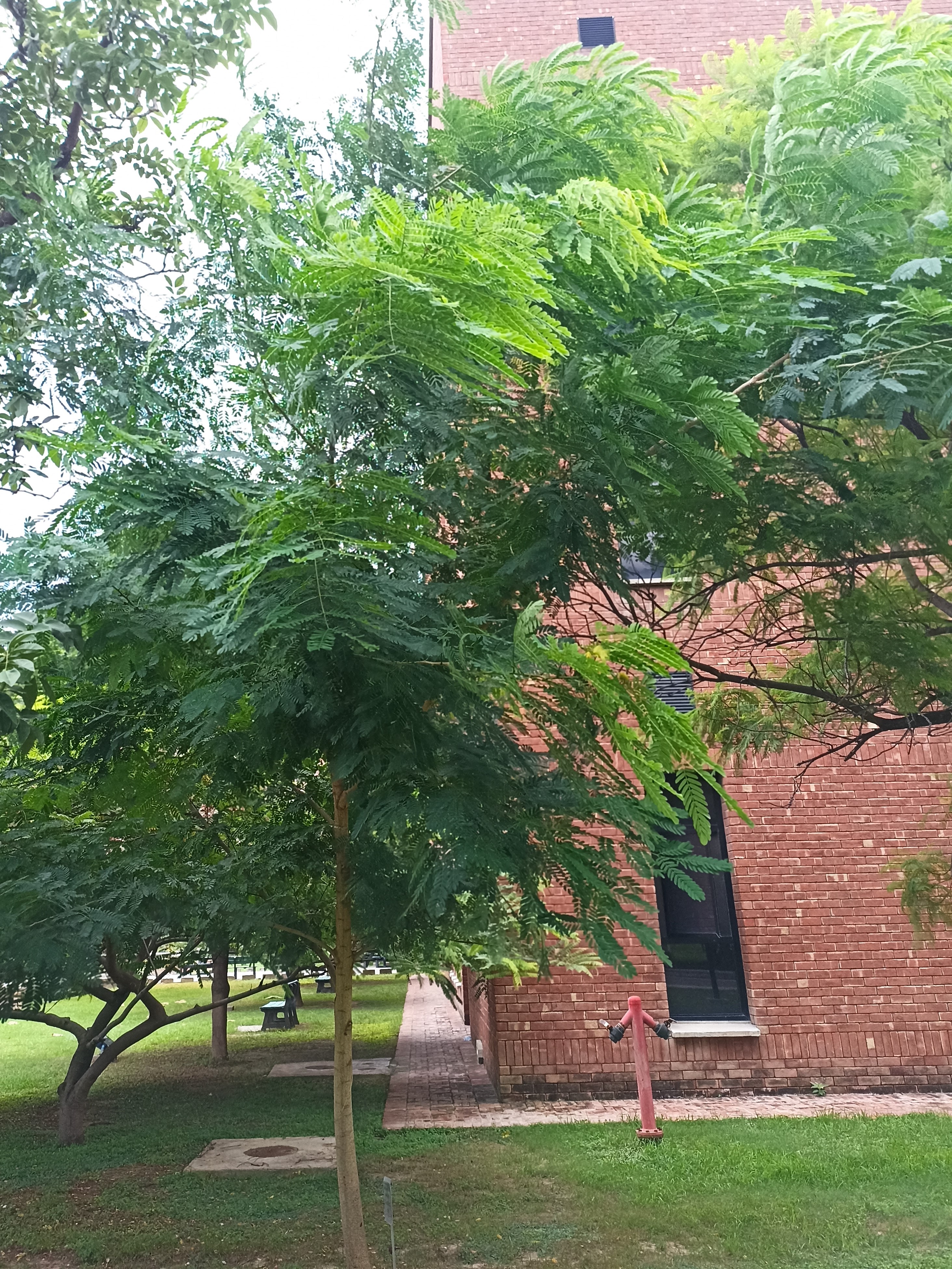
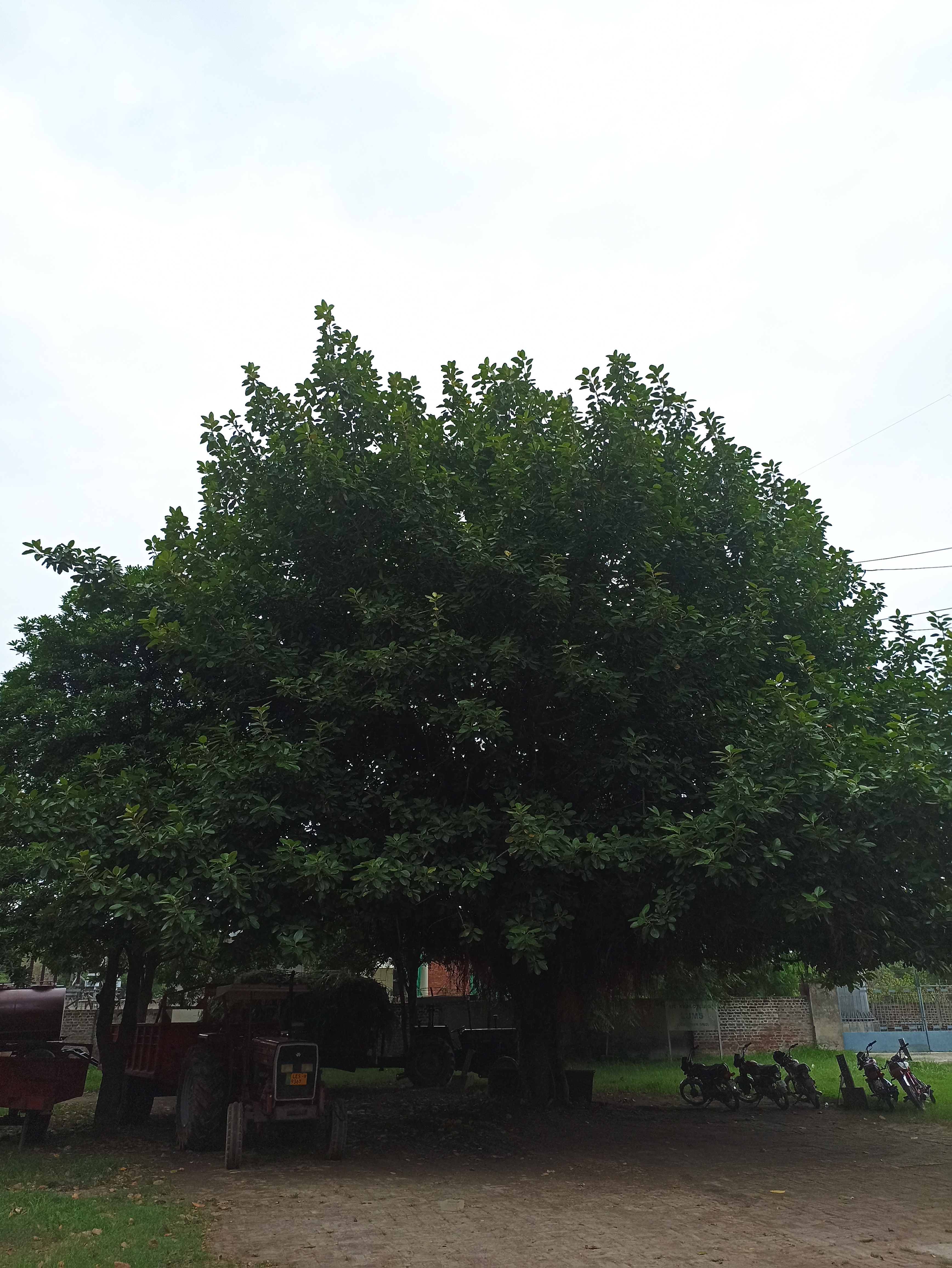
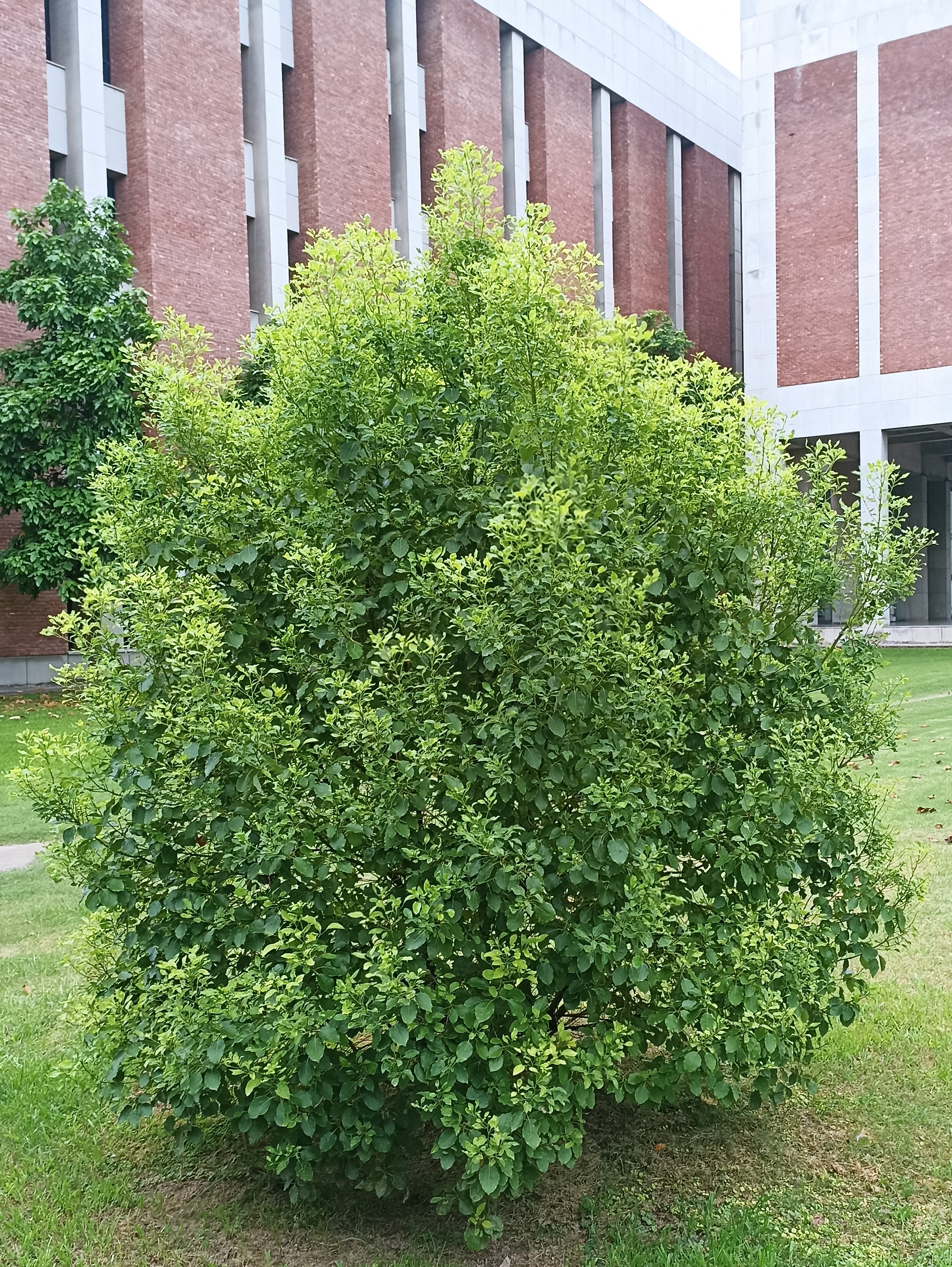
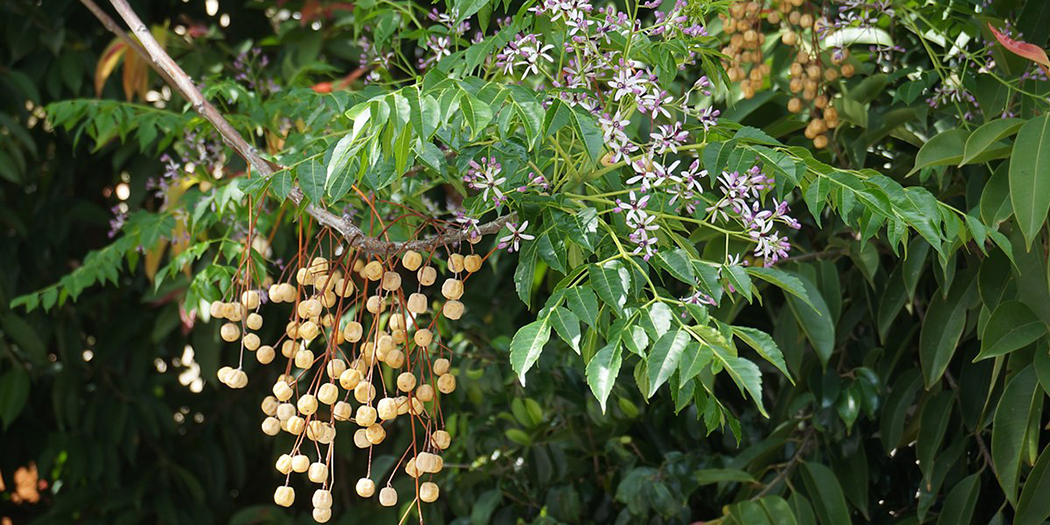
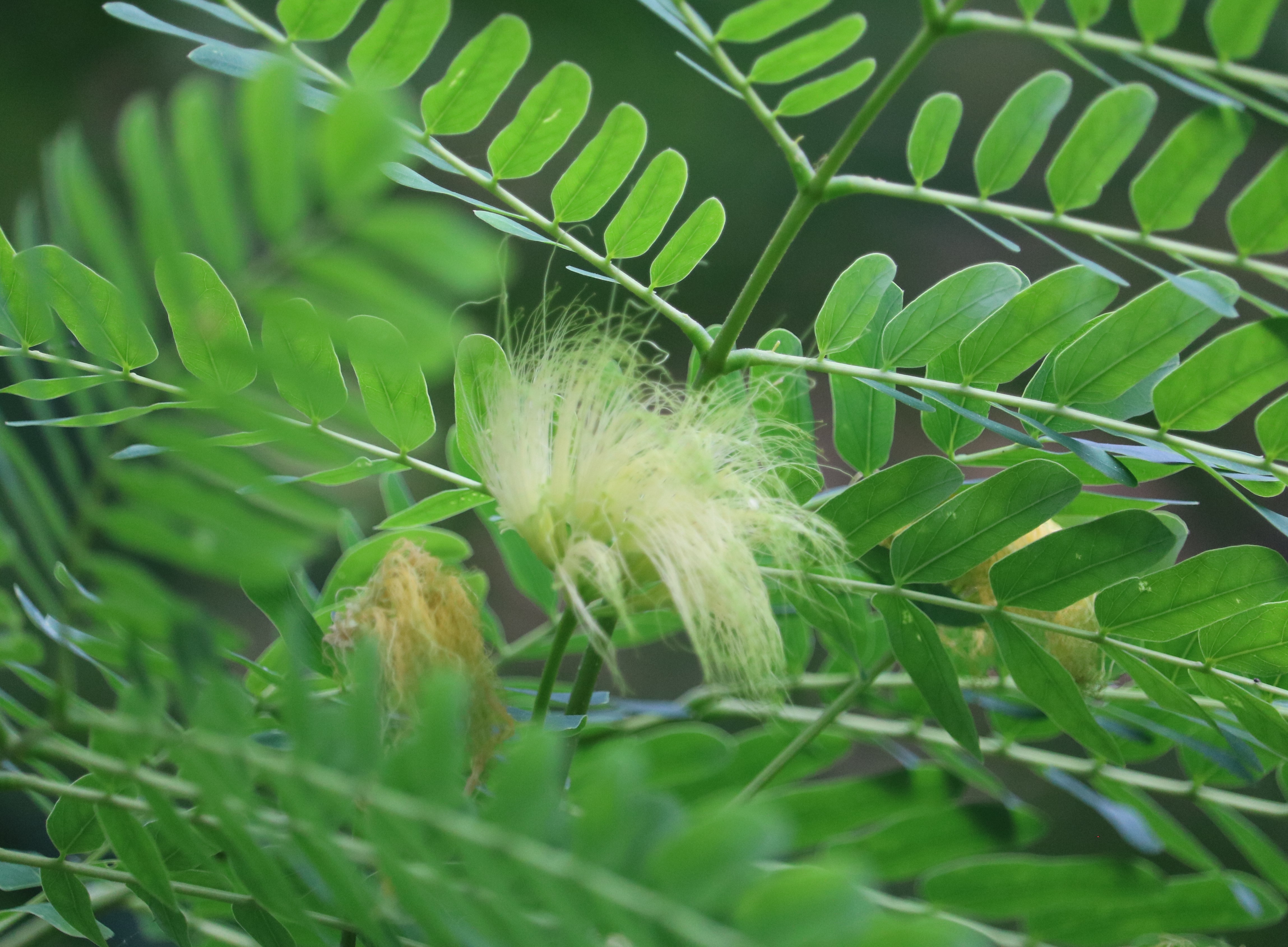
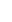
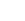
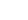
Albizia julibrissin is a small deciduous tree with a broad crown of level or arching branches, growing to 5–16 m (16–52 ft) tall. Its bark is dark greenish grey, becoming vertically striped with age. Its leaves are large and frond-like: They are bipinnate, divided into 6–12 pairs of pinnae, each with 20–30 pairs of leaflets. Individual leaflets are oblong, 1–1.5 cm (0.4–0.6 in) long and 2–4 cm (0.8–1.6 in) broad. The true leaves are 20–45 cm (8–18 in) long and 12–25 cm (5–10 in) broad.
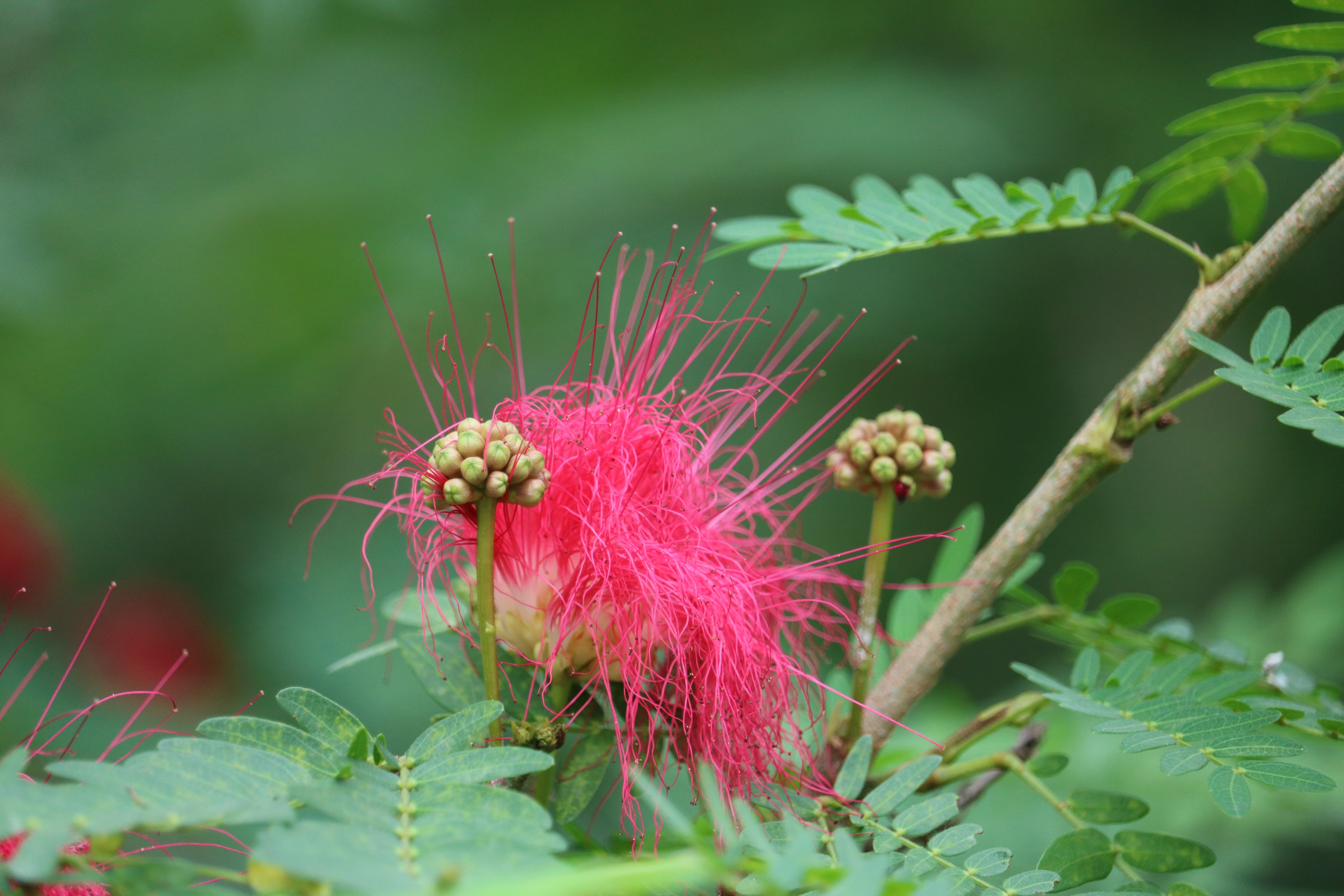
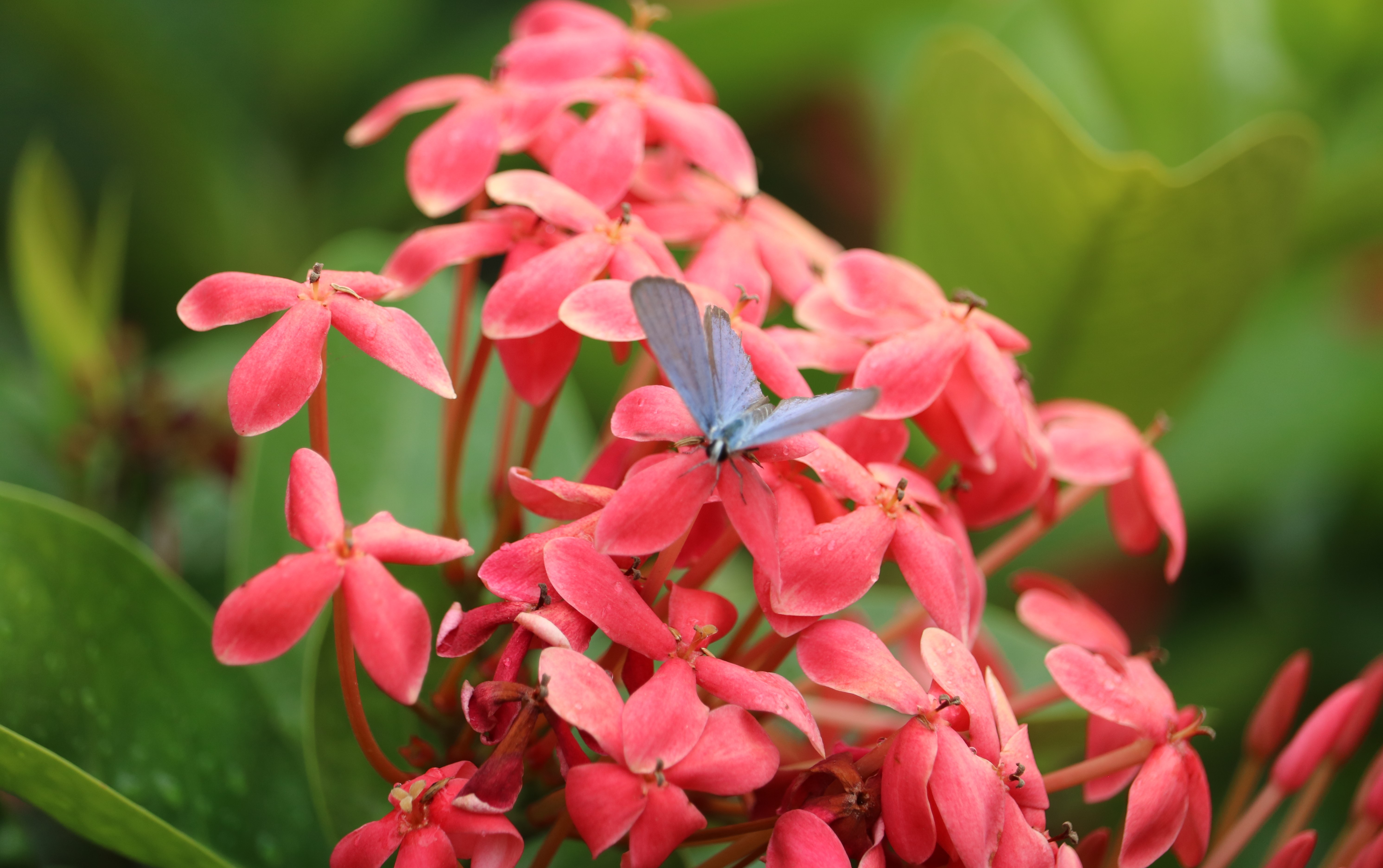
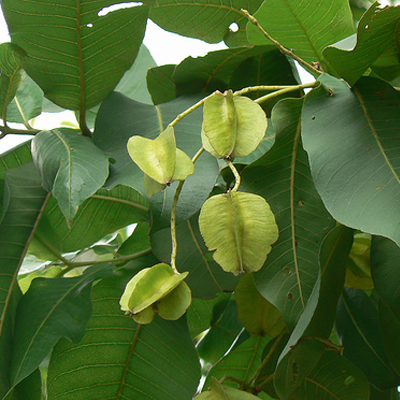
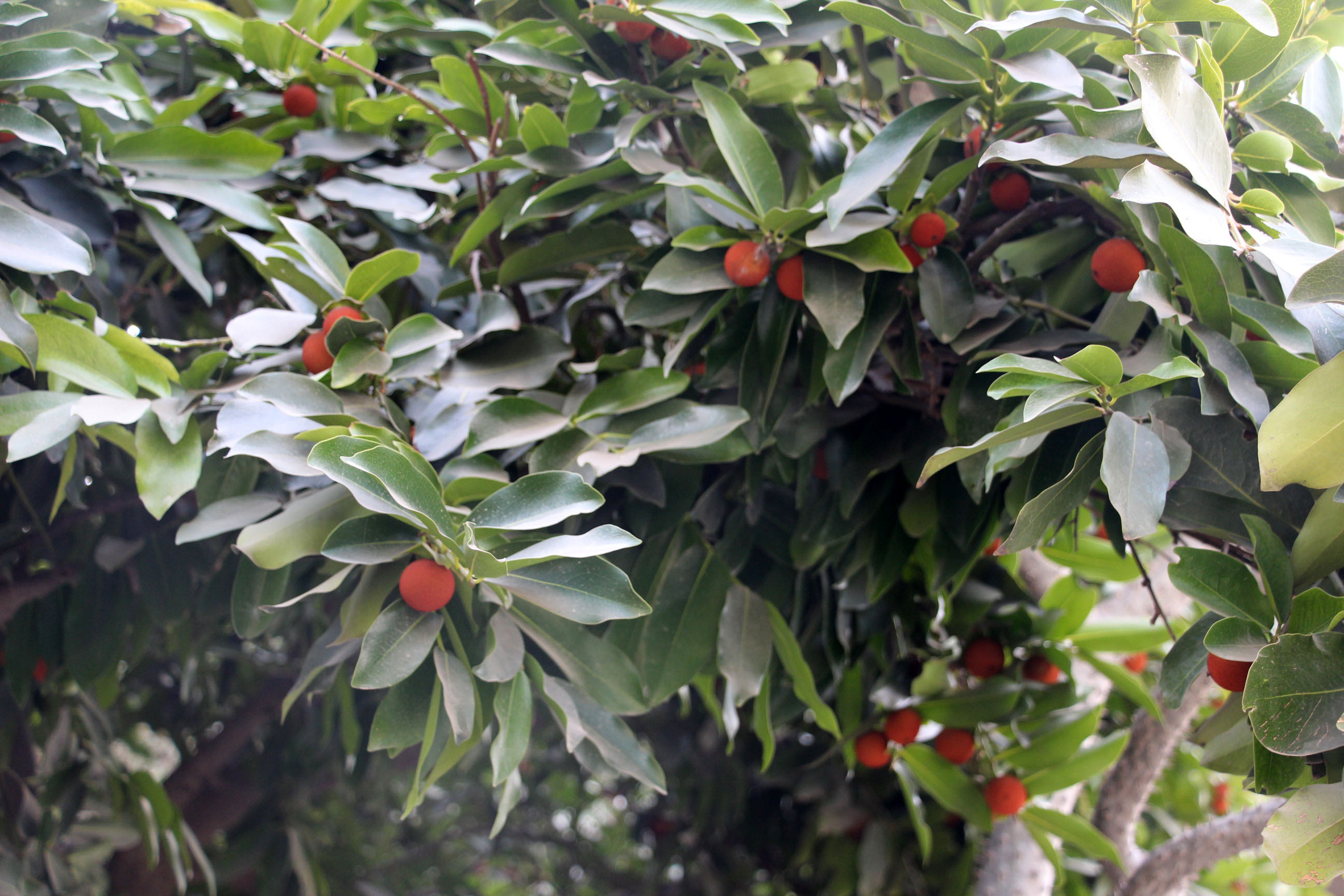
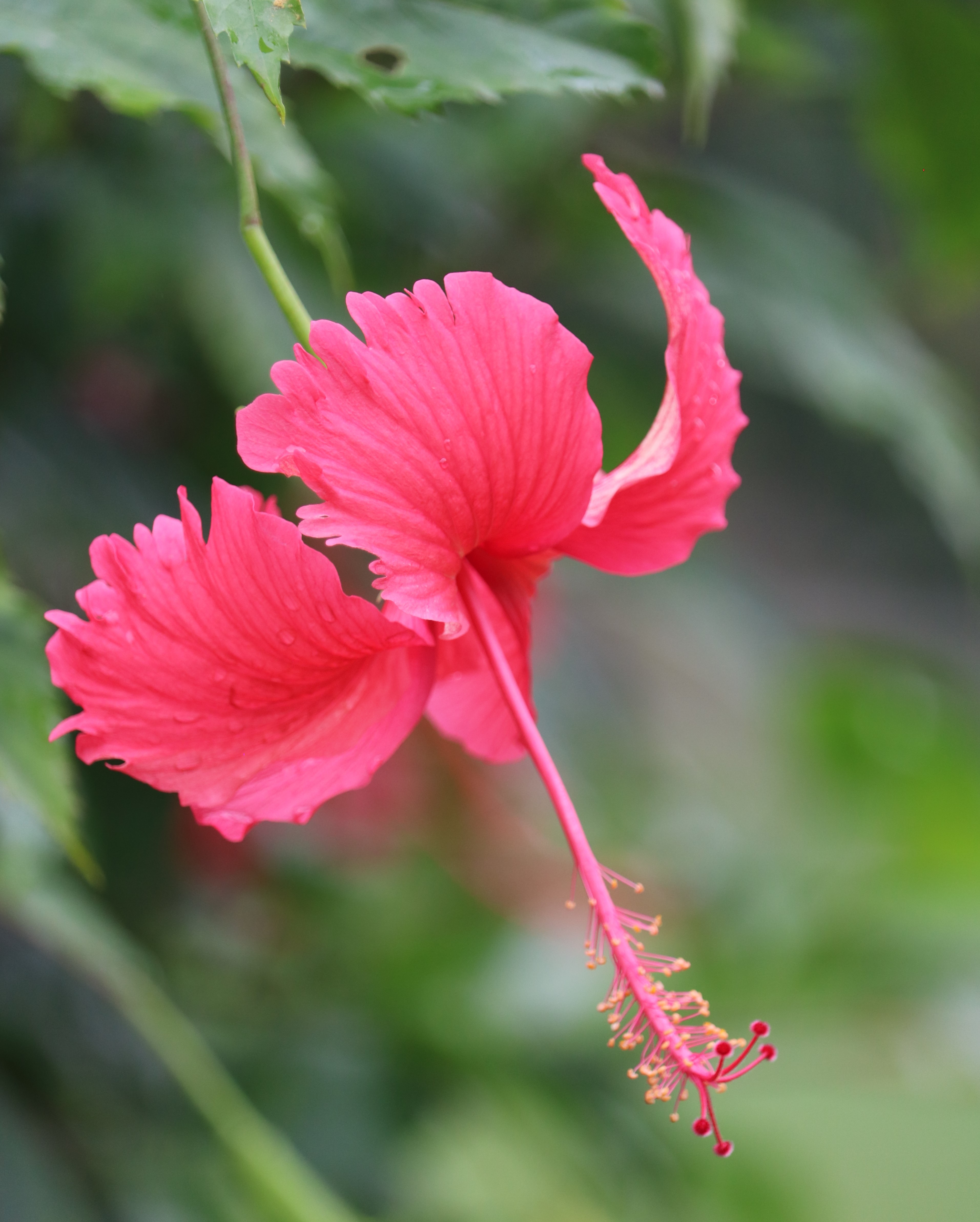
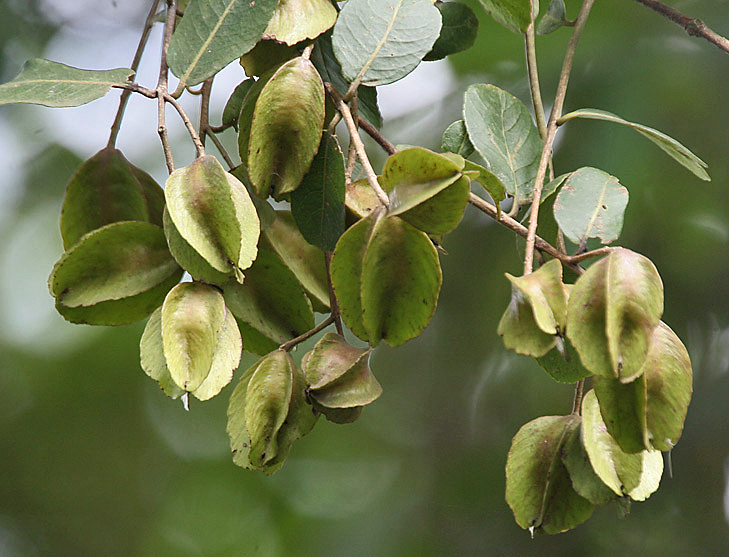
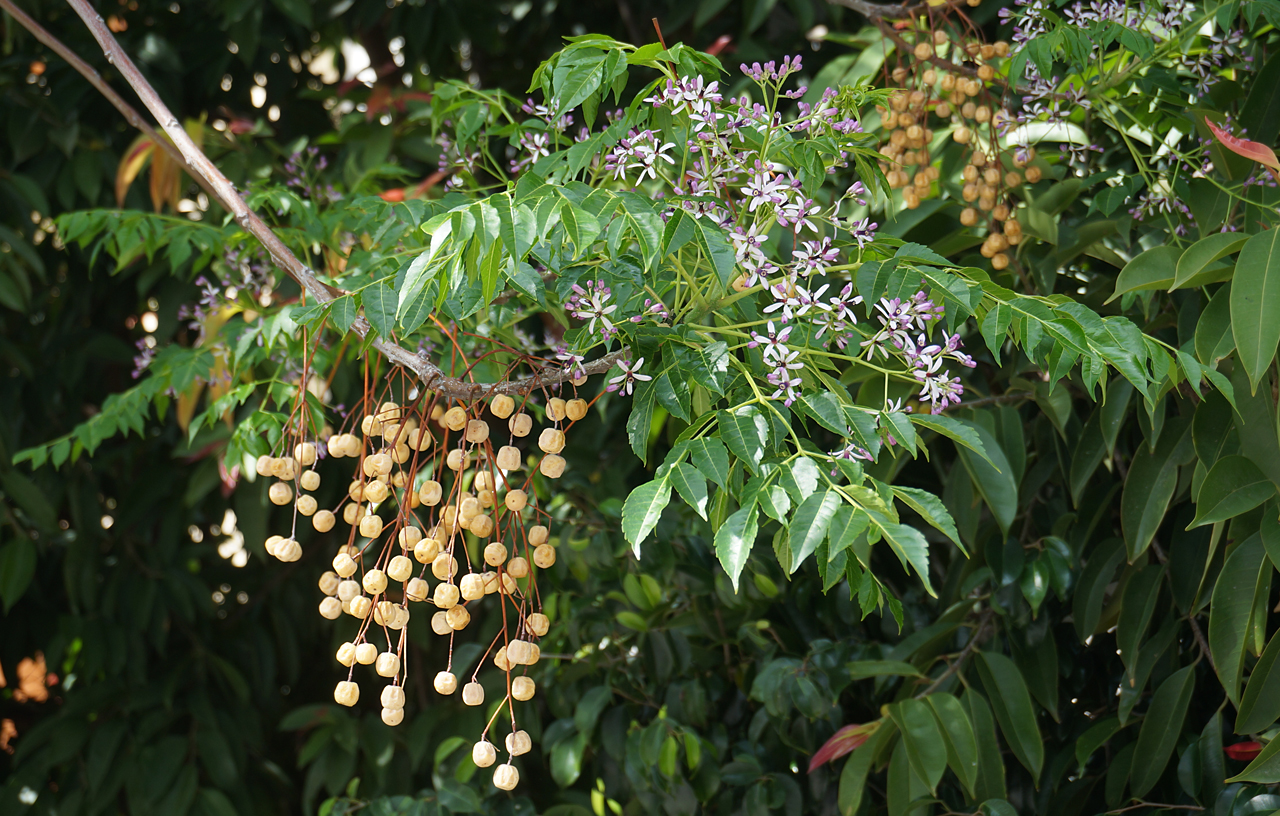
The flowers bloom throughout the summer in dense inflorescences, which resemble starbursts of pink silky threads. The true flowers have small calyx and corolla (except the central ones), with a tight cluster of prominent stamens, 2–3 cm long and white or pink with a white base. They have been observed to attract bees, butterflies and hummingbirds. Its fruit is a flat brown pod 10–20 cm (4–8 in) long and 2–2.5 cm (0.8–1.0 in) broad, containing several seeds inside.
Original habitats of the tree include regions from Iran (Persia) and the Republic of Azerbaijan to China and Korea.
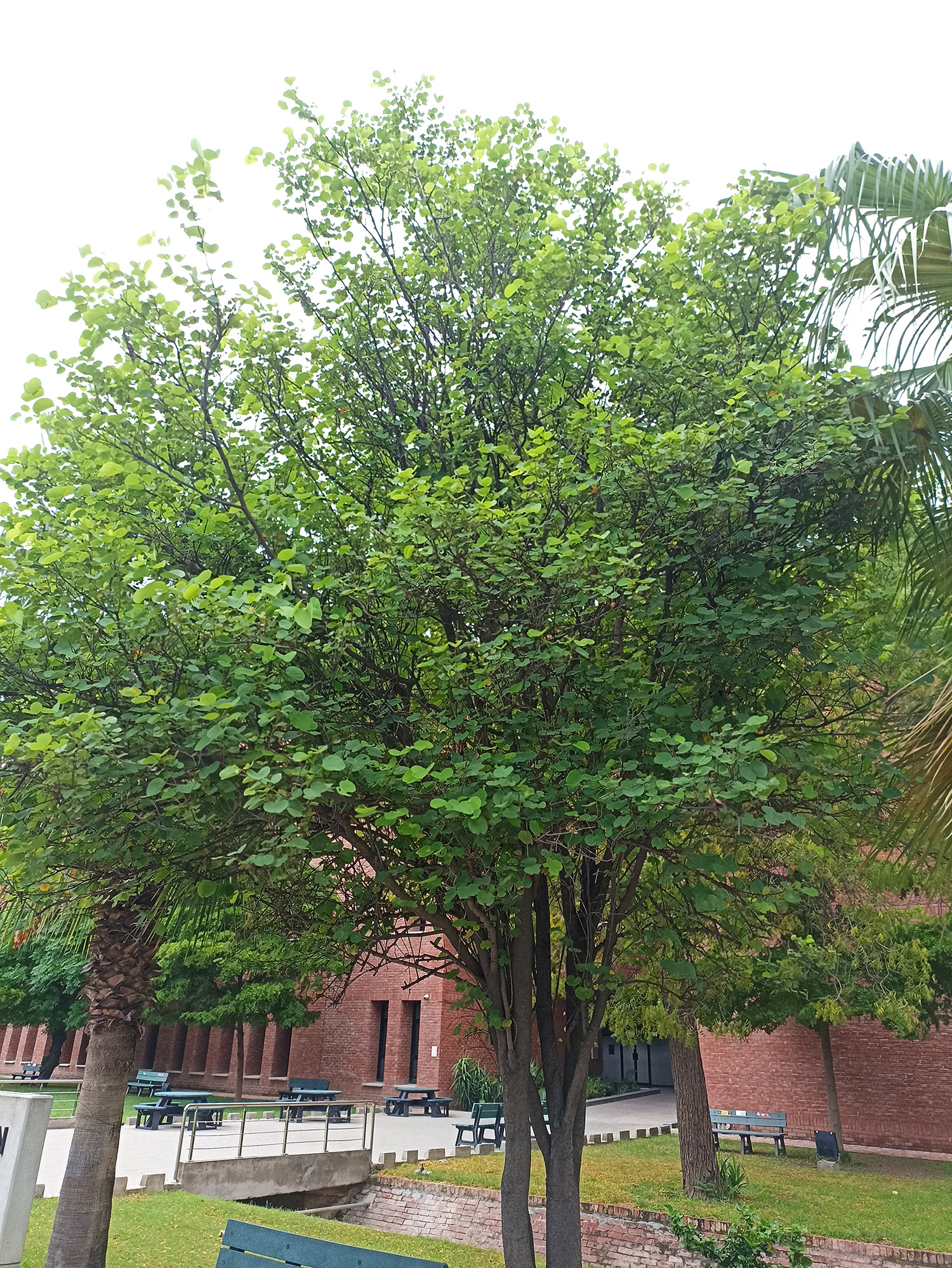
A. julibrissin is widely planted as an ornamental plant in parks and gardens, grown for its fine leaf texture, flowers and attractive horizontal canopy. Other positive attributes are a fast growth rate, low water requirements and the ability to thrive planted in full sun in hot summer climates. It is frequently planted in semi-arid areas like California's Central Valley, central Texas and Oklahoma. Although capable of surviving drought, growth will be stunted and the tree tends to look sickly. As such it should be given infrequent, deep waterings during the summer, which will benefit growth and flowering.
The broad crown of a mature tree makes it useful for providing dappled shade. The flower colour varies from white in A. julibrissin f. alba, to rich red-tipped flowers. Variants with cream or pale yellow flowers are also reported. Other cultivars are becoming available: 'Summer Chocolate' has red foliage ageing to dark bronze, with pale pink flowers; 'Ishii Weeping' (or 'Pendula') has a drooping growth habit.
There is also a form, A. julibrissin f. rosea (pink silk tree) which has, in the past, been classed either as a variety or as a cultivar. This is a smaller tree, only growing to 5–7 metres (16–23 ft) tall, with the flowers always pink. Native to the northeast of the species' range in Korea and Northern China, it is more cold-tolerant than the typical form, surviving temperatures down to at least −25 °C (−13 °F). The selected cultivar A. julibrissin 'Ernest Wilson' (also known as 'E.H.Wilson' or 'Rosea') is a cold-tolerant tree with deep pink flower colour. In Japan, A. julibrissin f. rosea is often used for non-traditional bonsai. The name nemunoki* Kanji: and its variants is a kigo representing the summer in haiku, especially a sleepy summer evening.
Other uses
The sweet-scented flowers are a good nectar source for honeybees and butterflies. In Central America, the thornbug (Umbonia spinosa) prefer its branches for mating and overwintering.
There is conflicting information on the toxicity of pods and seeds to humans and animals; some parts of the plant may contain neurotoxin. Pink silk tree can be used to treat the effects of stinging nettle (Urtica dioica) by rubbing the leaves in hand and then applying to the rash area. Relief is almost instantaneous.
In the wild, the tree tends to grow in dry plains, sandy valleys, and uplands. It has become an invasive species in the United States, where it has spread from southern New York, New Jersey and Connecticut, west to Missouri and Illinois, and south to Florida and Texas. It is cultivated in California and Oregon. Its seeds are wind-dispersed and numerous, and they are fertile even over long periods of drought. Each pod, which resembles a flattened bean pod made of paper, holds about 8 seeds on average. The pod bursts in strong winds, and the seeds can carry over surprisingly long distances.
Breeding work is currently underway in the United States to produce ornamental plants which will not set seed and can be planted without risk. However, in the eastern United States it is generally a short-lived tree, being highly susceptible to mimosa vascular wilt, a fungal disease caused by a species of Fusarium, though the disease does not seem to have seriously impacted its populations. Because of its invasive tendencies and disease susceptibility, it is rarely recommended as an ornamental plant in the United States, though it is still widely planted in parts of Europe.